Difference between revisions of "Nyssa biflora"
(→Ecology) |
(→Ecology) |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== | ===Habitat=== | ||
| − | + | Ideal soil for ''N. biflora'' is wet bottomland soils, such as mucks, heavy clays, and wet sands. Shallow moving water is ideal such as swamp banks, ponds, and estuaries. <ref name= "USDA"> [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CEAM USDA Plant Database]</ref> | |
<!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
<!--===Phenology===--> <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | <!--===Phenology===--> <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
Revision as of 11:52, 24 May 2018
| Nyssa biflora | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by Bobby Hattaway at the Discover Life Database | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Cornales |
| Family: | Cornaceae |
| Genus: | Nyssa |
| Species: | N. biflora |
| Binomial name | |
| Nyssa biflora Walter | |
| |
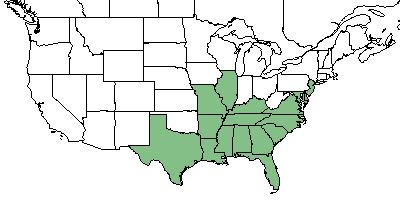
| Natural range of Nyssa biflora from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonym: N. sylvatica (Marshall)
Variety: none
Description
N. biflora is a perennial tree of the Cornaceae family that is native to North America. [1]
Distribution
N. biflora is found throughout the southeastern United States; specifically, Florida, Georgia, Alabama, South Carolina, North Carolina, Virginia, Maryland, Deleware, New Jersey, Tennessee, Kentucky, Mississippi, Louisiana, Texas, Arkansas, Missouri, and Illinois.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
Ideal soil for N. biflora is wet bottomland soils, such as mucks, heavy clays, and wet sands. Shallow moving water is ideal such as swamp banks, ponds, and estuaries. [1]
Use by animals
The White tail deer utilize the twigs and foliage. Small mammals and birds will eat the fruit. Also, birds and small mammals will make nests and cavities in the tree. The flowers provide nectar for bees. [1]