Difference between revisions of "Nothoscordum bivalve"
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
| − | Herbivory by grazers is low for this species,<ref name="Smith 1940"/> but trace amounts have been found in white tailed deer rumen of southern Texas.<ref name="Everitt & Drawe 1974">Everitt JH, Drawe DL (1974) Spring food habits of white-tailed deer in the south Texas plains. Journal of Range Management 27(1):15-20</ref> | + | Herbivory by grazers is low for this species,<ref name="Smith 1940"/> but trace amounts have been found in white tailed deer rumen of southern Texas.<ref name="Everitt & Drawe 1974">Everitt JH, Drawe DL (1974) Spring food habits of white-tailed deer in the south Texas plains. Journal of Range Management 27(1):15-20</ref> Relative abundance peaks in properly grazed prairies and overgrazed but uneroded prairies.<ref name="Smith 1940">Smith CC (1940) The effect of overgrazing and erosion upon the biota of the mixed-grass prairie of Oklahoma. Ecology 21(3):381-397.</ref> |
| + | |||
<!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | <!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | ||
Revision as of 16:08, 8 February 2018
| Nothoscordum bivalve | |
|---|---|
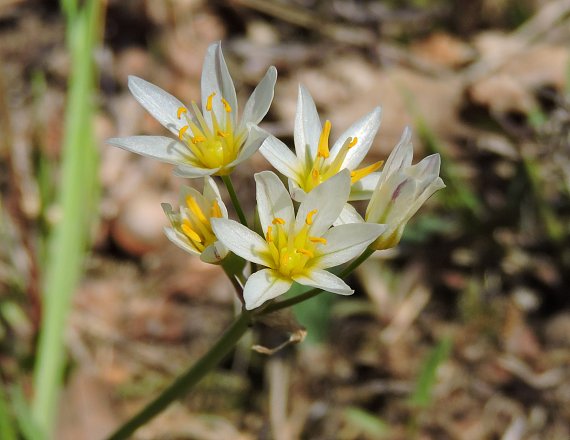

| |
| Photo from the Illinois Wildflowers Database | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Liliales |
| Family: | Liliaceae |
| Genus: | Nothoscordum |
| Species: | N. bivalve |
| Binomial name | |
| Nothoscordum bivalve L. | |
| |
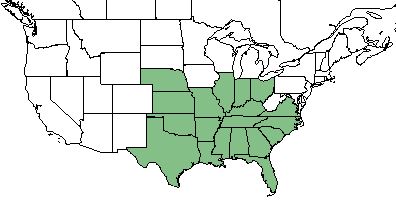
| Natural range of Nothoscordum bivalve from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: grace garlic; false garlic;[1] crowpoison[2]
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonym: Allium bivalve;[1][2] Ornithogalum bivalve[2]
Description
Nothoscordum bivalve is a bulbous[3] monoecious perennial forb/herb.[2] It is an onion-like plant but typically lacks an odor.[1]
Distribution
This species is found from southeastern Virginia, westward to southern Ohio and Kansas, southward to central peninsular Florida, Texas, and South America.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
N. bivalve occurs around granite flatrocks, in various glades and barrens, open woodlands, along roadsides, and in fields.[1]
Phenology
In the southeastern and mid-Atlantic United States, N. bivalve flowers from mid-March through mid-May and in September through December. Fruiting occurs in May through June and from October through January.[1] For the Florida panhandle, reports of flowering primarily occur from January through May, peaking between February and April. Records of flowering also occurred in September through November, but in reduced numbers compared to the spring.[4]
Use by animals
Herbivory by grazers is low for this species,[5] but trace amounts have been found in white tailed deer rumen of southern Texas.[6] Relative abundance peaks in properly grazed prairies and overgrazed but uneroded prairies.[5]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Weakley AS (2015) Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 USDA NRCS (2016) The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 08 February 2018). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ Baskin JM, Baskin CC (1979) The ecological life cycle of Nothoscordum bivalve in Tennessee cedar glades. Castanea 44(4):193-202
- ↑ Nelson G (08 February 2018) PanFlora. Retrieved from gilnelson.com/PanFlora/
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Smith CC (1940) The effect of overgrazing and erosion upon the biota of the mixed-grass prairie of Oklahoma. Ecology 21(3):381-397.
- ↑ Everitt JH, Drawe DL (1974) Spring food habits of white-tailed deer in the south Texas plains. Journal of Range Management 27(1):15-20