Difference between revisions of "Manfreda virginica"
(Created page with "{{italic title}} <!-- Get the taxonomy information from the NRCS Plants database --> {{taxobox | name = Manfreda virginica | image = Manfreda virginica_Gil.jpg | image_caption...") |
|||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| + | sandy loam habitats (Miller et al 1999). | ||
| + | Soils are upland coastal plain type with little slope and low fertility, in Louisiana (Thill 1983). | ||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
===Seed dispersal=== | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
===Seed bank and germination=== | ===Seed bank and germination=== | ||
===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| − | ===Pollination=== | + | ===Pollination=== |
| + | – M. virginica is pollinated both diurnally and nocturnally, with observations suggesting that bumblebees are the predominant floral visitors (Groman and Pellmyr 1999). Bombus pennsylvanicus and Hemaris diffinis are critical diurnal pollinators; however, diurnally pollinated plants were observed to produce significantly lower seed set than nocturnally and open pollinated plants (Groman and Pellmyr 1999). Hence nocturnal visitors contribute more to M. virginica reproduction despite frequent diurnal visits (Groman and Pellmyr 1999). | ||
===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
===Diseases and parasites=== | ===Diseases and parasites=== | ||
==Conservation and Management== | ==Conservation and Management== | ||
==Cultivation and restoration== | ==Cultivation and restoration== | ||
| + | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
| − | + | Groman, J. D. and O. Pellmyr (1999). "The pollination biology of Manfreda virginica (Agavaceae): relative contribution of diurnal and nocturnal visitors." Oikos 87: 373-381. | |
| + | |||
| + | Miller, J. H., R. S. Boyd, et al. (1999). "Floristic diversity, stand structure, and composition 11 years after herbicide site preparation." Canadian Journal of Forest Research 29: 1073-1083. | ||
Revision as of 14:53, 11 June 2015
| Manfreda virginica | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida – Monocotyledons |
| Order: | Liliales |
| Family: | Agavaceae |
| Genus: | Manfreda |
| Species: | M. virginica |
| Binomial name | |
| Manfreda virginica (L.) Salisb. ex Rose | |
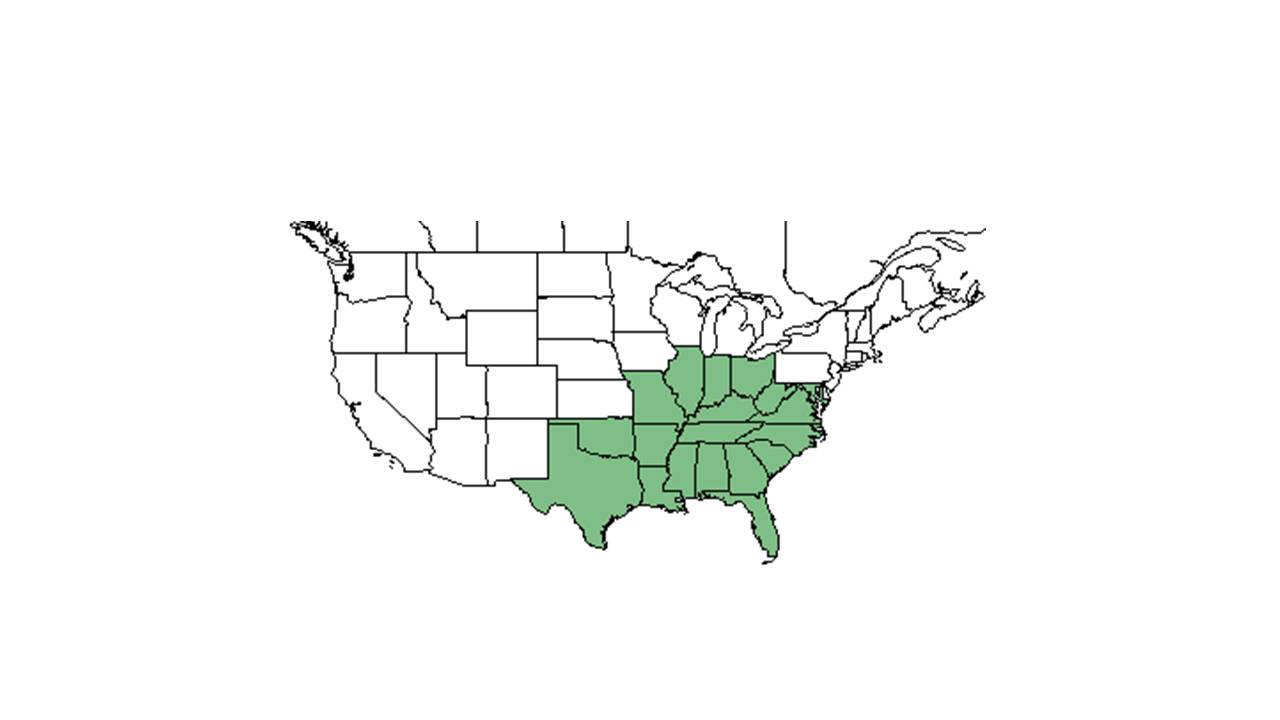
| |
| Natural range of Manfreda virginica from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Description
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
sandy loam habitats (Miller et al 1999). Soils are upland coastal plain type with little slope and low fertility, in Louisiana (Thill 1983).
Phenology
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
Pollination
– M. virginica is pollinated both diurnally and nocturnally, with observations suggesting that bumblebees are the predominant floral visitors (Groman and Pellmyr 1999). Bombus pennsylvanicus and Hemaris diffinis are critical diurnal pollinators; however, diurnally pollinated plants were observed to produce significantly lower seed set than nocturnally and open pollinated plants (Groman and Pellmyr 1999). Hence nocturnal visitors contribute more to M. virginica reproduction despite frequent diurnal visits (Groman and Pellmyr 1999).
Use by animals
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Groman, J. D. and O. Pellmyr (1999). "The pollination biology of Manfreda virginica (Agavaceae): relative contribution of diurnal and nocturnal visitors." Oikos 87: 373-381.
Miller, J. H., R. S. Boyd, et al. (1999). "Floristic diversity, stand structure, and composition 11 years after herbicide site preparation." Canadian Journal of Forest Research 29: 1073-1083.