Difference between revisions of "Lyonia ferruginea"
(→Pollination) |
|||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
A description of ''Lyonia ferruginea'' is provided in [http://efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=1&taxon_id=220007940 The Flora of North America]. | A description of ''Lyonia ferruginea'' is provided in [http://efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=1&taxon_id=220007940 The Flora of North America]. | ||
| − | |||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
Populations can be found in south South Carolina, southeast Georgia, and Florida <ref name="wildflower"/>. | Populations can be found in south South Carolina, southeast Georgia, and Florida <ref name="wildflower"/>. | ||
| − | |||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| Line 36: | Line 34: | ||
In a study at the Okefenokee Swamp, Schlesinger and Chabot (1977) found ''L. ferruginea'' to be the dominate, evergreen shrub in pine forests surrounding the swamp. It was also observed that the rate of water uptake falls behind the transpiration loss at midday. | In a study at the Okefenokee Swamp, Schlesinger and Chabot (1977) found ''L. ferruginea'' to be the dominate, evergreen shrub in pine forests surrounding the swamp. It was also observed that the rate of water uptake falls behind the transpiration loss at midday. | ||
| − | |||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
It has been observed flowering January through April and fruiting January through November (FSU Herbarium). | It has been observed flowering January through April and fruiting January through November (FSU Herbarium). | ||
| − | |||
<!--===Seed dispersal===--> | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> | ||
<!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
''L. ferruginea'' occurs in evergreen scrubs that experience a natural fire rotation. Populations occur in the scrubs of Cumberland Island located off the coast of Southern Georgia. These scrubs are pyric disclimaxes and have been found to have a natural fire rotation of 20 to 30 years that are related to coastal drought cycles and the occurrence of dry lightning (Salley and Bratton 1987). | ''L. ferruginea'' occurs in evergreen scrubs that experience a natural fire rotation. Populations occur in the scrubs of Cumberland Island located off the coast of Southern Georgia. These scrubs are pyric disclimaxes and have been found to have a natural fire rotation of 20 to 30 years that are related to coastal drought cycles and the occurrence of dry lightning (Salley and Bratton 1987). | ||
| − | |||
===Pollination=== | ===Pollination=== | ||
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of ''Lyonia ferruginea'' at Archbold Biological Station (Deyrup 2015): | The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of ''Lyonia ferruginea'' at Archbold Biological Station (Deyrup 2015): | ||
| Line 60: | Line 55: | ||
Vespidae: ''Stenodynerus lineatifrons'' | Vespidae: ''Stenodynerus lineatifrons'' | ||
<!--===Use by animals===--> <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | <!--===Use by animals===--> <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
| − | |||
===Diseases and parasites=== | ===Diseases and parasites=== | ||
''Exobasidium ferrugineae'' is a closely associated disease with ''L. ferruginea'' that is characterized by causing hypertrophied flowers (Kennedy et al. 2012). | ''Exobasidium ferrugineae'' is a closely associated disease with ''L. ferruginea'' that is characterized by causing hypertrophied flowers (Kennedy et al. 2012). | ||
| Line 66: | Line 60: | ||
It is considered to be a true host of the pest ''Stephanitis blatchleyi'' (Wheeler and Stoops 2013). | It is considered to be a true host of the pest ''Stephanitis blatchleyi'' (Wheeler and Stoops 2013). | ||
| − | + | ==Conservation and management== | |
| − | + | ==Cultivation and restoration== | |
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
<gallery widths=180px> | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| − | |||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA. | Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA. | ||
Revision as of 14:55, 24 June 2016
| Lyonia ferruginea | |
|---|---|
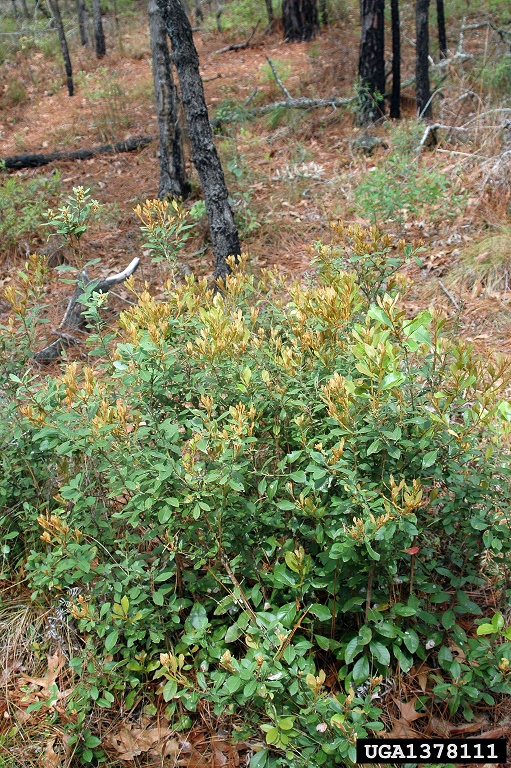

| |
| Photo by Chris Evans, University of Illinois, Bugwood.org | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Ericales |
| Family: | Ericaceae |
| Genus: | Lyonia |
| Species: | L. ferruginea |
| Binomial name | |
| Lyonia ferruginea (Walter) Nutt. | |
| |
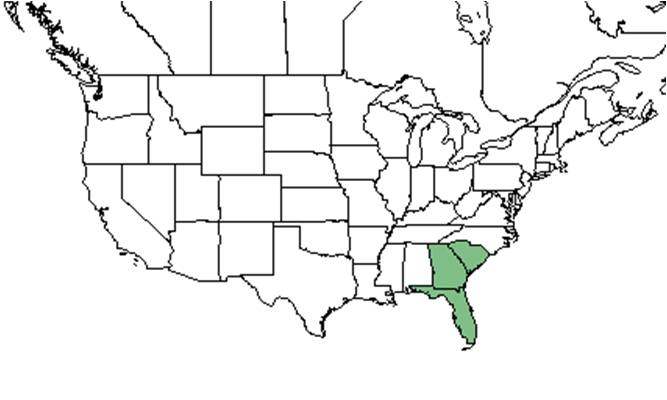
| Natural range of Lyonia ferruginea from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: rusty staggerbush
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonym: Xolisma ferruginea (Walter) Heller
The genus Lyonia is named for John Lyon, a 19th century botanist who is best known for his travels in southern Appalachians [1]. The species name is Latin for rust-colored, which refers to the rusty appearance on the abaxial side of the leaf [2].
Description
A description of Lyonia ferruginea is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
Populations can be found in south South Carolina, southeast Georgia, and Florida [2].
Ecology
Habitat
Habitats of L. ferruginea in the coastal plain include coastal dunes, titi thickets, longleaf/saw palmetto flatwoods, shrub bogs, live oak scrub sand ridges, and xeric scrubs. It has been found to occur in disturbed areas such as roadsides and powerline corridors. Soil types include sandy loam, loamy sand, peat and white sand. Associated species include Cyrilla, Cliftonia, Rhododendron, Myrica, Lyonia lucida, L. fruticosa, Ilex glabra, Pinus clausa, Quercus chapmanii,, Q. myrtifolia, Ilex ambigua, Serenoa repens, Pinus elliottii, Ilex coriaca, Liquidambar styraciflua, Quercus nigra, Q. incana, Gelsemium sempervirens, Smilax bona-nox, S. pumila, Pteridium aquilinum, and Aristida stricta (FSU Herbarium).
In a study at the Okefenokee Swamp, Schlesinger and Chabot (1977) found L. ferruginea to be the dominate, evergreen shrub in pine forests surrounding the swamp. It was also observed that the rate of water uptake falls behind the transpiration loss at midday.
Phenology
It has been observed flowering January through April and fruiting January through November (FSU Herbarium).
Fire ecology
L. ferruginea occurs in evergreen scrubs that experience a natural fire rotation. Populations occur in the scrubs of Cumberland Island located off the coast of Southern Georgia. These scrubs are pyric disclimaxes and have been found to have a natural fire rotation of 20 to 30 years that are related to coastal drought cycles and the occurrence of dry lightning (Salley and Bratton 1987).
Pollination
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of Lyonia ferruginea at Archbold Biological Station (Deyrup 2015):
Apidae: Apis mellifera, Bombus impatiens
Colletidae: Colletes brimleyi, C. productus
Halictidae: Agapostemon splendens, Augochlorella aurata, Augochloropsis sumptuosa
Megachilidae: Megachile xylocopoides
Sphecidae: Oxybelus laetus fulvipes, Stictiella serrata, Tachysphex apicalis
Vespidae: Stenodynerus lineatifrons
Diseases and parasites
Exobasidium ferrugineae is a closely associated disease with L. ferruginea that is characterized by causing hypertrophied flowers (Kennedy et al. 2012).
It is considered to be a true host of the pest Stephanitis blatchleyi (Wheeler and Stoops 2013).
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: October 2015. Collectors: Jame Amoroso, Loran C. Anderson, L. Baltzell, Tom Barnes, Linnie E. Beck, James R. Burkhalter, Andre F. Clewell, George R. Cooley, Steven P. Christman, Delzie Demaree, R.J. Eaton, Suellen Folensbee, Mark A. Garland, Angus Gholson, Robert K. Godfrey, D.W. Hall, Walter S. Judd, Robert Kral, H. Kurz, O. Lakela, Robert L. Lazor, Robert J. Lemaire, S.W. Leonard, Fred L. Lewton, Sidney McDaniel, Joseph Monachino, R.A. Norris, Kent D. Perkins, P.L. Redfearn Jr., Ann Redmond, Grady W. Reinert, Cecil R. Slaughter, Bian Tan, L.B. Trott, Kenneth A. Wilson, Carroll E. Wood, Jean Wooten. States and Counties: Florida: Bay, Clay, Columbia, Duval, Flagler, Franklin, Gulf, Hernando, Highlands, Jefferson, Lake, Leon, Levy, Liberty, Marion, Okaloosa, Orange, Osceola, Pinellas, Putnam, St. Johns, Sumter, Suwannee, Taylor, Volusia, Wakulla, Walton. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
Kennedy, A. H., N. A. Goldberg, et al. (2012). "Exobasidium ferrugineae sp. nov., associated with hypertrophied flowers of Lyonia ferruginea in the southeastern USA." Mycotaxon 120: 451-460.
Sally, T. and S. P. Bratton (1987). "The Recent Fire History of Cumberland Island, Georgia." Castanea 52(4): 300-303.
Schlesinger, W. H. and B. F. Chabot (1977). "The Use of Water and Minerals by Evergreen and Deciduous Shrubs in Okefenokee Swamp." Botanical Gazette 138(4): 490-497.
Wheeler, A. G. and C. A. Stoops (2013). "STEPHANITIS BLATCHLEYI (HEMIPTERA: TINGIDAE): FIRST HOST-PLANT ASSOCIATION FOR A RARELY COLLECTED LACE BUG." The Florida Entomologist 96(2): 673-675.