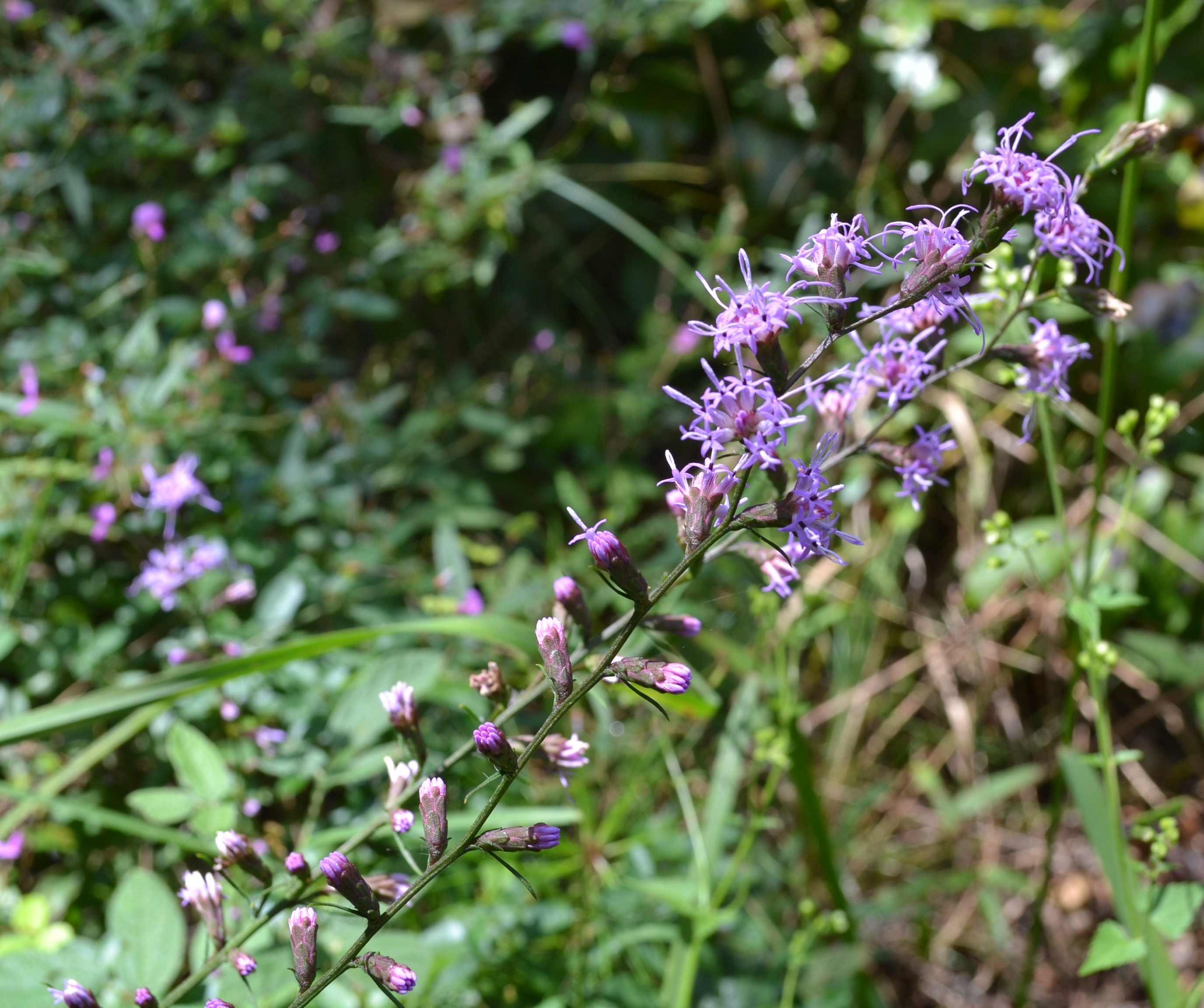
Liatris pilosa
| Liatris pilosa | |
|---|---|
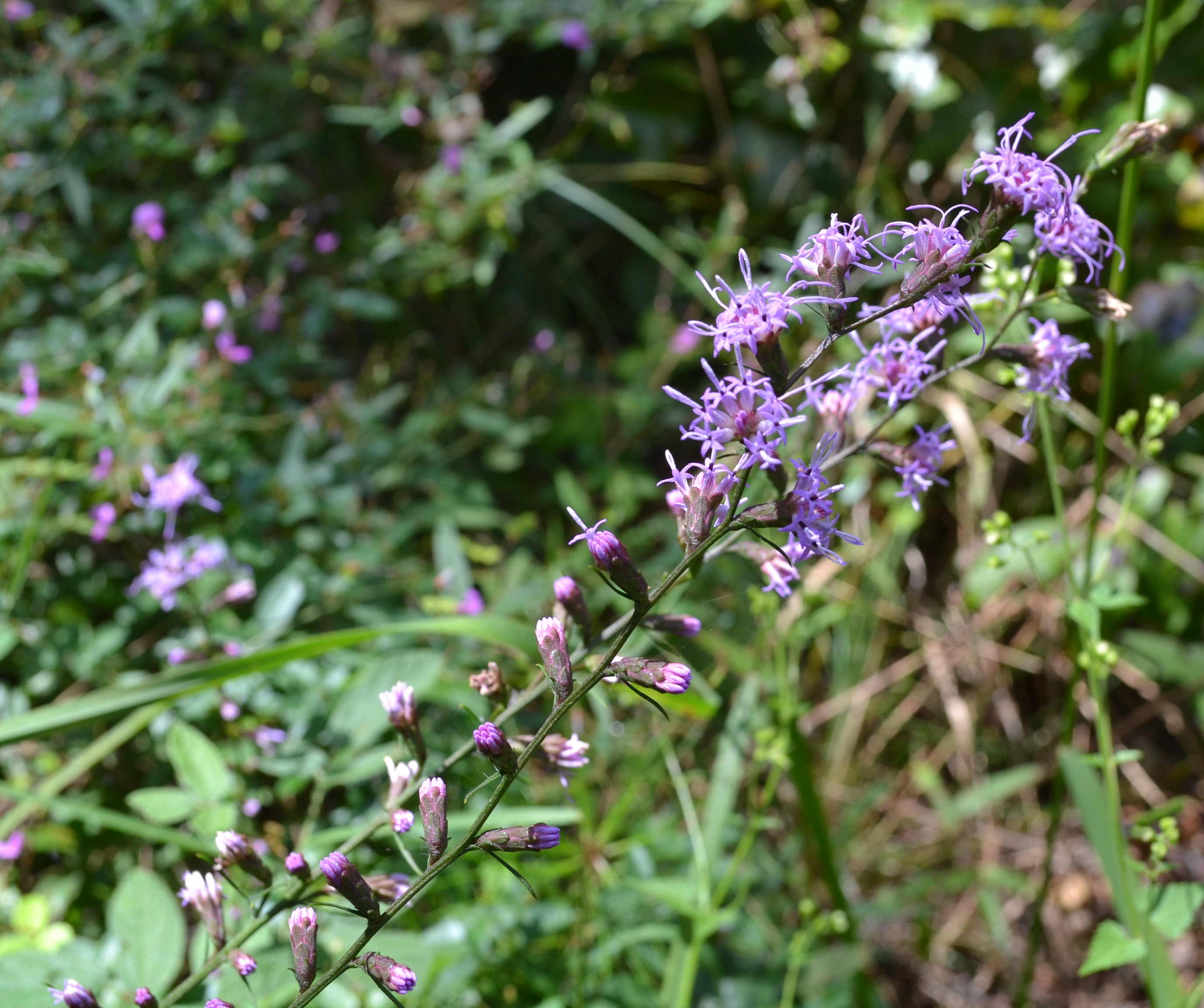

| |
| Photo taken by Kevin Robertson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae ⁄ Compositae |
| Genus: | Liatris |
| Species: | L. pilosa |
| Binomial name | |
| Liatris pilosa Willd. | |
| |
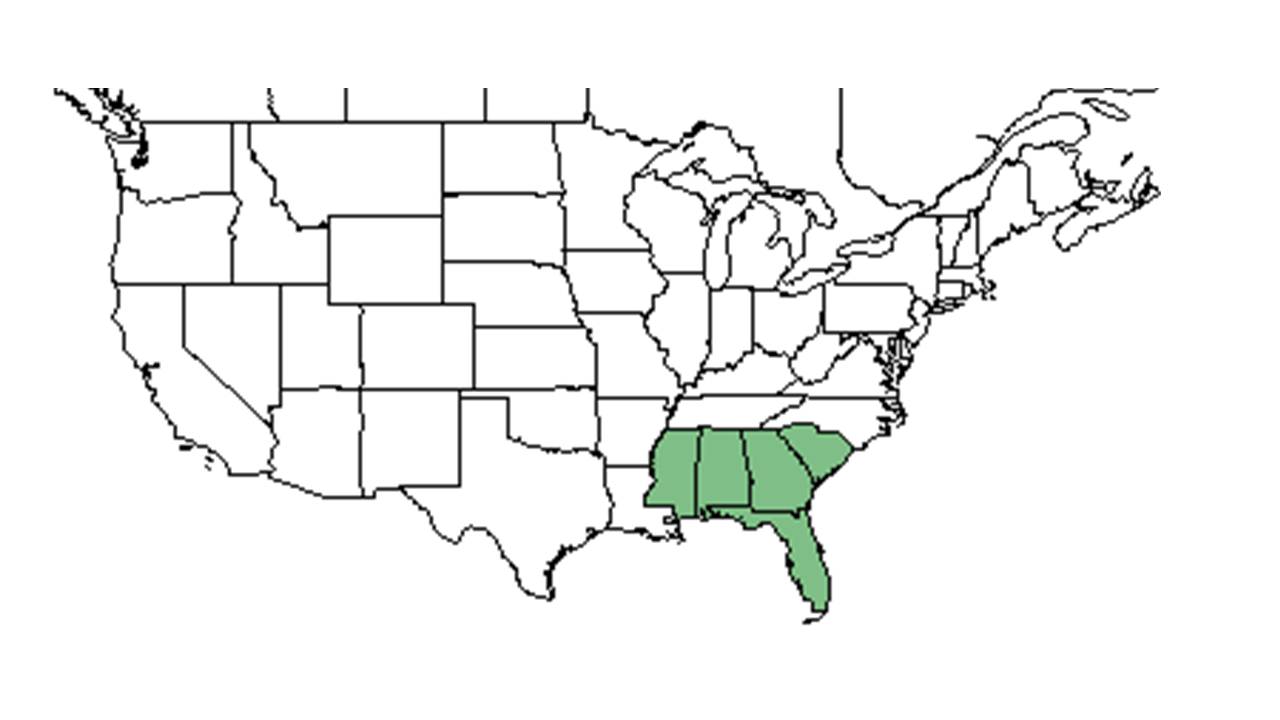
| Natural range of Liatris pilosa from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Shaggy blazing star; Grass-leaf gayfeather; Slender gayfeather
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Liatris graminifolia Willdenow; L. graminifolia var. graminifolia; L. graminifolia var. lasia Fernald & Griscom; L. graminifolia var. racemosa (A.P. de Candolle) Venard; L. graminifolia var. typica; L. graminifolia var. dubia (Barton) A. Gray; Laciniaria graminifolia (Walter) Kuntze.[1]
Varieties: none.[1]
Description
This species is abundant where it is found.[2]
A description of Liatris pilosa is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
The range of L. pilosa extends from New Jersey, Deleware, and Pennsylvania south to South Carolina.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
This species is found within well drained stands of longleaf pine, sandhill slopes, and mixed hardwood-pine flatwoods as well as disturbed areas such as clear-cut slash pine plantations.[2] It has been observed to grow in open light conditions in red, sandy clays.[2] L. pilosa responds negatively to soil disturbance by heavy silvilculture in North Carolina.[3] When exposed to soil disturbance by military training in West Georgia, L. pilosa responds negatively by way of absence.[4]
Phenology
This species has been observed flowering September through October and fruiting in October.[2]
Fire ecology
This species grows in areas that are burned.[2]
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: R. Kral, Wilson Baker, R. Komarek, Robert K. Godfrey, and Chris VanDerpoel. States and Counties: Florida: Gadsden, Leon, Levy, Liberty, and Taylor. Georgia: Grady and Thomas.
- ↑ Cohen, S., R. Braham, and F. Sanchez. (2004). Seed Bank Viability in Disturbed Longleaf Pine Sites. Restoration Ecology 12(4):503-515.
- ↑ Dale, V.H., S.C. Beyeler, and B. Jackson. (2002). Understory vegetation indicators of anthropogenic disturbance in longleaf pine forests at Fort Benning, Georgia, USA. Ecological Indicators 1(3):155-170.
