Difference between revisions of "Lachnocaulon anceps"
Emmazeitler (talk | contribs) |
HaleighJoM (talk | contribs) (→Ecology) |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
| − | This plant ranges from southern New Jersey to southern Florida, then west to southeastern Texas. There are disjunct populations in Tennessee | + | This plant ranges from southern New Jersey to southern Florida, then west to southeastern Texas. There are disjunct populations in Tennessee, the West Indies<ref name="weakley">Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref>, and Cuba.<ref>Sorrie, B. A. and A. S. Weakley 2001. Coastal Plain valcular plant endemics: Phytogeographic patterns. Castanea 66: 50-82.</ref> |
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
| − | + | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | |
| + | |||
| + | ''L. anceps'' has been found in marshes, flatwoods, pine-saw palmetto forests, lake margins, and cypress depressions.<ref name="FSU"> Florida State University Herbarium Database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2021. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, R.K. Godfrey, and Sidney McDaniel. States and counties: Florida: Broward, Franklin, Nassau, Orange, Union, and Volusia.</ref> It is also found in disturbed areas including cutover flatwoods, burned slash pine palmettos, roadsides, and drainage ditches.<ref name="FSU"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Associated species: ''Juncus spp., Calopogon tuberosus, Pogonia ophioglossoides, Sarracenia alata, Ctenium aromaticum, Lycopodiella, Eriocaulon, Xyris, Polygala nana, P. lutea, Lachnanthes, Lophiola, Rhexia lutea, Drosera capillaris, Pinus palustris, Aristida beyreichiana, Rhexia alifanus, Sarracenia flava, S. purpurea, Drosera tracyi, D. capillaris, Calopogon pallidus, Serenoa repens, Nolina atopocarpa, Pityopsis oligantha'', and ''Eleocharis tuberculosa''.<ref name="MMNS"> Mississippi Museum of Natural Science Herbarium accessed using Southeastern Regional Network of Expertise and Collections (SERNEC) data portal. URL: http://sernecportal.org/portal/collections/index.php Last accessed: June 2021. Collectors: Lucas C. Majure. States and Counties: Mississippi: Forrest and Lauderdale.</ref><ref name="MISSA"> Mississippi State University accessed using Southeastern Regional Network of Expertise and Collections (SERNEC) data portal. URL: http://sernecportal.org/portal/collections/index.php Last accessed: June 2021. Collectors: Mark Fishbein and Sula Vanderplank. States and Counties: Florida: Liberty. Mississippi: Jackson.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing of flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing of flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
''L. anceps'' flowers from May through October.<ref name="weakley">Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> | ''L. anceps'' flowers from May through October.<ref name="weakley">Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> | ||
| Line 39: | Line 44: | ||
<!--===Fire ecology===--> | <!--===Fire ecology===--> | ||
<!--===Pollination===--> | <!--===Pollination===--> | ||
| − | <!--=== | + | <!--===Herbivory and toxicology===--> |
<!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | ||
| − | ==Conservation and | + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== |
| − | == | + | ==Cultural use== |
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
<gallery widths=100px> | <gallery widths=100px> | ||
Latest revision as of 13:23, 14 July 2022
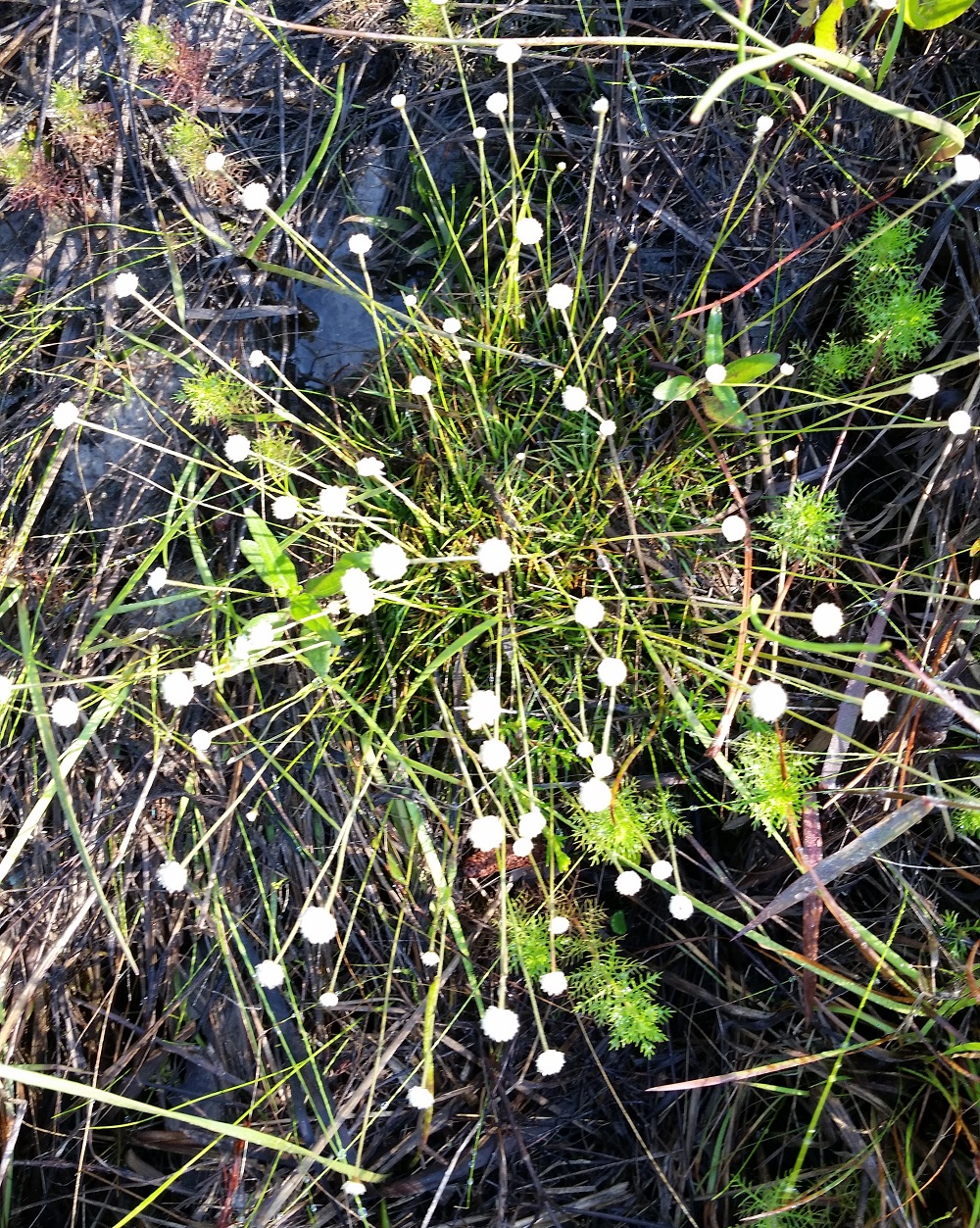
| Lachnocaulon anceps Kunth | |
|---|---|
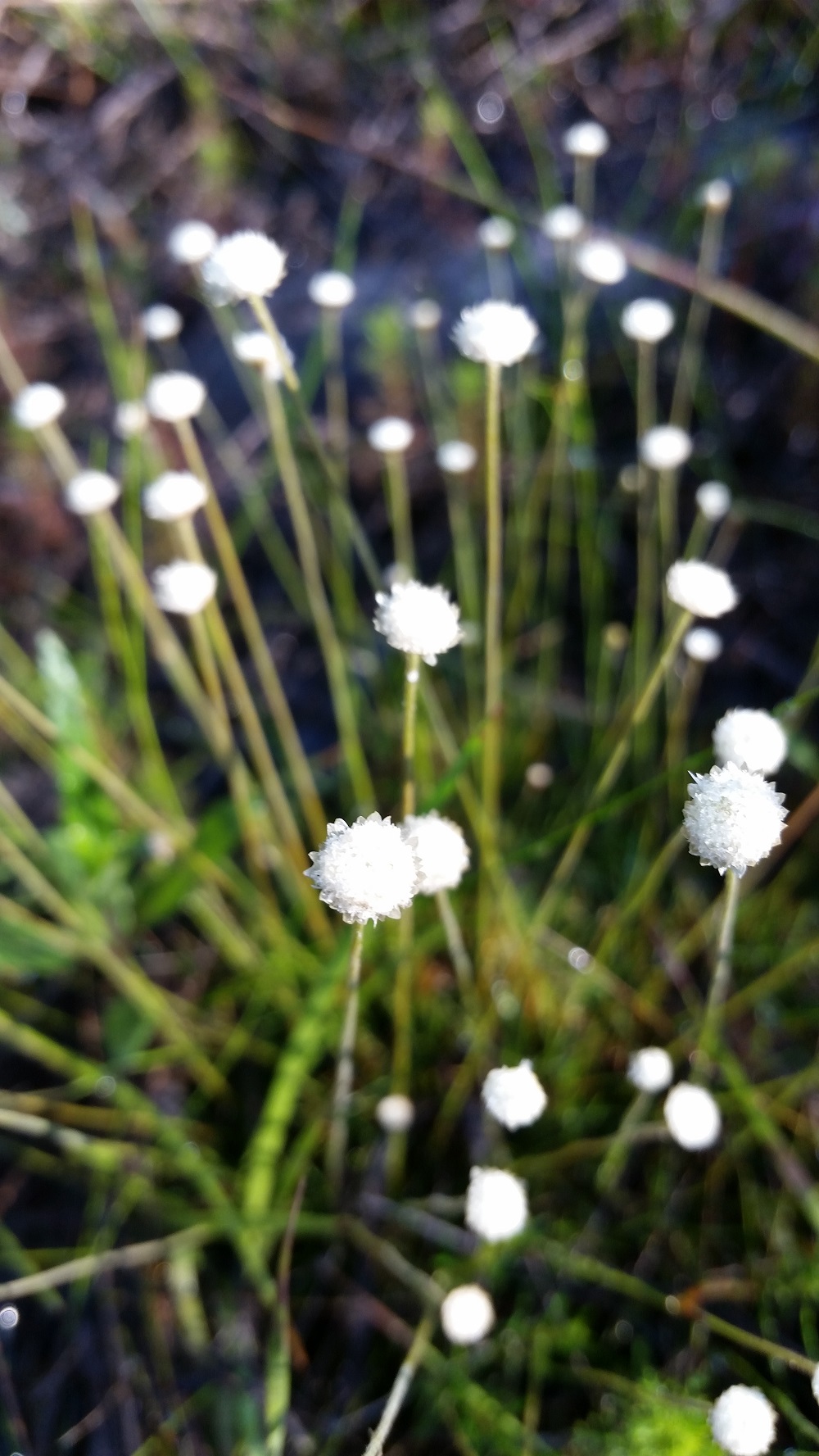

| |
| Photo by Katelin Pearson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Monocotyledons |
| Order: | Eriocaulales |
| Family: | Eriocaulaceae |
| Genus: | Lachnocaulon |
| Species: | L. anceps |
| Binomial name | |
| Lachnocaulon anceps Kunth | |
| |
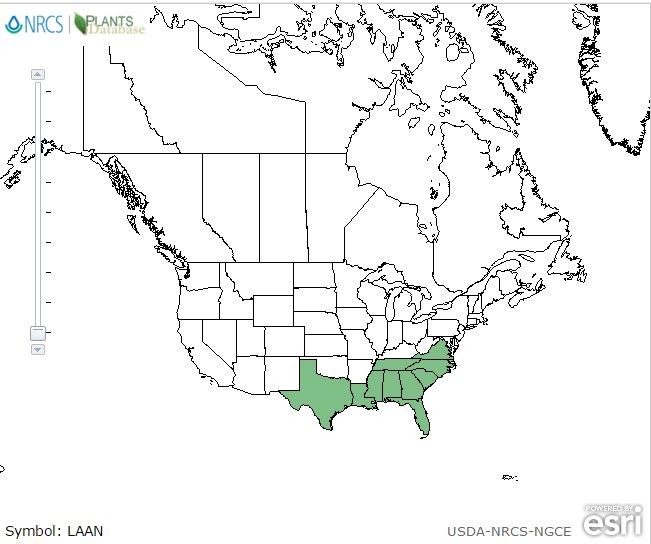
| Natural range of Lachnocaulon anceps from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Common bogbuttons[1]
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Lachnocaulon glabrum Körnicke; L. floridanum Small.[1]
Varieties: none.[1]
Description
Distribution
This plant ranges from southern New Jersey to southern Florida, then west to southeastern Texas. There are disjunct populations in Tennessee, the West Indies[1], and Cuba.[2]
Ecology
Habitat
L. anceps has been found in marshes, flatwoods, pine-saw palmetto forests, lake margins, and cypress depressions.[3] It is also found in disturbed areas including cutover flatwoods, burned slash pine palmettos, roadsides, and drainage ditches.[3]
Associated species: Juncus spp., Calopogon tuberosus, Pogonia ophioglossoides, Sarracenia alata, Ctenium aromaticum, Lycopodiella, Eriocaulon, Xyris, Polygala nana, P. lutea, Lachnanthes, Lophiola, Rhexia lutea, Drosera capillaris, Pinus palustris, Aristida beyreichiana, Rhexia alifanus, Sarracenia flava, S. purpurea, Drosera tracyi, D. capillaris, Calopogon pallidus, Serenoa repens, Nolina atopocarpa, Pityopsis oligantha, and Eleocharis tuberculosa.[4][5]
Phenology
L. anceps flowers from May through October.[1]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ Sorrie, B. A. and A. S. Weakley 2001. Coastal Plain valcular plant endemics: Phytogeographic patterns. Castanea 66: 50-82.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Florida State University Herbarium Database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2021. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, R.K. Godfrey, and Sidney McDaniel. States and counties: Florida: Broward, Franklin, Nassau, Orange, Union, and Volusia.
- ↑ Mississippi Museum of Natural Science Herbarium accessed using Southeastern Regional Network of Expertise and Collections (SERNEC) data portal. URL: http://sernecportal.org/portal/collections/index.php Last accessed: June 2021. Collectors: Lucas C. Majure. States and Counties: Mississippi: Forrest and Lauderdale.
- ↑ Mississippi State University accessed using Southeastern Regional Network of Expertise and Collections (SERNEC) data portal. URL: http://sernecportal.org/portal/collections/index.php Last accessed: June 2021. Collectors: Mark Fishbein and Sula Vanderplank. States and Counties: Florida: Liberty. Mississippi: Jackson.
