Difference between revisions of "Jacquemontia tamnifolia"
(→Description) |
(→Distribution) |
||
| (16 intermediate revisions by 10 users not shown) | |||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | Common name: hairy clustervine | + | Common name: hairy clustervine, jacquemontia, common jacquemontia<ref name=weakley>Weakley, A.S. 2020. Flora of the Southeastern United States. Edition of 20 October 2020. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> |
==Taxonomic notes== | ==Taxonomic notes== | ||
| + | Synonyms: ''Thyella tamnifolia'' (Linnaeus) Rafinesque<ref name=weakley/> > | ||
| + | |||
| + | Varieties: none<ref name=weakley/> | ||
| + | |||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| − | This species has a climbing and twining behavior | + | This species has a climbing and twining behavior.<ref name="FSU Herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Andre F. Clewell, J. D. Dwyer, W. E. Harmon, Lisa Keppner, R. Komarek, Robert L. Lazor, and R. A. Norris. States and Counties: Florida: Leon and Washington. Georgia: Colquitt, Decatur, Grady, and Thomas. Countries: Honduras.</ref> |
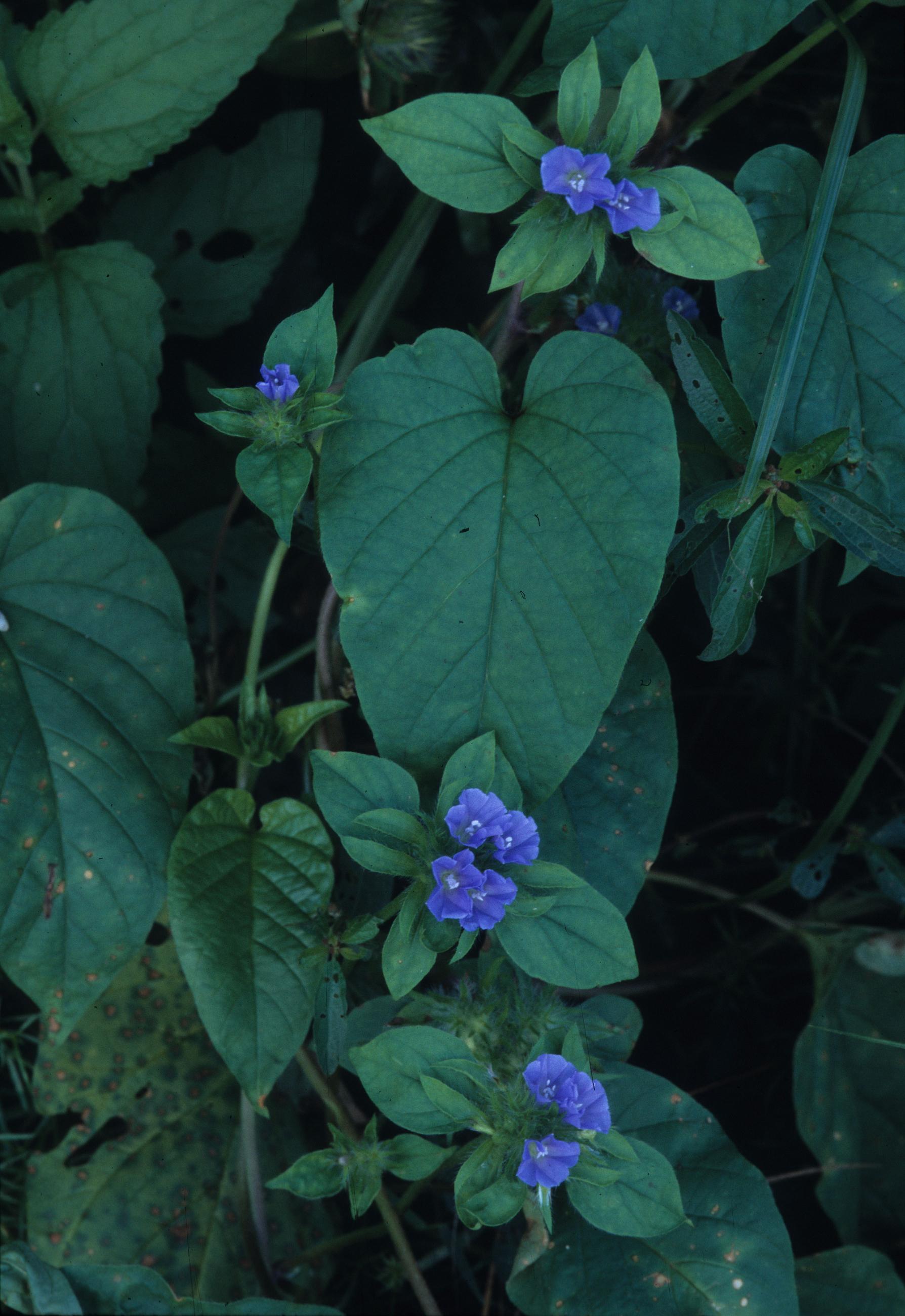
| − | "Herbaceous, annual, twining vine. Leaves ovate to elliptic-ovate, 5-12 cm long, acuminate, cordate, or the base rarely rounded. Peduncles equaling or longer than the subtending leaf; inflorescence capitate, 2-3 cm broad, subtended by lanceolate or elliptic, foliaceous bracts; sepals lanceolate to subulate, densely fulvous-hirsute; corolla blue, funnelform, 1-2 cm broad; stigma lobes 2, ovoid or oblong, styles fused, ovary 2-locular. Capsule subglobose, 4-6 mm broad; seeds brownish black, glabrous, ca. 2 mm long." Radford et al 1964 | + | "Herbaceous, annual, twining vine. Leaves ovate to elliptic-ovate, 5-12 cm long, acuminate, cordate, or the base rarely rounded. Peduncles equaling or longer than the subtending leaf; inflorescence capitate, 2-3 cm broad, subtended by lanceolate or elliptic, foliaceous bracts; sepals lanceolate to subulate, densely fulvous-hirsute; corolla blue, funnelform, 1-2 cm broad; stigma lobes 2, ovoid or oblong, styles fused, ovary 2-locular. Capsule subglobose, 4-6 mm broad; seeds brownish black, glabrous, ca. 2 mm long."<ref name="Radford et al 1964">Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 863. Print.</ref> |
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
| + | The original range of this plant is difficult to determine. In the United States, its range extends from southeast Virginia to Florida, and west to Texas and Arizona. It is also common in the West Indies, Central America, and South America.<ref name=weakley/> | ||
| + | |||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| + | This species has been found in floodplains and savannahs as well as disturbed areas such as old fields, corn fields, powerline corridors, along roadsides, and in grazed fallow fields.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> | ||
| + | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| + | ''J. tamnifolia'' flowers August to Spetember.<ref>Nelson, G. [http://www.gilnelson.com/ PanFlora]: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 12 DEC 2016</ref> | ||
| + | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> | ||
| + | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
| + | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| + | Populations of ''Jacquemontia tamnifolia'' have been known to persist through repeated annual burning.<ref>Glitzenstein, J. S., D. R. Streng, R. E. Masters, K. M. Robertson and S. M. Hermann 2012. Fire-frequency effects on vegetation in north Florida pinelands: Another look at the long-term Stoddard Fire Research Plots at Tall Timbers Research Station. Forest Ecology and Management 264: 197-209.</ref> | ||
| + | <!--===Pollination===--> | ||
| + | <!--===Herbivory and toxicology===--><!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
| + | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | ||
| − | + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== | |
| − | == | + | ==Cultural use== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
| + | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 10:21, 2 June 2023
| Jacquemontia tamnifolia | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo was taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Solanales |
| Family: | Convolvulaceae |
| Genus: | Jacquemontia |
| Species: | J. tamnifolia |
| Binomial name | |
| Jacquemontia tamnifolia (L.) Griseb. | |
| |
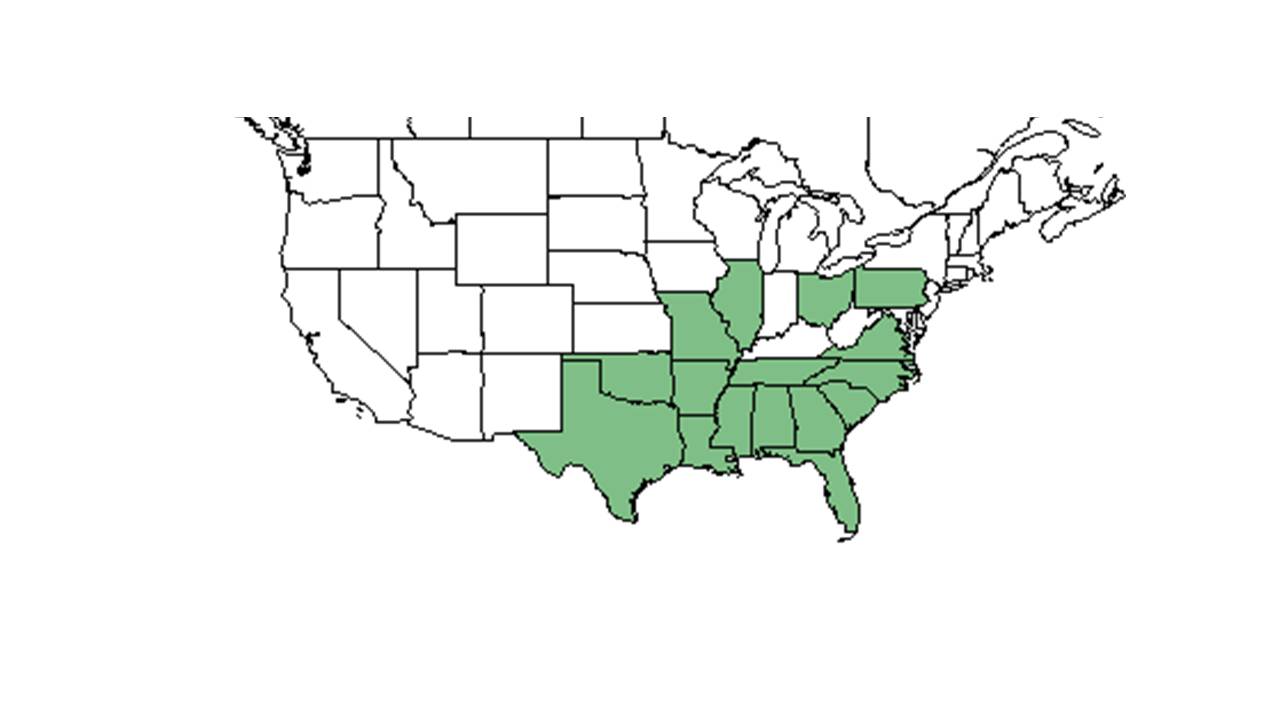
| Natural range of Jacquemontia tamnifolia from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: hairy clustervine, jacquemontia, common jacquemontia[1]
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Thyella tamnifolia (Linnaeus) Rafinesque[1] >
Varieties: none[1]
Description
This species has a climbing and twining behavior.[2]
"Herbaceous, annual, twining vine. Leaves ovate to elliptic-ovate, 5-12 cm long, acuminate, cordate, or the base rarely rounded. Peduncles equaling or longer than the subtending leaf; inflorescence capitate, 2-3 cm broad, subtended by lanceolate or elliptic, foliaceous bracts; sepals lanceolate to subulate, densely fulvous-hirsute; corolla blue, funnelform, 1-2 cm broad; stigma lobes 2, ovoid or oblong, styles fused, ovary 2-locular. Capsule subglobose, 4-6 mm broad; seeds brownish black, glabrous, ca. 2 mm long."[3]
Distribution
The original range of this plant is difficult to determine. In the United States, its range extends from southeast Virginia to Florida, and west to Texas and Arizona. It is also common in the West Indies, Central America, and South America.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
This species has been found in floodplains and savannahs as well as disturbed areas such as old fields, corn fields, powerline corridors, along roadsides, and in grazed fallow fields.[2]
Phenology
J. tamnifolia flowers August to Spetember.[4]
Fire ecology
Populations of Jacquemontia tamnifolia have been known to persist through repeated annual burning.[5]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Weakley, A.S. 2020. Flora of the Southeastern United States. Edition of 20 October 2020. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Andre F. Clewell, J. D. Dwyer, W. E. Harmon, Lisa Keppner, R. Komarek, Robert L. Lazor, and R. A. Norris. States and Counties: Florida: Leon and Washington. Georgia: Colquitt, Decatur, Grady, and Thomas. Countries: Honduras.
- ↑ Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 863. Print.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 12 DEC 2016
- ↑ Glitzenstein, J. S., D. R. Streng, R. E. Masters, K. M. Robertson and S. M. Hermann 2012. Fire-frequency effects on vegetation in north Florida pinelands: Another look at the long-term Stoddard Fire Research Plots at Tall Timbers Research Station. Forest Ecology and Management 264: 197-209.