Difference between revisions of "Ipomoea pandurata"
Emmazeitler (talk | contribs) (→Distribution) |
Emmazeitler (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | Grows in well drained uplands.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> This species has also been observed to grow in | + | Grows in well drained uplands, sandhills, and open pine-oak scrub.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/><ref name="weakley">Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> This species has also been observed to grow in disturbed areas, such as roadsides and open fields.<ref name="FSU Herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, R. F. Doren, R. Komarek, R. A. Norris, and Gwynn W. Ramsey. States and Counties: Florida: Gadsden and Leon. Georgia: Brooks, Grady, and Thomas.</ref> |
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
Revision as of 11:13, 17 September 2020
| Ipomoea pandurata | |
|---|---|

| |
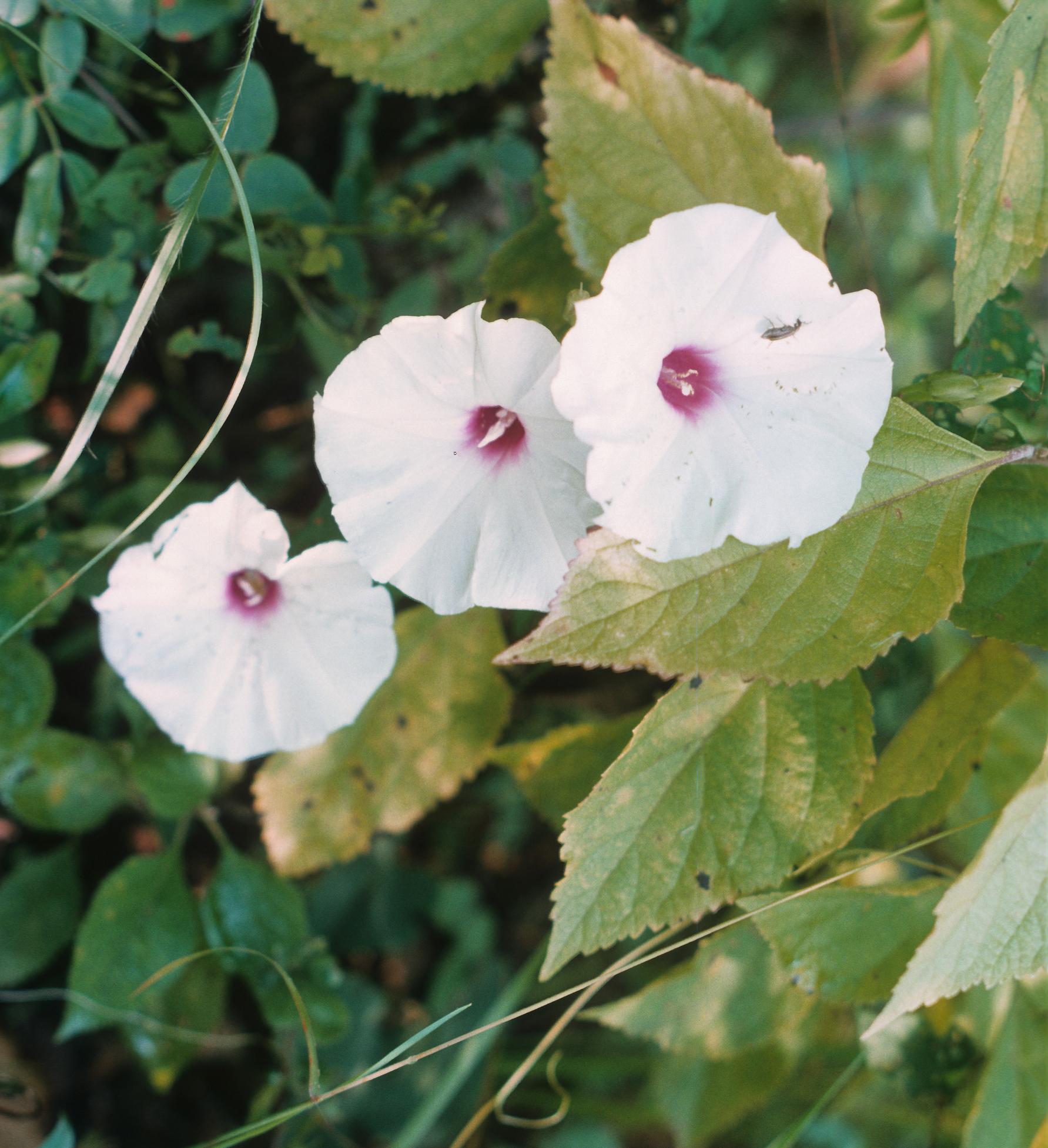
| Photo taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Solanales |
| Family: | Convolvulaceae |
| Genus: | Ipomoea |
| Species: | I. pandurata |
| Binomial name | |
| Ipomoea pandurata (L.) G. Mey. | |
| |
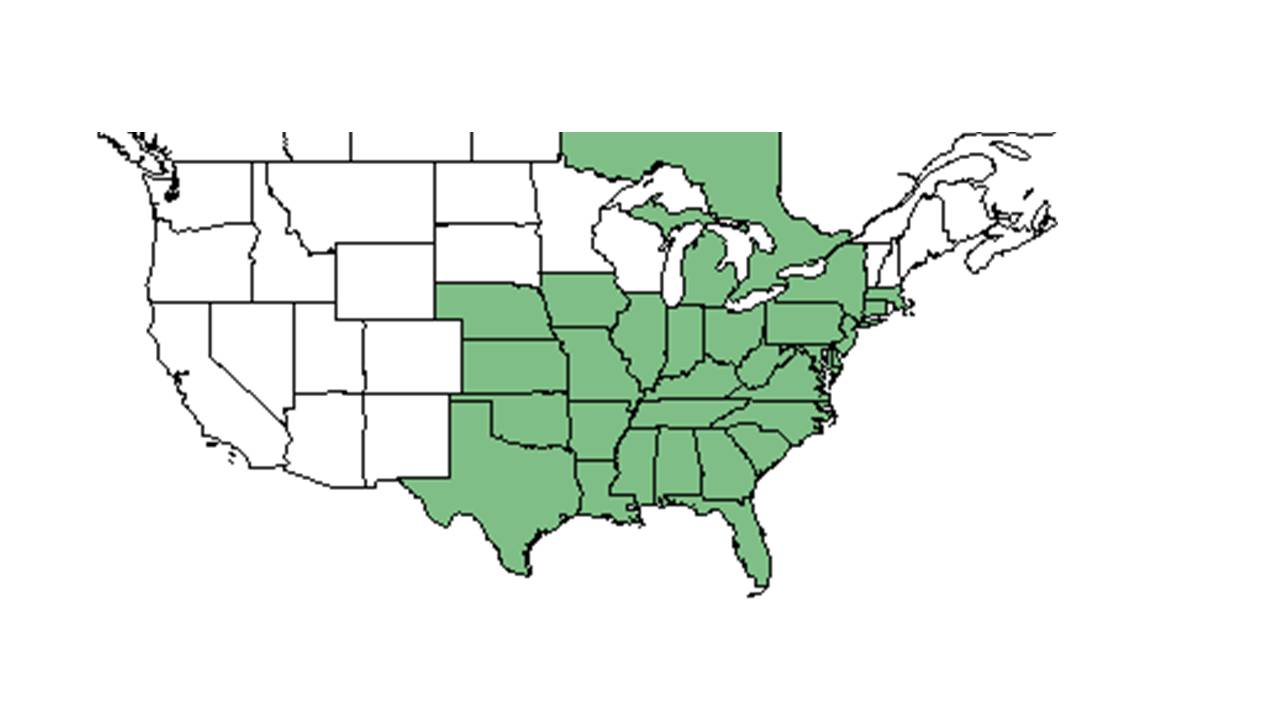
| Natural range of Ipomoea pandurata from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Man-of-the-earth, Wild sweet potato, Manroot[1]
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: none.[1]
Varieties: none.[1]
Description
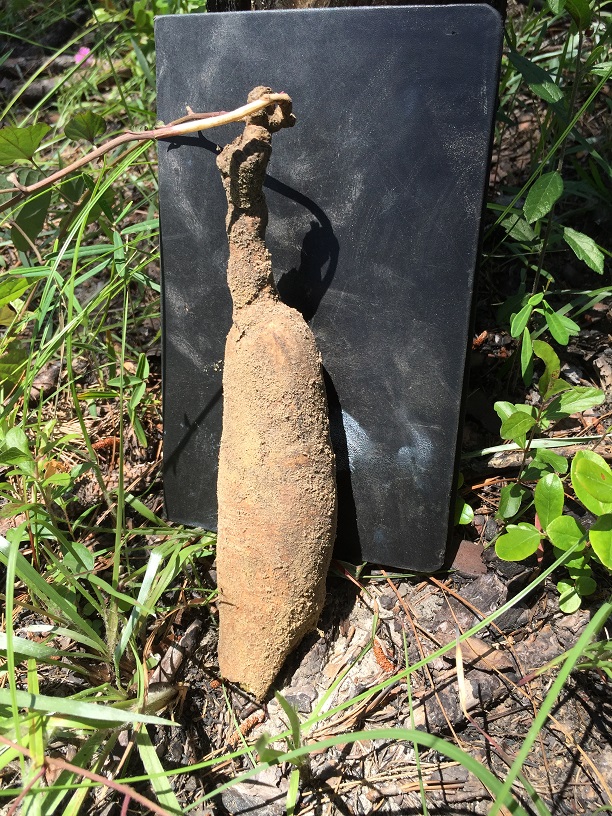
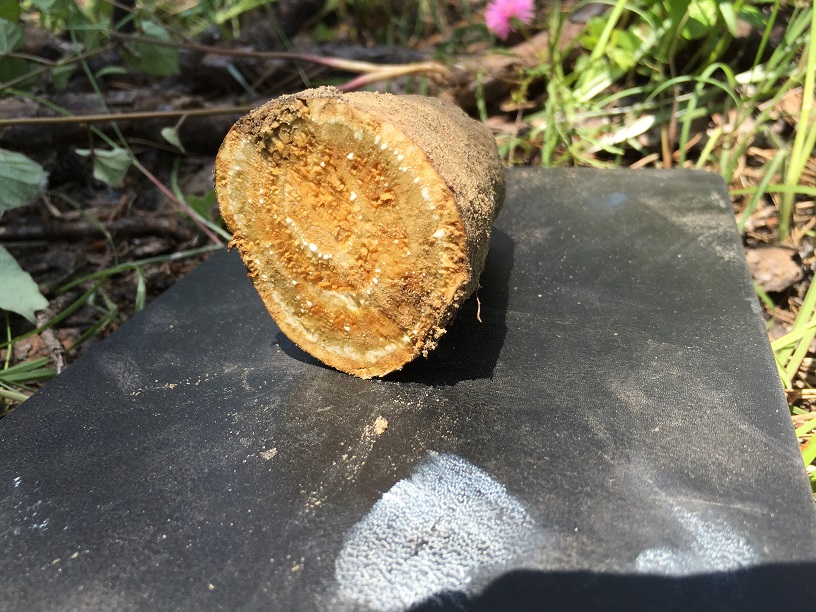
Ipomoea pandurata is a perennial trailing vine, with heart-shaped leaves, has a large storage root, and makes a new shoot every year.[2] The storage root can exceed 20 kg and can be cooked and eaten.[3] This species thrives in canopy opening and in thickets.[2]
Herbaceous annual or perennial vines, or rarely a shrubby perennial. Flowers axillary, solitary or in 2-5 flowered cymes. Calyx lobes 5, often imbricate; corolla campanulate to funnel-form, or salverform in 2 species; stamens 5, inserted in the corolla tube alternate with the lobes; stigma globose, entire or slightly lobed, style 1, ovary 2-or-4 locular. Capsule 2-4 valved; seeds 2-6, sometimes villous. A large genus of primarily tropical plants, some of which were introduced as horticultural plants and have escaped to become noxious weeds.[4]
Trailing, glabrate or weakly pubescent perennial from an enlarged root. Leaves ovate, entire or pandurate, 3.5-8 cm long, 2.5-8 cm wide, cordate, often pubescent beneath. Peduncles 1-5 flowered; pedicel glabrous, stout; calyx lobes coriaceous, oblong-elliptic, 12-15 mm long, glabrous, strongly imbricate; corolla campanulate, 6-8 cm long, about sa broad, the limb white, the tube lavender within; anthers 5-7 mm long, stamens and stigma included. Capsule ovoid, ca. 1 cm long; seeds villous on the angles.[4]
Distribution
This plant is found north in Connecticut, New York, and southern Ontario, west in Ohio, southern, Mississippi, and Kansas, then south in central peninsular FLorida and east Texas.[1]
Ecology
It was observed that I. pandurata’s growth in recently-burned areas is low. However, in areas that are unburned and have low disturbance, it exhibits higher growth rates.[2]
Habitat
Grows in well drained uplands, sandhills, and open pine-oak scrub.[5][1] This species has also been observed to grow in disturbed areas, such as roadsides and open fields.[5]
Phenology
I. pandurata has been observed to flower from May to September with peak inflorescence in May and June.[6][5] Observed growing after a burn at the end of May/early June (Arata 1959).
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by gravity.[7]
Fire ecology
Observed growing after a burn at the end of May/early June.[8] It occurs in mostly longleaf pine communities that are annually burned as well.[5]
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Freeman, D. Carl, Michelle L. Brown, Jeffrey J. Duda, John H. Graham, John M. Emlen, Anthony J. Krzysik, Harold E. Balbach, David A. Kovacic, and John C. Zak. "Photosynthesis and Fluctuating Asymmetry as Indicators of Plant Response to Soil Disturbance in the Fall‐Line Sandhills of Georgia: A Case Study Using Rhus Copallinum and Ipomoea Pandurata." International Journal of Plant Sciences 165.5 (2004): 805-16. Web. 24 June 2013.
- ↑ Hammer, Roger. 2016. Posted to Florida Ecology and Ecosystematics Facebook Group, 11 JAN 2017.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 864-8. Print.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, R. F. Doren, R. Komarek, R. A. Norris, and Gwynn W. Ramsey. States and Counties: Florida: Gadsden and Leon. Georgia: Brooks, Grady, and Thomas.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 12 DEC 2016
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.
- ↑ Arata, A. A. "Effects of burning on vegetation and rodent populations in a longleaf pine-turkey oak association in north central Florida." Quarterly Journal of the Florida Academy of Sciences 22 (1959): 94-104.

