Difference between revisions of "Hypericum tenuifolium"
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
| − | |||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| Line 40: | Line 39: | ||
<!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
<!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | <!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| − | |||
===Pollination=== | ===Pollination=== | ||
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of ''Hypericum tenuifolium'' at Archbold Biological Station (Deyrup 2015): | The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of ''Hypericum tenuifolium'' at Archbold Biological Station (Deyrup 2015): | ||
| Line 53: | Line 51: | ||
<!--===Use by animals===--> <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | <!--===Use by animals===--> <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
<!--===Diseases and parasites===> | <!--===Diseases and parasites===> | ||
| − | + | ==Conservation and management== | |
| − | + | ==Cultivation and restoration== | |
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
<gallery widths=180px> | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| − | |||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA. | Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA. | ||
Revision as of 10:58, 23 June 2016
| Hypericum tenuifolium | |
|---|---|
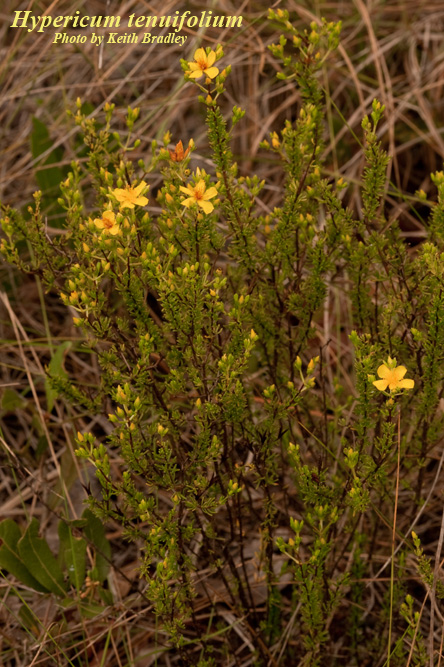

| |
| Photo by Keith Bradley, Atlas of Florida Vascular Plants | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Theales |
| Family: | Clusiaceae ⁄ Guttiferae |
| Genus: | Hypericum |
| Species: | H. tenuifolium |
| Binomial name | |
| Hypericum tenuifolium Pursh | |
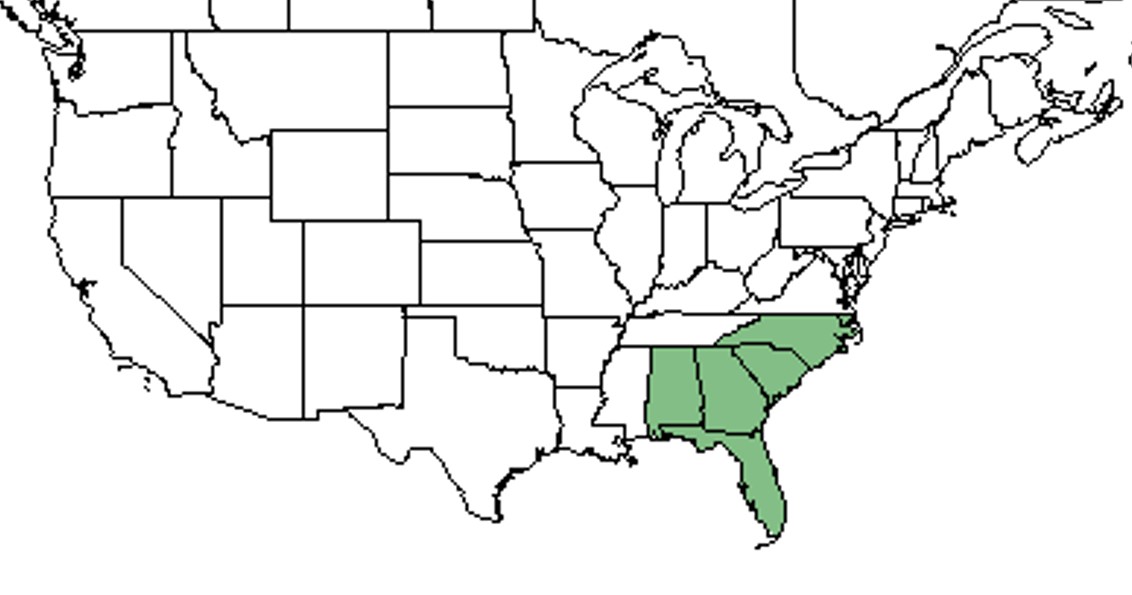
| |
| Natural range of Hypericum tenuifolium from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Atlantic St. Johnswort
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Hypericum reductum (Svenson) W.P. Adams; H. aspalathoides Willdenow
Description
H. tenuifolium is a short lived perennial herb that can reach heights of 12 to 18 inches. Stems are reddish brown and are covered with short needle-like shiny deep green leaves [1]. The flowers have 5 yellow petals, 5 persistent sepals, a superior ovary, and are bisexual and radially symmetrical [2]. A distinctive characteristic of this species is a long seed capsule, ranging from 6 to 9 mmm long [3].
“Usually glabrous herbs or shrubs. Leaves usually punctate, simple, opposite, entire, usually sessile or subsessile, exstipulate. Inflorescence basically cymose; flowers perfect, regular, bracteates, subsessile or short-pedicellate, sepals 2, 4, or 5, persistent; petals 4 or 5, usually marcescent, yellow or pink; stamens 5-numerous, separate or connate basally forming 3-5 clusters or fascicles, filaments usually persistent; carpels 2-5, stigmas and styles separate or fused, ovary superior, 1-locular or partly or wholly 2-5 locular, placentation axile or parietal. Capsules basically ovoid, longitudinally dehiscent, styles usually persistent; seeds numerous, lustrous, areolate, cylindric or oblong. In general our species form a polymorphic complex with many intergrading taxa.” – Radford et al 1964
"Decumbent, matted shrub, 1-5 dm tall, stems usually angled. Leaves linear-subulate, the largest 5-13 mm long, 0.5-1 mm wide, acute, slightly revolute, base notched, sessile. Cymules or dichasia terminal and axillary, or flower solitary, axillary. Sepals 5, similar to leaves, usually less than4.5 mm long; petals 5, 4-10 mm long; styles 3, united or usually separate in fruit, 0.8-3 mm long, ovary 3-locular. Capsules subcylindric, 6-9 mm long, 1.5-2 mm broad; seeds blackish, ca. 0.5 mm long." - Radford et al 1964
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
This species is found in dry, sandy, open sites with good drainage such as sandy woods, dunes and dune hollows, lowland and coastal areas [4]. It is drought tolerant, however does not favor well in soils that remain wet for extended periods[1]. Associated species include Polygonella polygama, Pinus palustris and Paronychia chartacea (FSU Herbarium).
Phenology
Flowering occurs during late spring and early summer with more than a dozen flowers open at any time [1]. Flowers are yellow and aromatic with the fruit capsule ranging from 6 to 9 mm in length[3].
Pollination
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of Hypericum tenuifolium at Archbold Biological Station (Deyrup 2015):
Apidae: Apis mellifera, Bombus griseocollis, B. impatiens
Colletidae: Colletes distinctus, C. productus, C. sp. A, Hylaeus confluens
Halictidae: Augochlorella aurata, A. gratiosa, Augochloropsis anonyma, A. metallica, A. sumptuosa, Lasioglossum miniatulus, L. nymphalis, L. placidensis, L. tamiamensis
Megachilidae: Anthidiellum perplexum, Dianthidium floridiense, Megachile albitarsis, M. brevis pseudobrevis, M. rugifrons