Difference between revisions of "Habenaria quinqueseta"
Laurenloria (talk | contribs) (→Seed dispersal) |
(→Seed dispersal) |
||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
===Seed dispersal=== | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
| − | This species | + | This species is thought to be dispersed by gravity. <ref>Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.</ref> |
<!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
<!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | <!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
Revision as of 10:06, 4 September 2018
| Habenaria quinqueseta | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo was taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida – Monocotyledons |
| Order: | Orchidales |
| Family: | Orchidaceae |
| Genus: | Habenaria |
| Species: | H. quinqueseta |
| Binomial name | |
| Habenaria quinqueseta (Michx.) Eaton | |
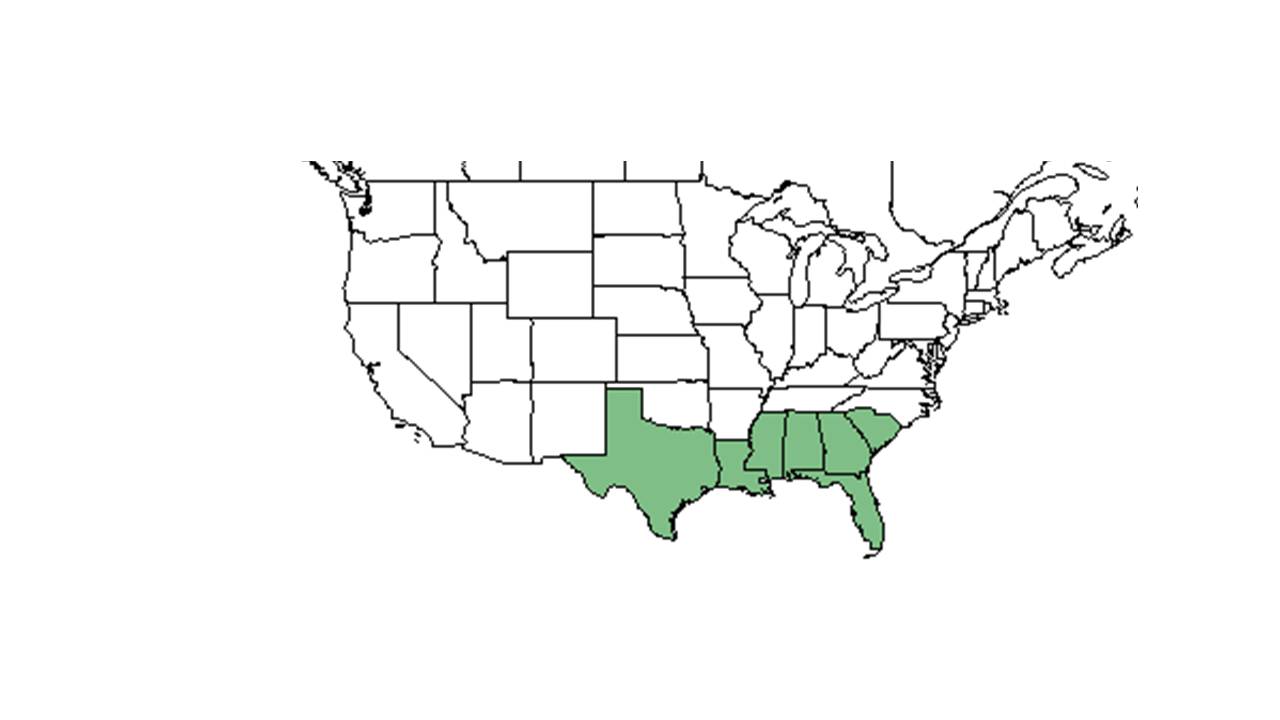
| |
| Natural range of Habenaria quinqueseta from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Longhorn bog orchid; Long-horned habenaria; Michaux’s orchid; Longhorn false reinorchid
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonym: Habenaria quinqueseta var. quinqueseta
Description
A description of Habenaria quinqueseta is provided in The Flora of North America.
Habenaria quinqueseta is a perennial herbaceous species.
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
H. quinqueseta can be found in moist to dry loamy or sandy soils of longleaf pine savannas and open mixed woodlands.[1] Associated species include Pinus, Quercus, Magnolia, Cornus, Liquidambar styraciflua, Vaccinium, Pinus taeda, and Quercus nigra.[1]
Phenology
Flowering and fruiting has been observed in September and October.[1]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by gravity. [2]
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, R. Kral, U. Reis, Richard R. Clinebell II, Leon Neel, and Paul C. Standley. States and Counties: Florida: Leon. Georgia: Dougherty and Thomas. Country: Honduras
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.