Difference between revisions of "Gymnopogon brevifolius"
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| − | It flowers in August.<ref name="Flint 1887">Flint, C. L. (1887). Grasses and forage plants: a practical treatise comprising their natural history; comparative nutritive value; methods of cultivating, cutting, and curing. Boston, MA, Lee and Shepard Publishers.</ref> | + | It has been observed to flower and fruit in January, April, September through October, and December (FSU Herbarium). It also flowers in August.<ref name="Flint 1887">Flint, C. L. (1887). Grasses and forage plants: a practical treatise comprising their natural history; comparative nutritive value; methods of cultivating, cutting, and curing. Boston, MA, Lee and Shepard Publishers.</ref> |
===Seed dispersal=== | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
Revision as of 15:56, 13 July 2015
| Gymnopogon brevifolius | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida – Monocotyledons |
| Order: | Cyperales |
| Family: | Poaceae ⁄ Gramineae |
| Genus: | Gymnopogon |
| Species: | G. brevifolius |
| Binomial name | |
| Gymnopogon brevifolius Trin. | |
| |
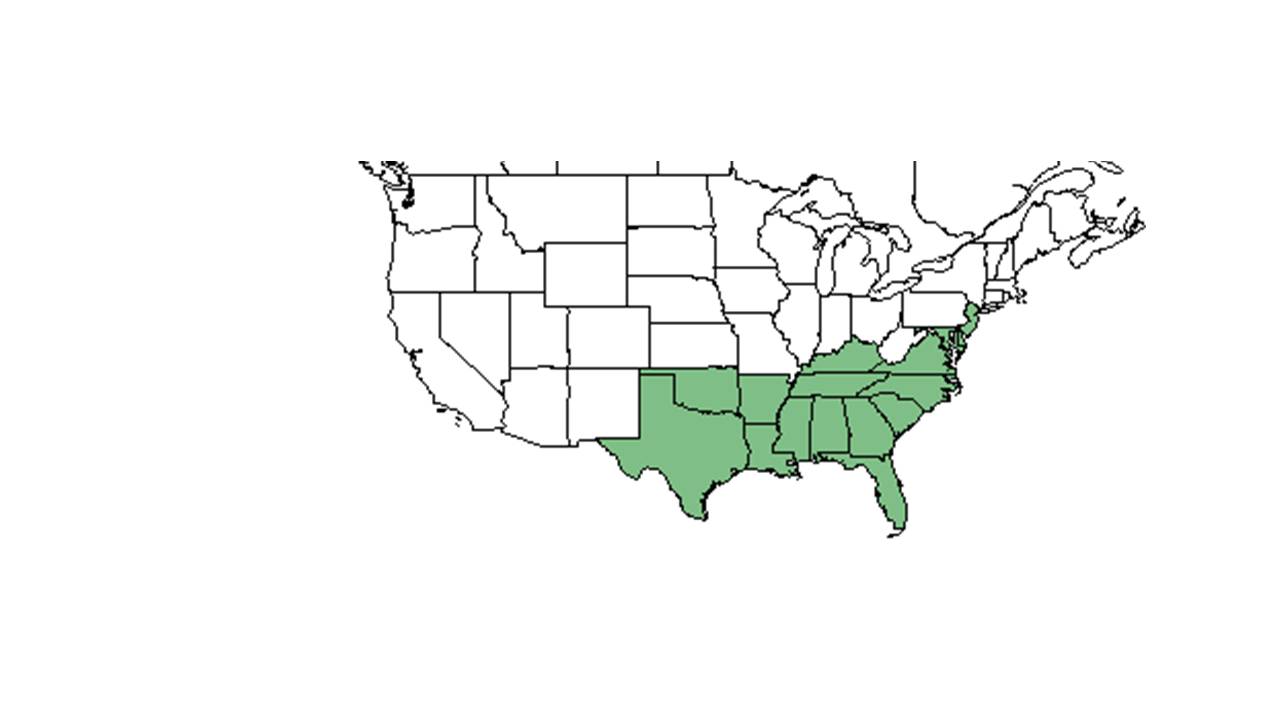
| Natural range of Gymnopogon brevifolius from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Description
Common Name: shortleaf skeletongrass
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
This species is found on longleaf pine sandhills, open wiregrass-pinewoods savannas, mesic pine flatwoods, palmetto-wiregrass-longleaf pine woodlands, pine barrens, and mixed woodlands (FSU Herbarium). They occur on dry and moist sandy loam in these environments as well as human disturbed habitats such as along back roads (FSU Herbarium).
Phenology
It has been observed to flower and fruit in January, April, September through October, and December (FSU Herbarium). It also flowers in August.[1]
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
Pollination
Use by animals
Comprised deer diets more in the summer than in the winter.[2]
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ Flint, C. L. (1887). Grasses and forage plants: a practical treatise comprising their natural history; comparative nutritive value; methods of cultivating, cutting, and curing. Boston, MA, Lee and Shepard Publishers.
- ↑ Thill, R. E. (1983). Deer and cattle forage selection on Louisiana pine-hardwood sites. New Orleans, LA, USDA Forest Service.