Difference between revisions of "Galactia regularis"
(→Description) |
|||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
It is a legume.<ref name="Bolin 2009"/> | It is a legume.<ref name="Bolin 2009"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Common Name: eastern milkpea | ||
| + | |||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
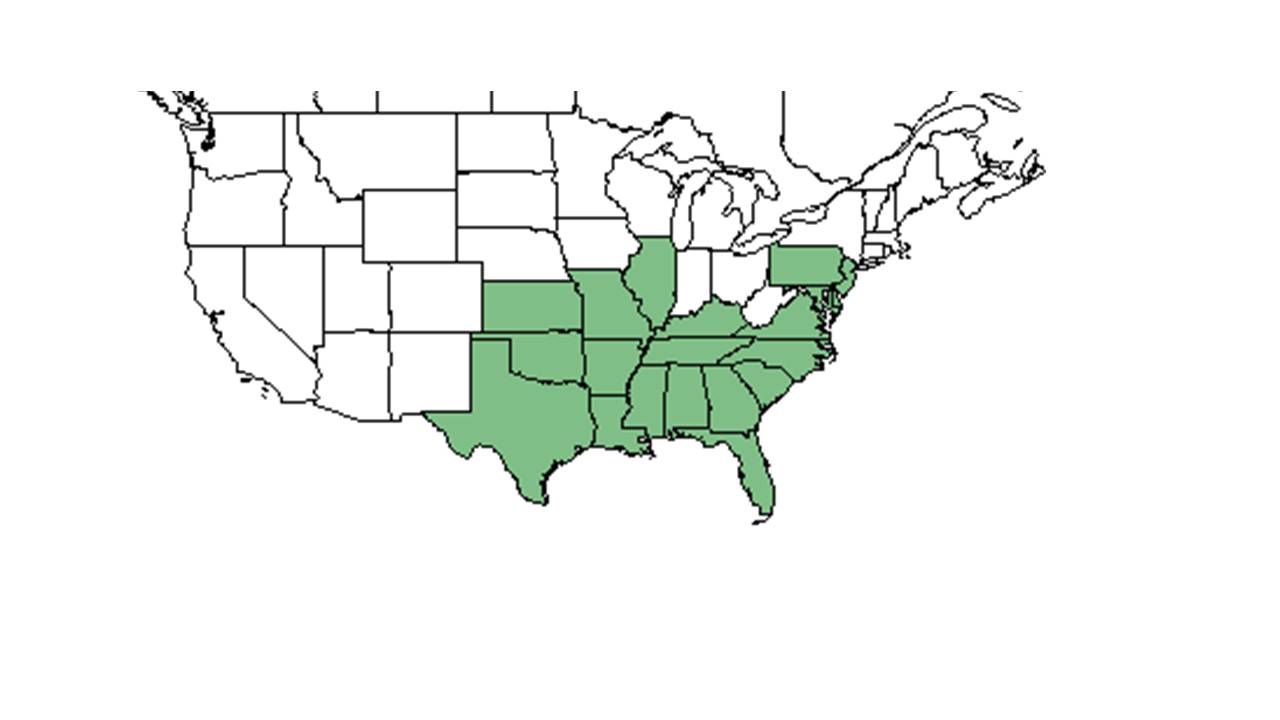
“It occurs in pine lands and sandy woods from New York to Florida and Mississippi.”<ref name="Graham 1941">Graham, E. H. (1941). Legumes for erosion control and wildlife. Washington, USDA</ref> Occurs in Pinus elliottii plantation in South Carolina.<ref name="Mou et al 2005">Mou, P., R. H. Jones, et al. (2005). "Regeneration strategies, disturbance and plant interactions as organizers of vegetation spatial patterns in a pine forest." Landscape Ecology 20: 971-987.</ref> | “It occurs in pine lands and sandy woods from New York to Florida and Mississippi.”<ref name="Graham 1941">Graham, E. H. (1941). Legumes for erosion control and wildlife. Washington, USDA</ref> Occurs in Pinus elliottii plantation in South Carolina.<ref name="Mou et al 2005">Mou, P., R. H. Jones, et al. (2005). "Regeneration strategies, disturbance and plant interactions as organizers of vegetation spatial patterns in a pine forest." Landscape Ecology 20: 971-987.</ref> | ||
Revision as of 14:19, 2 July 2015
| Galactia regularis | |
|---|---|
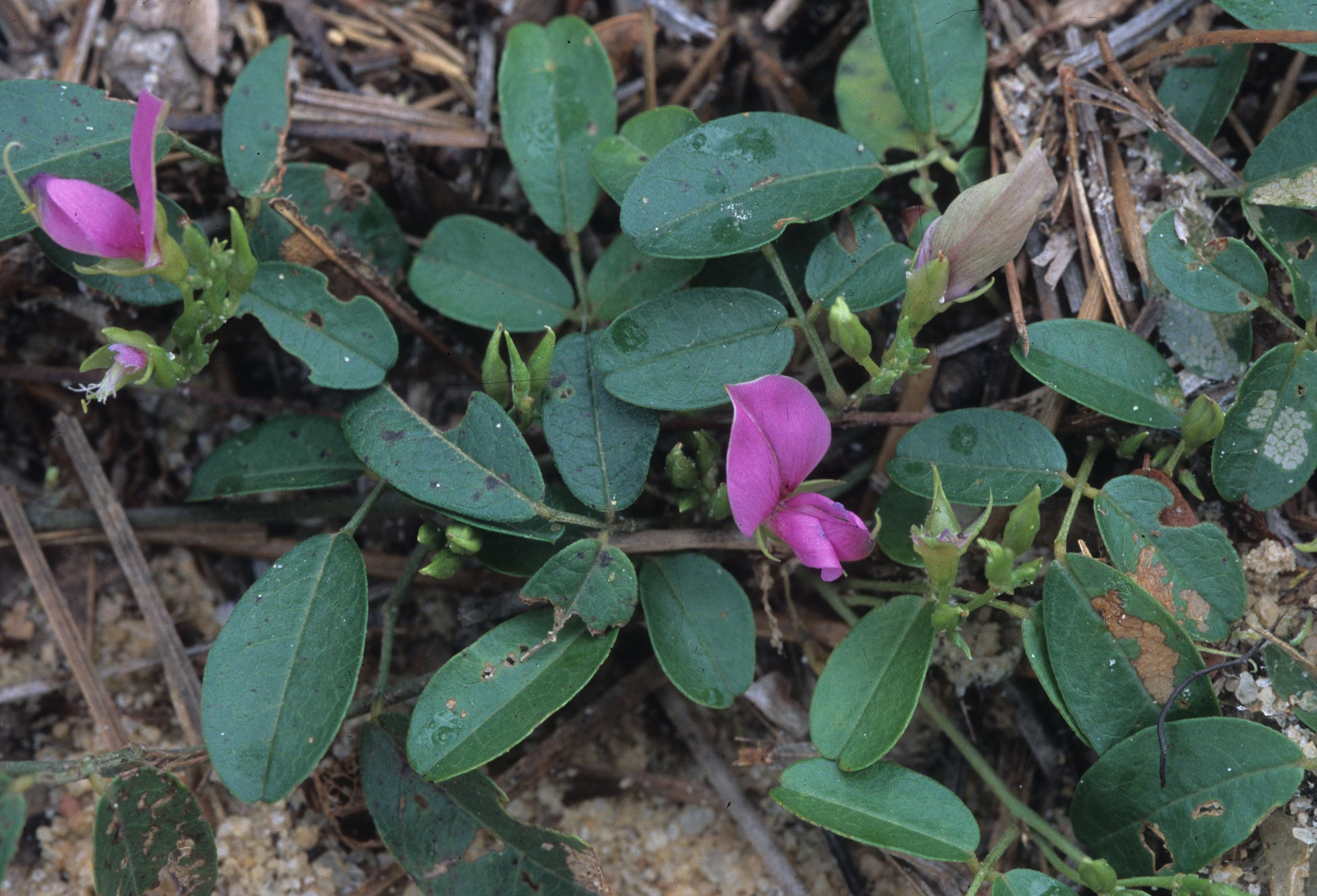

| |
| Photo was taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae ⁄ Leguminosae |
| Genus: | Galactia |
| Species: | G. regularis |
| Binomial name | |
| Galactia regularis (L.) Britton, Sterns & Poggenb. | |
| |
| Natural range of Galactia regularis from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Description
It is a legume.[1]
Common Name: eastern milkpea
Distribution
“It occurs in pine lands and sandy woods from New York to Florida and Mississippi.”[2] Occurs in Pinus elliottii plantation in South Carolina.[3]
Ecology
Habitat
It can be found in xeric areas with hot, wet summers and mild, dry winters.[4] Pine sandhill communities.[5] It can be found in shrubland.[4]
Phenology
“A prostrate perennial with showy violet-purple flowers, frequently found climbing over bushes.”[2]
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
Maximum germination was observed for G. regularis at the 80 degrees Celsius dry heat shock treatment. Wet heat (boiling water) treatments, however, resulted in 100% mortality of seeds.[1] Soil scarification seems to impede germination.[3] It reproduces by resprouting after fire.[6]
Fire ecology
In a field study of vegetation change in Florida scrub, G. regularis cover increased after fire.[7] However, this increase may not be the direct result of fire. Heat shock germination may play a role in its post-fire recruitment.[1] The amount of G. regularis decreased after a spring burn; decreased slightly after a summer burn; and increased in the control plots.[8] A total of 24 plants in four new quadrants were recruited postburn study in the Florida scrub – Lake Wales Ridge area.[9] “Results from previous studies[10] indicate that leguminous plants and seed respond best to “hot” f i r e s - - i . e., those in which a high proportion of the ground fuel is consumed. Laboratory tests[11] have also shown that seed from several leguminous species germinate best after scarification with moist heat at temperatures near 80” C., a situation requiring a hot fire. The response of the leguminous plants and seed in this study, therefore, would probably have been greater if the pine stands had been burned with more intense fires. Nevertheless, further work will be necessary before we can make final conclusions about the value of prescribed burning to quail and other wildlife in the 2.5 million acres of pine in the South Carolina Piedmont.”[8] As an herbaceous vine, the amount of groundcover of G. regularis increased slightly when the area has not been burned (controlled treatment). The amount of groundcover decreased from ~58 to 23% after a burn. (Michelle’s understanding that the G. regularis had a higher population when the area was burned previously before the experiments were conducted).[12]
Pollination
Mark Deyrup at Archbold Biological Station observed these Hymenoptera species on Galactia regularis
Apidae: Apis mellifera
Apidae: Bombus impatiens
Apidae: Svastra atripes
Halictidae: Augochlorella aurata
Halictidae: Augochloropsis metallica
Halictidae: Augochloropsis sumptuosa
Halictidae: Nomia maneei
Megachilidae: Anthidiellum notatum rufomaculatum
Megachilidae: Anthidiellum perplexum
Megachilidae: Anthidium maculifrons
Megachilidae: Coelioxys germana
Megachilidae: Coelioxys sayi
Megachilidae: Megachile albitarsis
Megachilidae: Megachile brevis pseudobrevis
Megachilidae: Megachile brimleyi
Megachilidae: Megachile deflexa
Megachilidae: Megachile exilis parexilis
Megachilidae: Megachile georgica
Megachilidae: Megachile integra
Megachilidae: Megachile mendica
Megachilidae: Megachile petulans
Sphecidae: Trypargilum clavatum johannis
Vespidae: Stenodynerus fundatiformis
Use by animals
Deyrup (2002) observed these bees, Augochlorella aurata, A,gochloropsis metallica, A. szcmptuosa, Nomia maaeei, Anthidiellurn lzotatum rufimaculatum, A. perplexurn, Anthidiuln maczclifrons,Coelioxys gerrnana, C. sayi, Megachilealbitarsis, M. brevis pseudobrevis, M. brirnleyi, M. deflexa, M. exilis parexilis, M. georgica, M.integra, M. mendica, M. petulans, Svastraatripes, Apis mellifera, Bonzbus impatiens, on G. regularis.[13] On occasion, occurred in White-tailed deer’s diet.[14] “Seeds have been found in stomachs of the bobwhite, for which it is considered an important food.”[2]
Diseases and parasites
G. regularis reposnded moderately resistant to a root-knotnematodes study. A nematode, M. incognita, showed an immune response to the root galls and egg masses in the 2004 study but only a highly resistant response in 2001.[15]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Bolin, J. F. (2009). "Heat shock germination responses of three eastern North American temperate species." Castanea 74: 160-167.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Graham, E. H. (1941). Legumes for erosion control and wildlife. Washington, USDA
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Mou, P., R. H. Jones, et al. (2005). "Regeneration strategies, disturbance and plant interactions as organizers of vegetation spatial patterns in a pine forest." Landscape Ecology 20: 971-987.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Hawkes, C. V. and E. S. Menges (2003). "Effects of lichens on seedling emergence in a xeric Florida shrubland." Southeastern Naturalist 2: 223-234.
- ↑ Downer, M. R. (2012). Plant species richness and species area relationships in a Florida sandhill community. Integrative Biology. Ann Arbor, MI, University of South Florida. M.S.: 52.
- ↑ Reinhart, K. O. and E. S. Menges (2004). "Effects of re-introducing fire to a central Florida sandhill community." Applied Vegetation Science 7: 141-150.
- ↑ Weekley, C.W. and E.S. Menges. 2003. Species and vegetation responses to prescribed fire in a long-unburned, endemic-rich Lake Wales ridge scrub. J. Torrey Bot. Soc. 130: 265-282. Bolin, J. F. (2009). "Heat shock germination responses of three eastern North American temperate species." Castanea 74: 160-167.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Cushwa, C. T., M. Hopkins, et al. (1970). Response of legumes to prescribed burns in loblolly pine stands of the South Carolina Piedmont. Asheville, NC, USDA Forest Service, Research Note SE-140: 6.
- ↑ Weekley, C.W. and E.S. Menges. 2003. Species and vegetation responses to prescribed fire in a long-unburned, endemic-rich Lake Wales ridge scrub. J. Torrey Bot. Soc. 130: 265-282.
- ↑ Cushwa, C. T., Czuhai, Eugene, Cooper, R. W., and Julian, W. H. 1969. Burning clearcut openings in Ioblolly pine to improve wildlife habitat. Ga. Forest Res. Count. Res. Pap. 61, 5 pp. Cushwa, C. T. and Redd, J. B. 1966. One prescribed burn and its effects on habitat of the Powhatan Game Management Area. Southeast. Forest Exp. %a., U. S. Forest Serv. Res. Note SE-61, 2 pp.
- ↑ Cushwa, C. T., Martin, R. E., and Miller, R. L. 1968. The effects of fire on seed germination. J. Range Manage. 21: 250-254. M a r t i n , R . E., a n d C u s h w a , C . T. 1966. Effects of heat and moisture on leguminous seed. Fifth Annu. Tall Timbers Fire Ecol. Conf. Proc. 1966: 159-175.
- ↑ Reinhart, K. O. and E. S. Menges (2004). "Effects of re-introducing fire to a central Florida sandhill community." Applied Vegetation Science 7: 141-150.
- ↑ Deyrup, M. J. E., and Beth Norden (2002). "The diversity and floral hosts of bees at the Archbold Biological Station, Florida (Hymenoptera: Apoidea)." Insecta mundi 16(1-3).
- ↑ Gee, K. L., M. D. Porter, et al. (1994). White-tailed deer : their foods and management in the cross timbers. Ardmore, OK, Samuel Roberts Noble Foundation.
- ↑ Quesenberry, K. H., J. M. Dampier, et al. (2008). "Response of native southeastern U.S. legumes to root-knot nematodes." Crop Science 48: 2274-2278.