Eupatorium hyssopifolium
| Eupatorium hyssopifolium | |
|---|---|
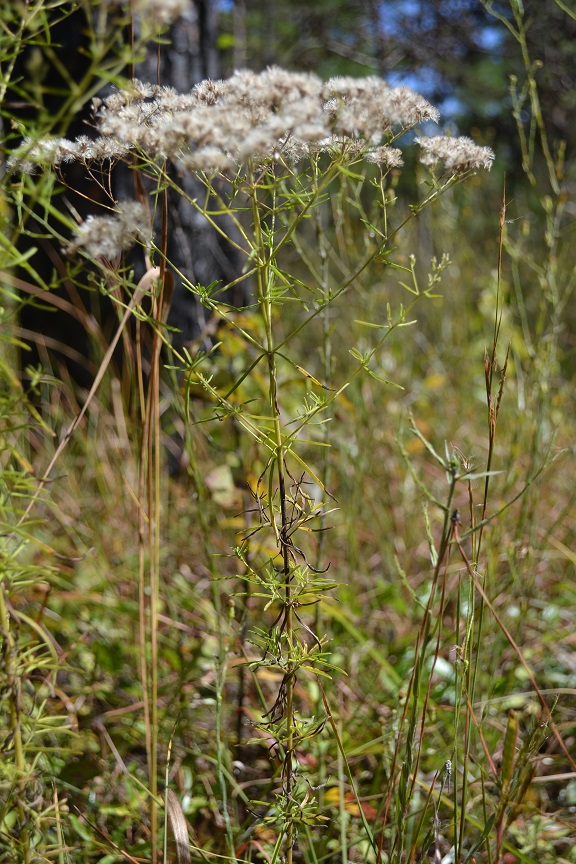

| |
| Photo taken by Kevin Robertson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae ⁄ Compositae |
| Genus: | Eupatorium |
| Species: | E. hyssopifolium |
| Binomial name | |
| Eupatorium hyssopifolium L. | |
| |
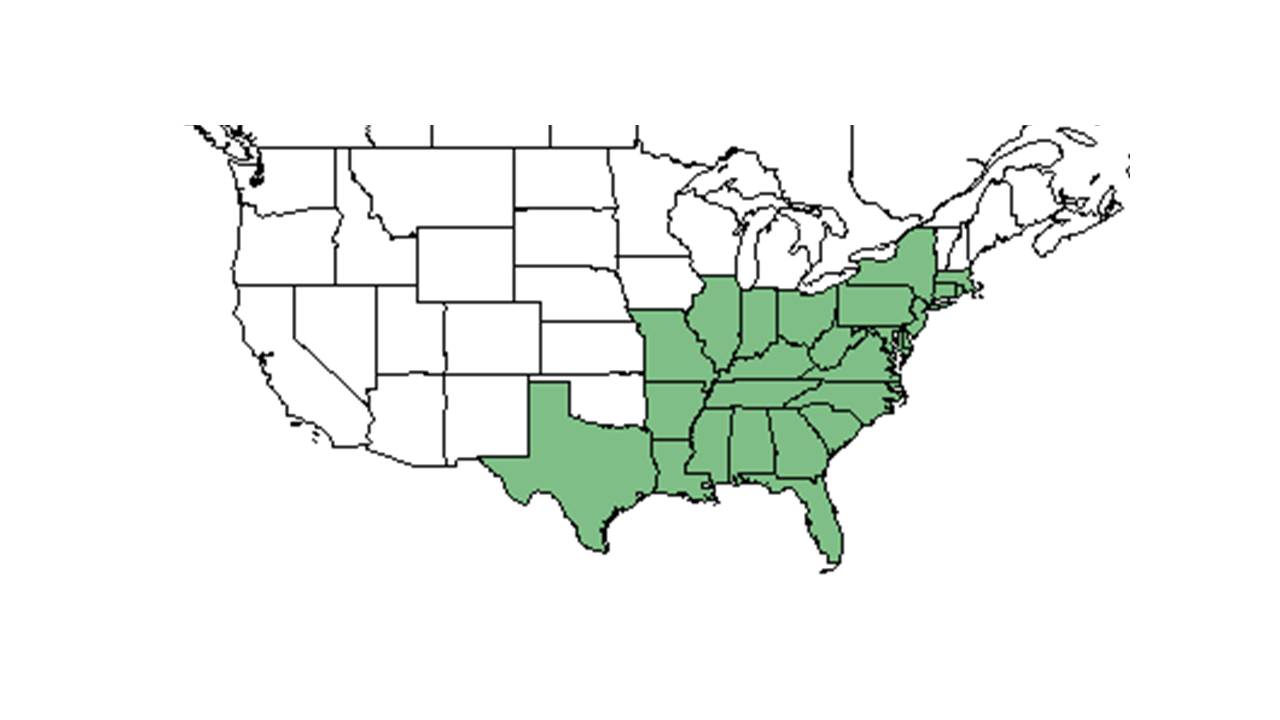
| Natural range of Eupatorium hyssopifolium from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: hyssopleaf thoroughwort; hyssopleaf Eupatorium
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Eupatorium hyssopifolium L. var. hyssopifolium; E. hyssopifolium L. var. calcaratum Fernald & Schubert; E. lecheifolium Greene; E. sessilifolium L.
Description
A description of Eupatorium hyssopifolium is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
E. hyssopifolium is generally distributed from Massachusetts south to Georgia and west to Tennessee and Louisiana.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
Habitats of this species include pastures, roadbanks, fields and disturbed areas, and dry woodlands.[1] It is found in Longleaf pine-Turkey oak sand ridges, Longleaf pine sandhills and flatwoods, pine-palmetto flatwoods, Turkey oak scrubs, Longleaf pine-wiregrass savannas, and in open meadows. It is also found in human disturbed areas such as old fields, roadsides and areas that have been clear cut and bulldozed. It requires high levels of light. It is associated with sandy loam, sand-clay loam, and sandy soil types.[2] As well, it is considered an indicator species of the clayhill longleaf woodlands in northern Florida.[3]
Associated species include Andropogon, Pinus palustris, Quercus laevis, Quercus stellata, Aristida sp., Helianthus sp., and Conoclinium coelestinum.[2]
Phenology
Generally, this species flowers from late July until October.[1] It has been observed flowering from July to November.[2]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by wind. [4]
Fire ecology
It increased in frequency after 12 prescribed burns over an 18 year period.[5] It occurs in pinelands and savannas that are burned annually.[2]
Use by animals
The species attracts various birds.[6]
Conservation and management
E. hyssopifolium is listed as endangered by the Ohio Department of Natural Resources, Division of Natural Areas and Preserves.[7] It is also listed as endangered by the Illinois Endangered Species Protection Board.[8]
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: R. Lazor, Loran C. Anderson, J. P. Gillespie, R.K. Godfrey, Gary R. Knight, R. Kral, Angus Gholson, A. F. Clewell, N. C. Henderson, Victoria I. Sullivan, Carol Havlik, Richard S. Mitchell, R. Komarek, R. A. Norris, and R. F. Doren. States and Counties: Florida: Escambia, Gadsden, Jackson, Leon, Madison, Taylor, and Wakulla. Georgia: Grady and Thomas.
- ↑ Carr, S. C., et al. (2010). "A Vegetation Classification of Fire-Dependent Pinelands of Florida." Castanea 75(2): 153-189.
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.
- ↑ Niering, W. A. and G. D. Dreyer (1989). "Effects of prescribed burning on Andropogon scoparius in postagricultural grasslands in Connecticut." American Midland Naturalist 122: 88-102.
- ↑ [[1]] Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center. Accessed: May 10, 2019
- ↑ USDA, NRCS. (2016). The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 10 May 2019). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ Board, I. E. S. P. (2015). "Checklist of Illinois Endangered and Threatened Animals and Plants."