Difference between revisions of "Elephantopus elatus"
(→Pollination) |
|||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
It responded positively to late winter annual and biennial burns.<ref name="Glitzenstein et al 2003">Glitzenstein, J. S., D. R. Streng, et al. (2003). "Fire frequency effects on longleaf pine (Pinus palustris, P.Miller) vegetation in South Carolina and northeast Florida, USA." Natural Areas Journal 23: 22-37.</ref> | It responded positively to late winter annual and biennial burns.<ref name="Glitzenstein et al 2003">Glitzenstein, J. S., D. R. Streng, et al. (2003). "Fire frequency effects on longleaf pine (Pinus palustris, P.Miller) vegetation in South Carolina and northeast Florida, USA." Natural Areas Journal 23: 22-37.</ref> | ||
| − | ===Pollination=== | + | ===Pollination=== |
| + | Mark Deyrup at Archbold Biological Station observed these Hymenoptera species on ''Elephantopus elatus'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Halictidae: Augochlora pura | ||
| + | |||
| + | Halictidae: Augochlorella aurata | ||
| + | |||
| + | Halictidae: Augochloropsis metallica | ||
| + | |||
| + | Leucospididae: Leucospis slossonae | ||
| + | |||
| + | Megachilidae: Anthidiellum perplexum | ||
| + | |||
| + | Megachilidae: Megachile albitarsis | ||
| + | |||
| + | Megachilidae: Megachile brevis pseudobrevis | ||
| + | |||
| + | Megachilidae: Megachile xylocopoides | ||
| + | |||
| + | Sphecidae: Isodontia exornata | ||
| + | |||
| + | Vespidae: Pachodynerus erynnis | ||
| + | |||
| + | Vespidae: Stenodynerus fundatiformis | ||
| + | |||
===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
These bees, Azcgochlora pura, Augochlorella aurata, Azegochloropsis metallica, Anthidiellum perplexurn, Megachile albitarsis, M. brevis pseudobrevis, and M. xylocopoides, were found on E. elatus.<ref>Deyrup, M. J. E., and Beth Norden (2002). "The diversity and floral hosts of bees at the Archbold Biological Station, Florida (Hymenoptera: Apoidea)." Insecta mundi 16(1-3).</ref> | These bees, Azcgochlora pura, Augochlorella aurata, Azegochloropsis metallica, Anthidiellum perplexurn, Megachile albitarsis, M. brevis pseudobrevis, and M. xylocopoides, were found on E. elatus.<ref>Deyrup, M. J. E., and Beth Norden (2002). "The diversity and floral hosts of bees at the Archbold Biological Station, Florida (Hymenoptera: Apoidea)." Insecta mundi 16(1-3).</ref> | ||
Revision as of 13:40, 26 June 2015
| Elephantopus elatus | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae ⁄ Compositae |
| Genus: | Elephantopus |
| Species: | E. elatus |
| Binomial name | |
| Elephantopus elatus Bertol. | |
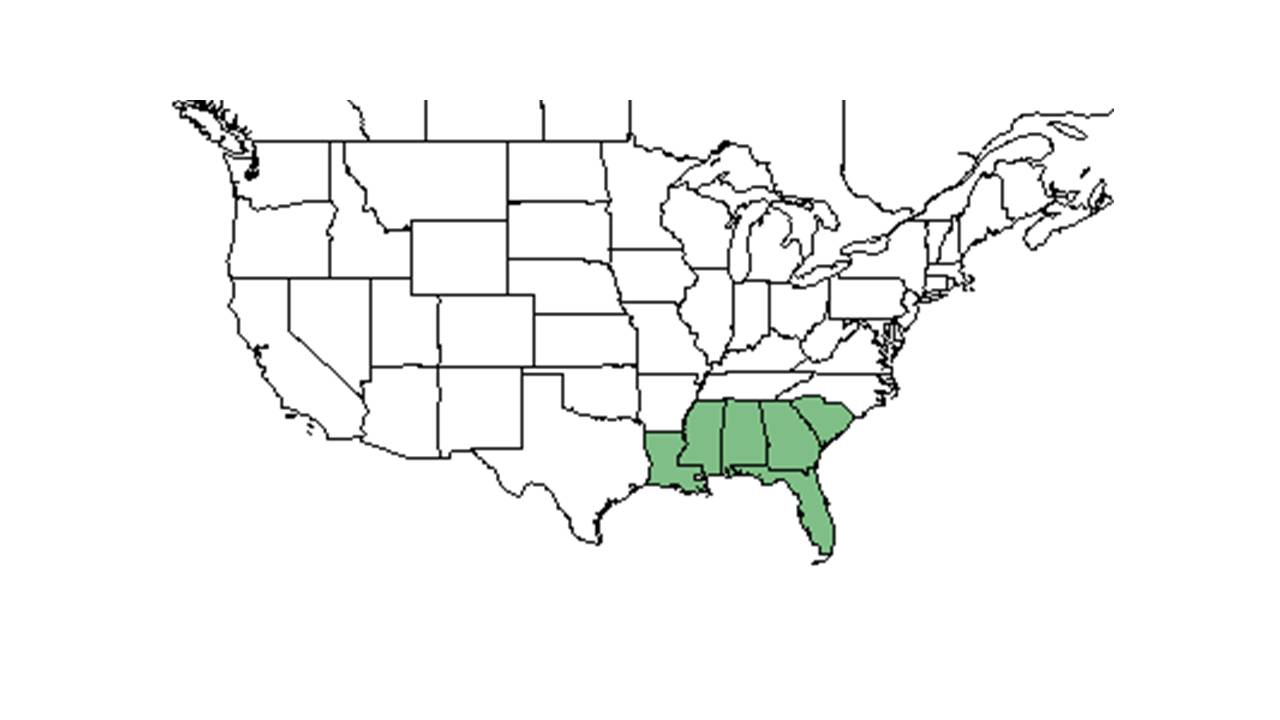
| |
| Natural range of Elephantopus elatus from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Description
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
It prefers dry soil to wetter soil.[1] It is found in dry flatwoods and sandhill communities.[1] Found in sandhills that were consistently higher densities of sandhill plants with showy flowers and higher species richness of sandhill species in the burn than control patches. The most notable difference in the vigor of the flowering response occurred 1 month after the burns and in the fall flowering censuses.[2]
Phenology
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
It responded positively to late winter annual and biennial burns.[1]
Pollination
Mark Deyrup at Archbold Biological Station observed these Hymenoptera species on Elephantopus elatus
Halictidae: Augochlora pura
Halictidae: Augochlorella aurata
Halictidae: Augochloropsis metallica
Leucospididae: Leucospis slossonae
Megachilidae: Anthidiellum perplexum
Megachilidae: Megachile albitarsis
Megachilidae: Megachile brevis pseudobrevis
Megachilidae: Megachile xylocopoides
Sphecidae: Isodontia exornata
Vespidae: Pachodynerus erynnis
Vespidae: Stenodynerus fundatiformis
Use by animals
These bees, Azcgochlora pura, Augochlorella aurata, Azegochloropsis metallica, Anthidiellum perplexurn, Megachile albitarsis, M. brevis pseudobrevis, and M. xylocopoides, were found on E. elatus.[3]
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Glitzenstein, J. S., D. R. Streng, et al. (2003). "Fire frequency effects on longleaf pine (Pinus palustris, P.Miller) vegetation in South Carolina and northeast Florida, USA." Natural Areas Journal 23: 22-37.
- ↑ Heuberger, K. A. and F. E. Putz (2003). "Fire in the suburbs: ecological impacts of prescribed fire in small remnants of longleaf pine (Pinus palustris) sandhill." Restoration Ecology 11: 72-81.
- ↑ Deyrup, M. J. E., and Beth Norden (2002). "The diversity and floral hosts of bees at the Archbold Biological Station, Florida (Hymenoptera: Apoidea)." Insecta mundi 16(1-3).