Difference between revisions of "Eleocharis melanocarpa"
Krobertson (talk | contribs) |
(→Conservation and Management) |
||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
==Conservation and Management== | ==Conservation and Management== | ||
| + | This species is listed as endangered by the Maryland Department of Natural Resources, Natural Heritage Program, by the New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection and Energy, Office of Natural Lands Management, and by the Rhode Island Department of Environmental Management. It is also listed as threatened by the Indiana Department of Natural Resources, Division of Nature Preserves.<ref name= "USDA"/> | ||
==Cultivation and restoration== | ==Cultivation and restoration== | ||
Revision as of 14:50, 3 May 2019
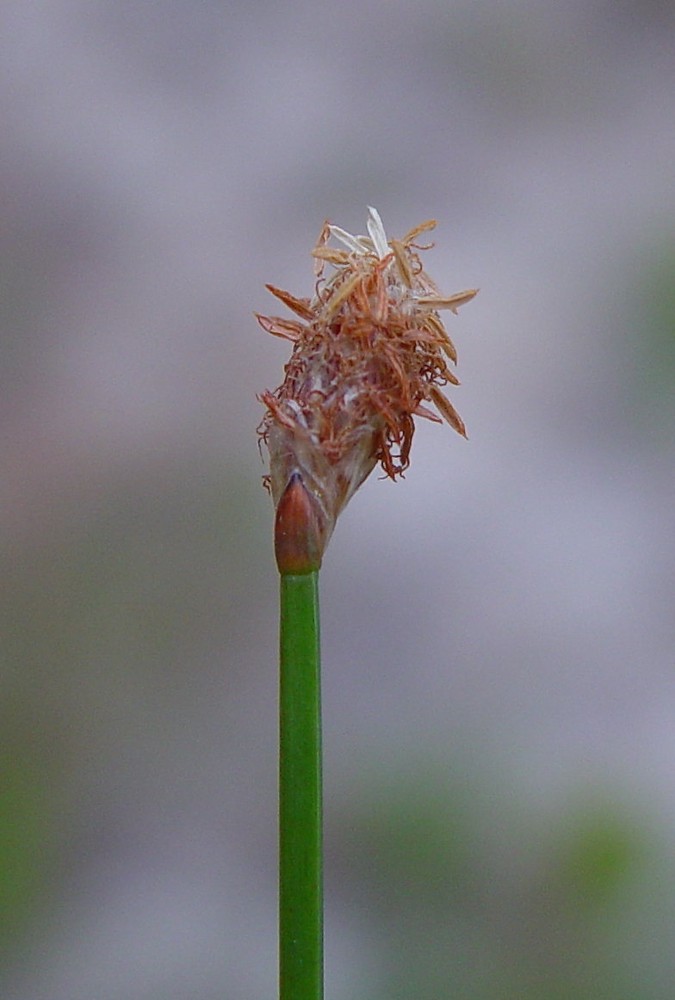
| Eleocharis melanocarpa | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by © Arthur Haines, New England Wild Flower Society | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Poales |
| Family: | Cyperaceae |
| Genus: | Eleocharis |
| Species: | E. melanocarpa |
| Binomial name | |
| Eleocharis melanocarpa Torr. | |
| |
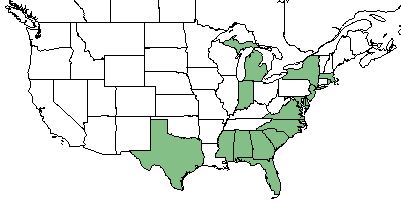
| Natural range of Eleocharis melanocarpa from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Black-fruited spikerush, blackfruit spikerush[1][2]
Contents
Description
E. melanocarpa is a perennial, monoecious, graminoid, sedge.[2] On its seed, the tubercle is very short and dilated with its projecting edge rolled over and surrounding the top of the nut.[3] The tips of the culms of E. melanocarpa often arch over and root in the substrate forming a dense tangle. [4] It commonly grows in stools containing several roots and five to 20 stems. Stems range in length from 1 to 3.6 ft (0.3 to 1.1 m) in length. Stools are commonly bunched together into clusters 1 ft (0.3 m) or more in diameter.[3]
Distribution
E. melanocarpa ranges from Massachusetts to Florida and Mississippi, disjunct to eastern Texas, southern Michigan, and northern Indiana. [2][4][1] Despite most studies not listing E. melanocarpa as occurring in Louisiana, the species has been found in parts of Bienville Parish in 2008 suggesting a more connective distribution along its southern range.[5][6]
Ecology
Habitat
E. melanocarpa is a facultative wetland species found in moist to wet ditches and freshwater pond margins,[7] wet pine savannas, and coastal plain bogs.[1] Such occurrences in these habitats are often ephemeral, sandy, and can range from sunny to shady.[5]
Phenology
E. melanocarpa blooms during the months of June and July in more northern parts of its range[8] and in July through September in its southern range.[1]
Fire ecology
Despite typically inhabiting wet areas, fires from adjacent habitats (e.g. longleaf pine savannas, sandhill pines, old-field, etc.) are thought to burn into drawn-down areas of wet ponds/ditches. Such burns likely maintain more open canopy conditions benefiting populations of E. melanocarpa. [5]
Pollination
E. melanocarpa has no organs for attracting insects for pollination. Instead, it relies on the wind to disseminate pollen.[8]
Conservation and Management
This species is listed as endangered by the Maryland Department of Natural Resources, Natural Heritage Program, by the New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection and Energy, Office of Natural Lands Management, and by the Rhode Island Department of Environmental Management. It is also listed as threatened by the Indiana Department of Natural Resources, Division of Nature Preserves.[2]
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Weakley A. S.(2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 USDA, NRCS. (2016). The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 30 November 2017). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Hill E. J. (1894). Eleocharis melanocarpa a proliferous plant. Bulletin of the Torrey Botanical Club. 25(7):392-394.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Sorrie B. A. and Leonard S. W. (1999). Noteworthy records of Mississippi vascular plants. Sida 18:889-908.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Reid C. S. and Faulkner P. L. (2010). Louisiana. Castanea 75(1):138-140.
- ↑ Sorrie B. A. and Weakley A. S. (2001). Coastal plain vascular plant endemics: Phytogeographic patterns. Castanea 66(1/2):50-82.
- ↑ Contributions to the flora of Florida: 8, Eleocharis (Cyperaceae). Castanea 40(1):16-36.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Harper R. M. (1918). The vegetation of the Hempstead Plains. Proceedings of the semi-centennial anniversary of the Torry Botanical Club. Memoirs of the Torrey Botanical Club 17:262-286.