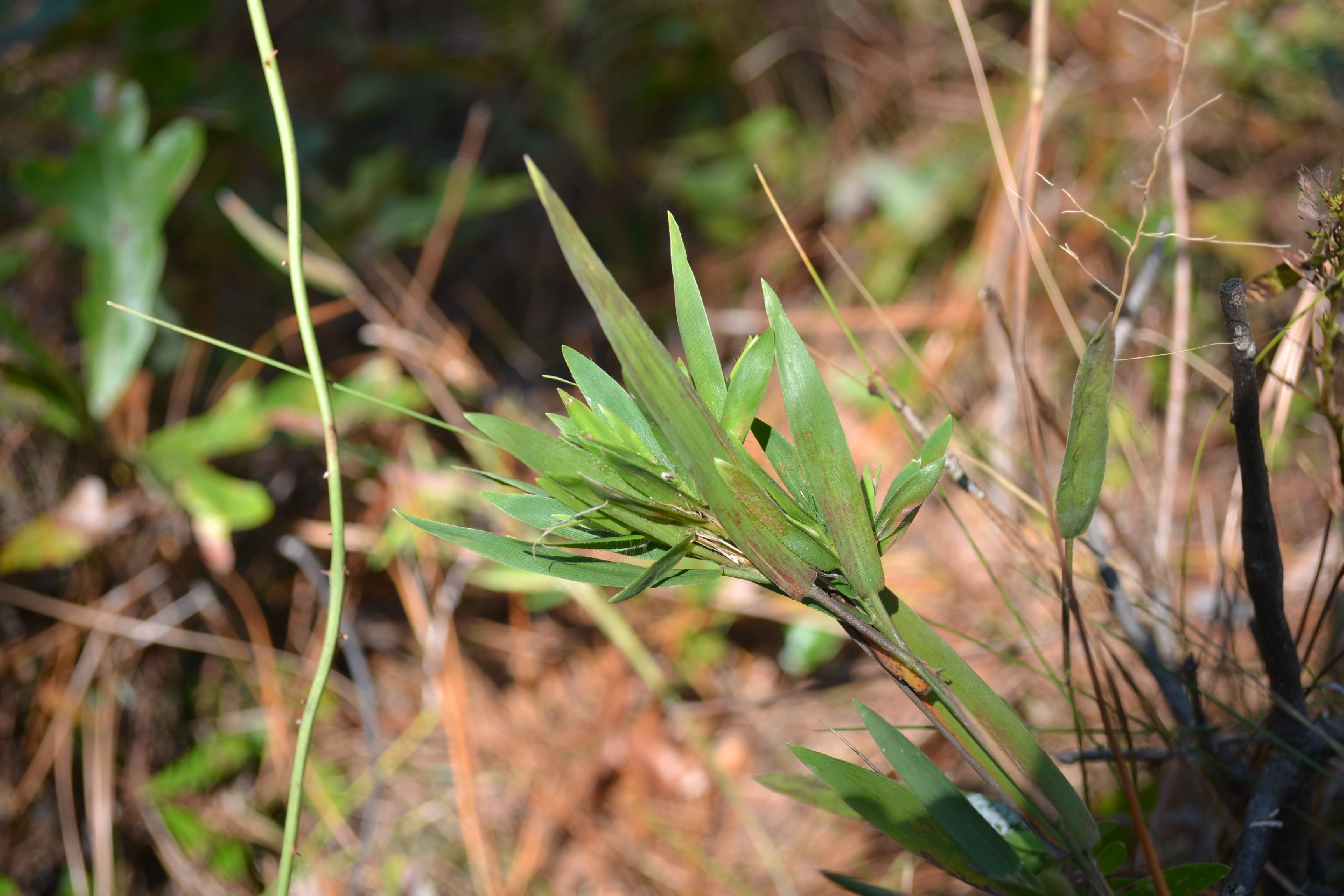
Dichanthelium ovale
oval-flowered witchgrass; low stiff witchgrass
| Dichanthelium ovale | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by Kevin Robertson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Poales |
| Family: | Poaceae |
| Genus: | Dichanthelium |
| Species: | D. ovale |
| Binomial name | |
| Dichanthelium ovale (Elliot) Gould & C.A. | |
| |
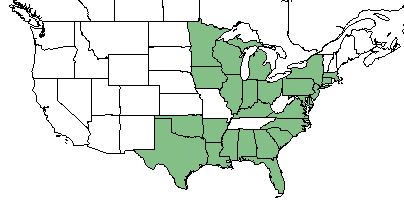
| Natural range of Dichanthelium ovale from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: Panicum commonsianum Ashe; Panicum commonsianum Ashe var. commonsianum; P. commonsianum Ashe var. addisonii (Nash) Fernald; P. mundum Fernald; P. addisonii Nash; P. wilmingtonense Ashe; Panicum ovale Elliott; P. ovale Elliott var. ovale; P. ovale Elliott var. pseudopubescens (Nash) Lelong; Dichanthelium ovale (Elliott) Gould & Clark ssp. ovale; Dichanthelium ovale (Elliott) Gould & Clark ssp. pseudopubescens (Nash) Freckmann & Lelong; D. commonsianum (Ashe) Freckmann
Varieties: Dichanthelium ovale (Elliott) Gould & Clark var. addisonii (Nash) Gould & Clark; Dichanthelium ovale (Elliott) Gould & Clark var. ovale
Description
Also known as eggleaf rosette grass, D. ovale is a native perennial graminoid that is a member of the Poaceae family. It has a rapid growth rate reaching a mature height of 1.7 meters on average, and a short lifespan. [1]
Distribution
D. ovale grows in the eastern United States, ranging from east Texas up to New York and Michigan, excluding West Virginia, Tennessee, and Missouri. [1]
Ecology
Habitat
D. ovale grows in a range of dry to damp soils, in sandy pinelands and woods and fields. [2] More specifically, D. ovale can be found in habitats ranging from open limestone glades, moist soil, longleaf pineland bogs, moist sandy peat, coarse sand habitats, abandoned fields, sandhills, and other sandy loams. [3] It has been seen to be more abundant in disturbed areas. [4]
Associated species - Aristida beyrichiana, Sorghastrum secundum, Schizachyrium scoparium var. stoloniferum [5]
Phenology
The species flowers in the springtime beginning in May, and continues to develop fruit throughout October. [2] Fruit has been seen in the months March through June and August. [3]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by gravity. [6]
Fire ecology
The species does not have any tolerance to fire. [1]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 USDA Plants Database URL: https://plants.usda.gov/java/charProfile?symbol=DIOV
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Wilson Baker, Cecil R. Slaughter, R. Kral, R. K. Godfrey, R. L. Wilbur, G. W. Pamelee, John W. Thieret, A. E. Radford, Steve Mortellaro, Brenda Herring, Don Herring, D. L. Martin, S. T. Cooper, R. Wunderlin, Bruce Hansen, G. Robinson, Steve L. Orzell, E. L. Bridges, R. Komarek, Andre F. Clewell, George R. Cooley, Richard J. Eaton, Leonard J. Brass, R. D. Houlk, J. B. McFarlin, J. Beckner, C. Chapman, R. R. Smith, A. H. Curtiss, Robert F. Thome, R. A. Davidson, Sidney McDaniel, Nancy Coile, G. Smith, N. MacLeish, M. Garland, D. Coile, Richard Carter, Raymond Athey, D. J. Banks, H. Kurz, and Annie Schmidt. States and counties: Florida: Leon, Liberty, Bay, Gadsden, Madison, Wakulla, Calhoun, Jackson, Clay, Franklin, Okaloosa, Duval, Walton, Escambia, Highlands, Gilchrist, Levy, Citrus, Suwannee, Sumter, Columbia, Lee, and Volusia. Alabama: Washington, Lee, Mobile, and Monroe. North Carolina: Pender, Beaufort, and Brunswick. Georgia: Wheeler, Thomas, Decatur, Baker, Walker, and Emanuel. Michigan: Allegan, and Montcalm. Louisiana: Allen, Ouachita, Union, and Natchitoches. South Carolina: Kershaw. Virginia: Roanoke. South Carolina: Berkeley. Tennessee: Coffee. Kentucky: Crittenden.
- ↑ Rodgers, H. L. and L. Provencher (1999). "Analysis of Longleaf Pine Sandhill Vegetation in Northwest Florida." Castanea 64(2): 138-162.
- ↑ Carr, S. C., et al. (2010). "A Vegetation Classification of Fire-Dependent Pinelands of Florida." Castanea 75(2): 153-189.
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.