Difference between revisions of "Dichanthelium curtifolium"
Lsandstrum (talk | contribs) |
Lsandstrum (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | ''D. curtifolium'' proliferates in bogs, sphagnous streamhead swamps, mountain streams, and marl meadows. <ref name= "Weakley 2015"> Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium. </ref> It responds both negatively and positively to soil disturbance by roller chopping in South Florida.<ref>Lewis, C.E. (1970). Responses to Chopping and Rock Phosphate on South Florida Ranges. Journal of Range Management 23(4):276-282.</ref> | + | ''D. curtifolium'' proliferates in bogs, sphagnous streamhead swamps, mountain streams, and marl meadows. <ref name= "Weakley 2015"> Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium. </ref> It responds both negatively and positively to soil disturbance by roller chopping in South Florida.<ref>Lewis, C.E. (1970). Responses to Chopping and Rock Phosphate on South Florida Ranges. Journal of Range Management 23(4):276-282.</ref> However, it responds negatively to soil disturbance by agriculture in Southwest Georgia.<ref>Kirkman, L.K., K.L. Coffey, R.J. Mitchell, and E.B. Moser. Ground Cover Recovery Patterns and Life-History Traits: Implications for Restoration Obstacles and Opportunities in a Species-Rich Savanna. (2004). Journal of Ecology 92(3):409-421.</ref> |
| + | |||
<!--===Phenology===--> <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | <!--===Phenology===--> <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
<!--===Seed dispersal===--> | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> | ||
Revision as of 14:00, 16 July 2019
| Dichanthelium curtifolium | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Cyperales |
| Family: | Poaceae |
| Genus: | Dichanthelium |
| Species: | D. curtifolium |
| Binomial name | |
| Dichanthelium curtifolium Nash | |
| |
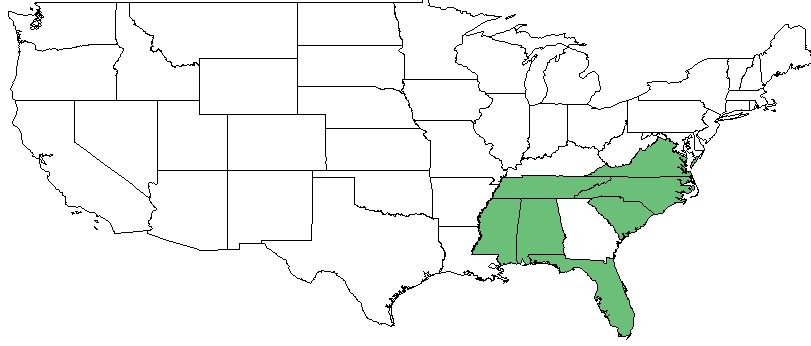
| Natural range of Dichanthelium curtifolium from Weakley. [1] | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: Panicum curtifolium Nash; D. ensifolium (Baldwin ex Elliott) Gould ssp. curtifolium (Nash) Freckmann & Lelong; D. acuminatum (Swartz) Gould & C.A. Clark var. implicatum (Scribner) Gould & C.A. Clark; Panicum ensifolium Baldwin ex Elliott var. curtifolium (Nash) Lelong
Varieties: none
Description
D. curtifolium is a native perennial with a graminoid growth habit that is a member of the Poaceae family. [2]
Distribution
D. curtifolium is found in the southeastern corner of the United States excluding Georgia, ranging along the coast from Mississippi to Virginia. [3]
Ecology
Habitat
D. curtifolium proliferates in bogs, sphagnous streamhead swamps, mountain streams, and marl meadows. [3] It responds both negatively and positively to soil disturbance by roller chopping in South Florida.[4] However, it responds negatively to soil disturbance by agriculture in Southwest Georgia.[5]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ Weakley, Alan S. 2015. Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States: Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, North Carolina. 1320 pp.
- ↑ USDA Plants Database URL: https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=DIDIE
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ Lewis, C.E. (1970). Responses to Chopping and Rock Phosphate on South Florida Ranges. Journal of Range Management 23(4):276-282.
- ↑ Kirkman, L.K., K.L. Coffey, R.J. Mitchell, and E.B. Moser. Ground Cover Recovery Patterns and Life-History Traits: Implications for Restoration Obstacles and Opportunities in a Species-Rich Savanna. (2004). Journal of Ecology 92(3):409-421.