Difference between revisions of "Cyperus croceus"
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) |
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| − | It is fire tolerant | + | It is fire tolerant<ref name=fsu/>. |
<!--===Pollination===--> | <!--===Pollination===--> | ||
<!--===Use by animals===--> <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | <!--===Use by animals===--> <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
<!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | ||
| + | |||
==Conservation and Management== | ==Conservation and Management== | ||
==Cultivation and restoration== | ==Cultivation and restoration== | ||
Revision as of 14:30, 15 April 2016
| Cyperus croceus | |
|---|---|
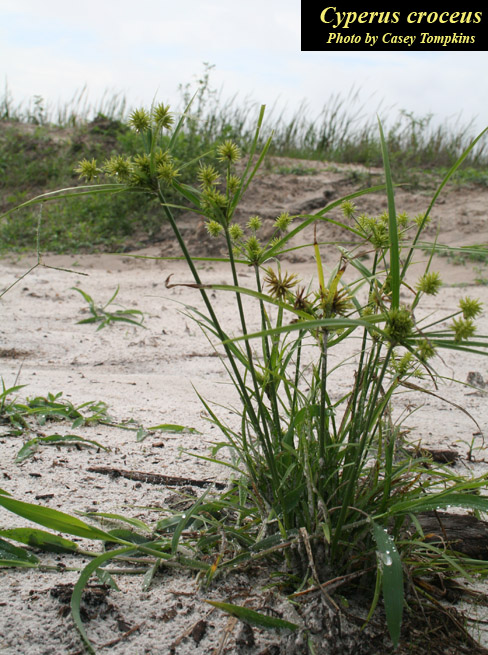

| |
| Photo by Casey Tompkins, Atlas of Florida Vascular Plants | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida – Monocotyledons |
| Order: | Cyperales |
| Family: | Cyperaceae |
| Genus: | Cyperus |
| Species: | C. croceus |
| Binomial name | |
| Cyperus croceus Vahl | |
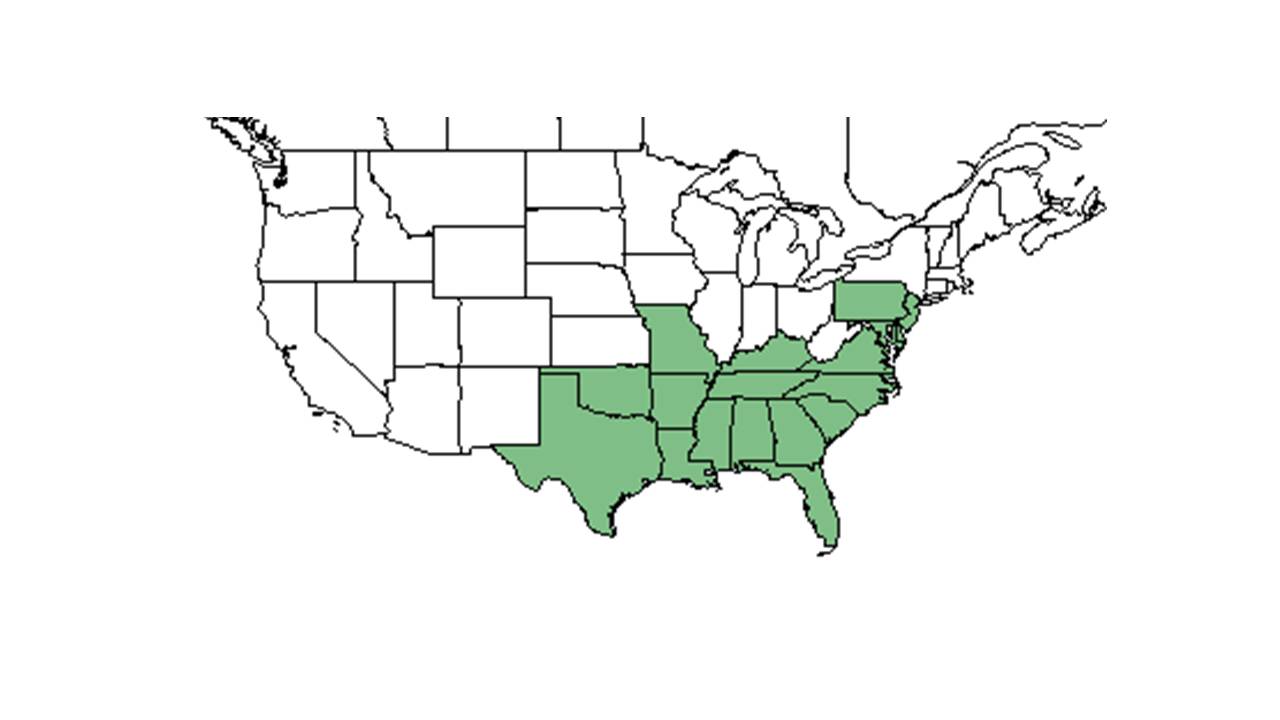
| |
| Natural range of Cyperus croceus from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Baldwin's flatsedge
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Cyperus globosus; C. multiflorus (Britton) Small; C. globosus; C. retrorsus Chapman var. robustus (Böckler) Kükenthal; C. plankii Britton
Description
A description of Cyperus croceus is provided in The Flora of North America. This species is a perennial graminoid.
Distribution
Ecology
It is one of the first plants to appear after clear-cutting; it can appear within three years.[1]
Habitat
Cyperus croceus requires a semi-tropical climate and can dwell in temperatures from -1 to 37 degrees Celsius. It prefers moist areas, including fluvial environments and floodplains, but can occur in a range of soils, from sand, to sandy peat, loam, and drying loamy sand[2].
It can be found in mixed-pine forests,[1] upland hardwood forests, swampy woodlands, and dry ponds. It can also occur in disturbed habitat such as roadsides, citrus groves, spoil banks, and pastures[2].
Associated species includes Alternanthera, Carex, Cephalanthus, Polygonum[2].
Phenology
C. croceus has been observed flowering and fruiting in May through November (FSU Herbarium).
Fire ecology
It is fire tolerant[2].
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Richard Carter, Angus Gholson, Robert K. Godfrey, N. C. Henderson, M. Kral, R. Kral, H. Kurz, S. W. Leonard, J. B. McFarlin, Richard S. Mitchell, P. L. Redfearn, Paul O. Schallert, H. L. Blomquist, William R. Stimson, R. A. Norris, K. E. Blum, Ed Keppner, and Lisa Keppner. States and Counties: Florida: Calhoun, Columbia, Dade, Dixie, Escambia, Franklin, Hernando, Highlands, Indian River, Jackson, Jefferson, Lamar, Leon, Liberty, Martin, Okaloosa, Orange, Palm Beach, Pasco, Santa Rosa, Seminole, St. Lucie, Sumter, Wakulla, and Walton. Georgia: Clinch.
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Archer, J. K., D. L. Miller, et al. (2007). "Changes in understory vegetation and soil characteristics following silvicultural activities in a southeastern mixed pine forest." Journal of the Torrey Botanical Society 134: 489-504.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedfsu