Difference between revisions of "Clinopodium ashei"
(→Taxonomic notes) |
Krobertson (talk | contribs) (→Taxonomic notes) |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
Common names: Ashe's calamint; Ashe's savory; Ohoopee Dunes wild basil | Common names: Ashe's calamint; Ashe's savory; Ohoopee Dunes wild basil | ||
==Taxonomic notes== | ==Taxonomic notes== | ||
| − | Synonyms: ''Calamintha ashei'' (Weatherby) Shinners; ''Satureja ashei'' Weatherby | + | Synonyms: ''Calamintha ashei'' (Weatherby) Shinners; ''Satureja ashei'' Weatherby.<ref name="weakley">Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
| Line 27: | Line 25: | ||
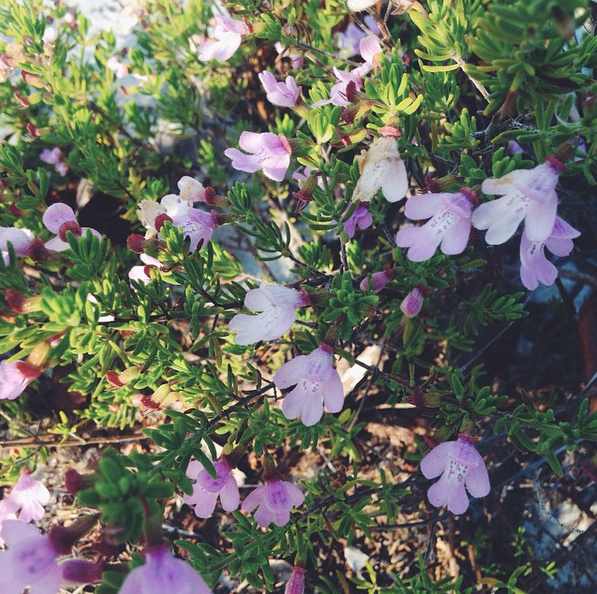
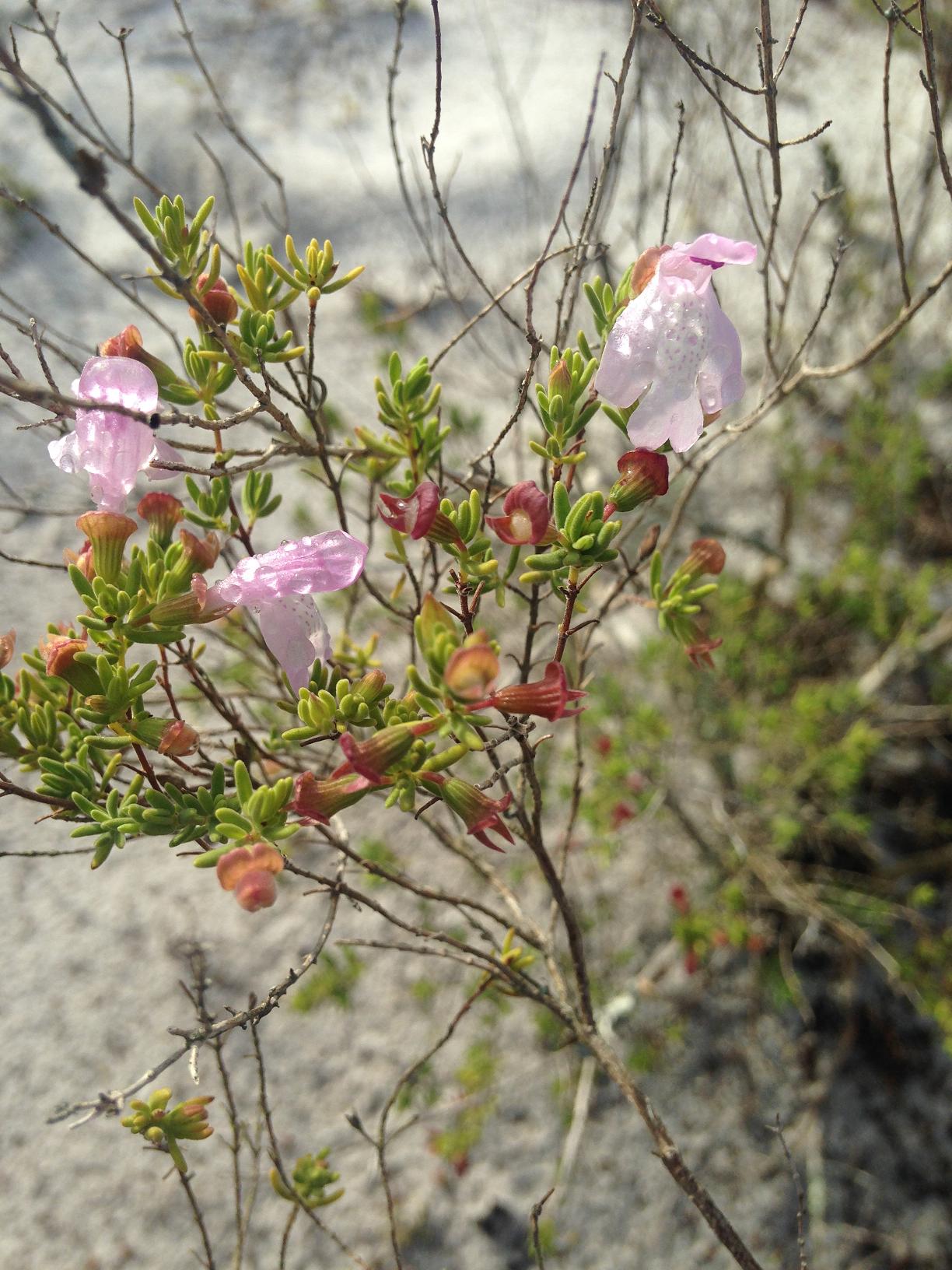
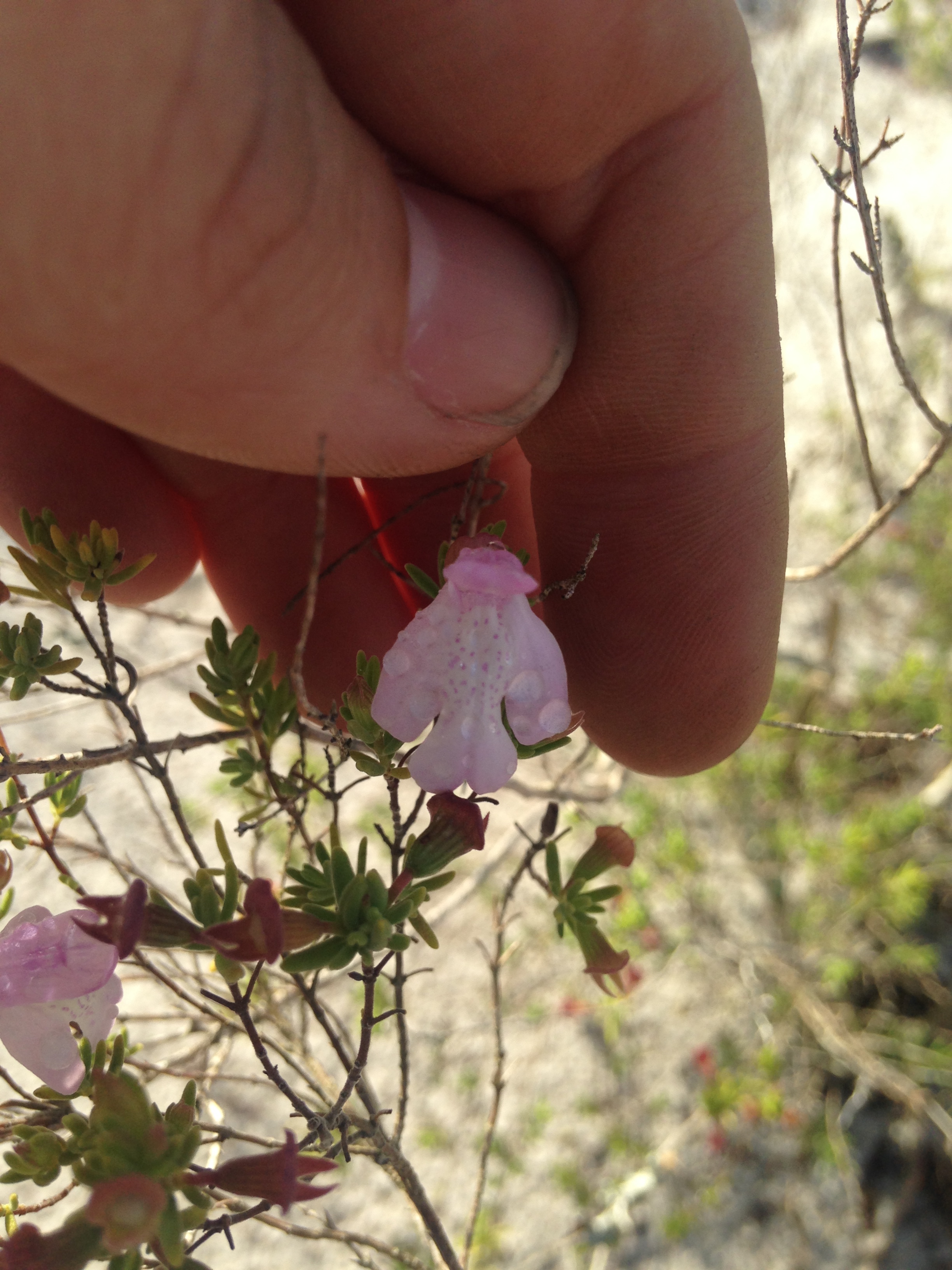
''C. ashei'' is a perennial, aromatic shrub with linear leaves arranged in opposite clusters.<ref name="USDA">[[http://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=Clas2 USDA Plants]] Accessed December 3, 2015</ref> <ref name="Natureserve">[[http://explorer.natureserve.org/servlet/NatureServe?searchName=Clinopodium+ashei NatureServe]]Accessed December 3, 2015</ref> The bisexual flowers are pinkish-purple.<ref name="Natureserve"/><ref name=Ladybird>[[https://www.wildflower.org/plants/result.php?id_plant=CLAS2 Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center]]Accessed: December 3, 2015</ref> | ''C. ashei'' is a perennial, aromatic shrub with linear leaves arranged in opposite clusters.<ref name="USDA">[[http://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=Clas2 USDA Plants]] Accessed December 3, 2015</ref> <ref name="Natureserve">[[http://explorer.natureserve.org/servlet/NatureServe?searchName=Clinopodium+ashei NatureServe]]Accessed December 3, 2015</ref> The bisexual flowers are pinkish-purple.<ref name="Natureserve"/><ref name=Ladybird>[[https://www.wildflower.org/plants/result.php?id_plant=CLAS2 Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center]]Accessed: December 3, 2015</ref> | ||
| − | ==Distribution== | + | ==Distribution== |
| + | ''C. ashei'' is endemic to the Florida central highlands and southeastern Georgia.<ref name="Natureserve"/><ref name="FSU"/> | ||
| + | |||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat===<!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat===<!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | ''C. ashei'' | + | ''C. ashei'' occurs in pine-oak scrub ridges, and in ''Ceratiola'' scrubs.<ref name="Natureserve"/><ref name="FSU">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: October 2015. Collectors: John R. Bozeman, D. Burch, Buswell, L.J. Brass, Chas. C. Deam, R.K. Godfrey, O. Lakela, Sidney McDaniel, Elmer C. Prichard, D.B. Ward. States and Counties: Florida: Highlands, Marion, Polk, Volusia. Georgia: Tattnall. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.</ref> It thrives in open areas of pine scrubs and disturbed sites such as abandoned fields, roadsides, and fire lanes.<ref name="Natureserve"/><ref name="Center">[[http://www.centerforplantconservation.org/collection/CPC_ViewProfile.asp?CPCNum=665 Center for Plant Conservation]] Accessed December 3, 2015</ref> |
In order to reduce competition, ''C. ashei'' releases allelopathic compounds that prevent germination of other species' seeds, creating un-vegetated patches of sand.<ref name="Georgia">[[http://georgiawildlife.com/sites/default/files/uploads/wildlife/nongame/pdf/accounts/plants/calamintha_ashei.pdf Georgia Wildlife]] Accessed: December 3, 2015</ref> | In order to reduce competition, ''C. ashei'' releases allelopathic compounds that prevent germination of other species' seeds, creating un-vegetated patches of sand.<ref name="Georgia">[[http://georgiawildlife.com/sites/default/files/uploads/wildlife/nongame/pdf/accounts/plants/calamintha_ashei.pdf Georgia Wildlife]] Accessed: December 3, 2015</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Associated species include ''Osmanthus megacarpus, Ilex cumulicola'' and, ''Ceratiola ericoides.''<ref name="FSU"></ref> | ||
===Phenology===<!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology===<!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| Line 41: | Line 43: | ||
===Pollination=== | ===Pollination=== | ||
| − | + | ''Calamintha ashei'' has been observed at the Archbold Biological Station to be visited by bees from the Apidae family such as ''Apis mellifera, Bombus impatiens, Epeolus erigeronis'' and ''E. zonatus'', sweat bees from the Halictidae family such as ''Agapostemon splendens, Augochlorella aurata, Augochloropsis sumptuosa, Halictus poeyi, Lasioglossum nymphalis'' and ''L. puteulanum'', and leafcutting bees from the Megachilidae family such as ''Anthidiellum notatum rufomaculatum, A.perplexum, Coelioxys germana, Hoplitis truncata, Lithurgus gibbosus, Megachile brevis pseudobrevis, M. campanulae, M. exilis parexilis, M. georgica, M. inimica, M. mendica, M. petulans, M. policaris, M. rugifrons, M. texana'' and ''Osmia calaminthae''.<ref>Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.</ref> Additionally, this species has been observed to be visited by bees from the Apidae family such as ''Melissodes communis'' and ''Nomada fervida'', as well as leafcutting bees from the Megachilidae family such as ''Anthidiellum perplexum, Coelioxys sayi, Dianthidium floridiense, Megachile albitarsis, M. exilis, M. mendica'' and ''M. pruina''.<ref>Discoverlife.org [https://www.discoverlife.org/20/q?search=Bidens+albaDiscoverlife.org|Discoverlife.org]</ref> | |
| − | |||
| − | Apidae | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <!--===Herbivory and toxicology===--> | |
| − | <!--=== | ||
<!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | ||
| − | ==Conservation and | + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== |
Controlled burning is important for management of ''C. ashei''. It is also important to open the canopy and expose bare sand using methods such as clear cutting and root raking.<ref name="Natureserve"/> | Controlled burning is important for management of ''C. ashei''. It is also important to open the canopy and expose bare sand using methods such as clear cutting and root raking.<ref name="Natureserve"/> | ||
| − | |||
Global rank: G3 | Global rank: G3 | ||
Florida: S3<ref name="Center"/> | Florida: S3<ref name="Center"/> | ||
| + | ==Cultural use== | ||
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
Latest revision as of 16:08, 16 May 2023
| Clinopodium ashei | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Lamiales |
| Family: | Lamiaceae ⁄ Labiatae |
| Genus: | Clinopodium |
| Species: | C. ashei |
| Binomial name | |
| Clinopodium ashei (Weath.) Shinners | |
| |
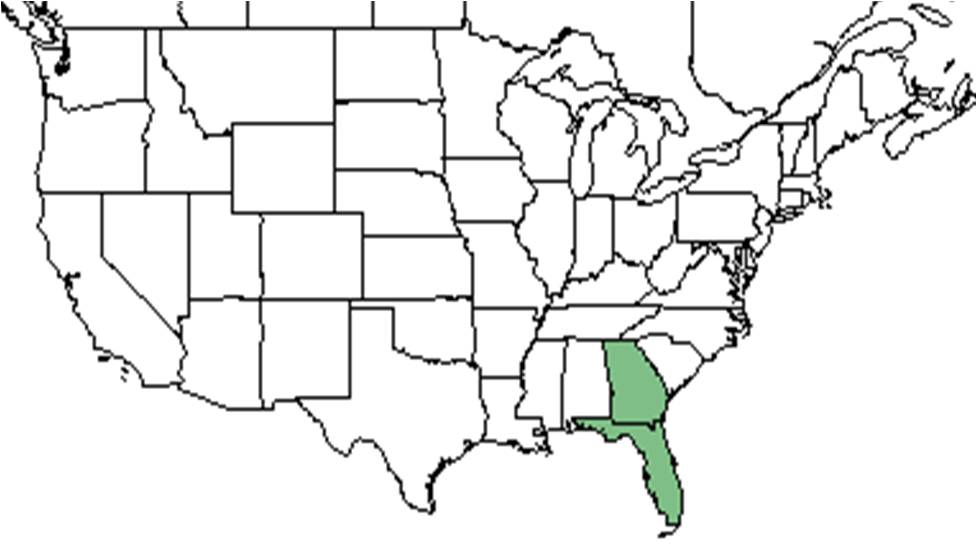
| Natural range of Clinopodium ashei from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Ashe's calamint; Ashe's savory; Ohoopee Dunes wild basil
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Calamintha ashei (Weatherby) Shinners; Satureja ashei Weatherby.[1]
Description
C. ashei is a perennial, aromatic shrub with linear leaves arranged in opposite clusters.[2] [3] The bisexual flowers are pinkish-purple.[3][4]
Distribution
C. ashei is endemic to the Florida central highlands and southeastern Georgia.[3][5]
Ecology
Habitat
C. ashei occurs in pine-oak scrub ridges, and in Ceratiola scrubs.[3][5] It thrives in open areas of pine scrubs and disturbed sites such as abandoned fields, roadsides, and fire lanes.[3][6]
In order to reduce competition, C. ashei releases allelopathic compounds that prevent germination of other species' seeds, creating un-vegetated patches of sand.[7]
Associated species include Osmanthus megacarpus, Ilex cumulicola and, Ceratiola ericoides.[5]
Phenology
Flowers and fruits have been observed January through June.[5]
Fire ecology
Fire has been observed to kill all adult C. ashei individuals.[8] Seedling frequency increases around ten months post-fire, with seedling probably established from seeds stored in a seed bank due to the absence of adult individuals.[8]
Pollination
Calamintha ashei has been observed at the Archbold Biological Station to be visited by bees from the Apidae family such as Apis mellifera, Bombus impatiens, Epeolus erigeronis and E. zonatus, sweat bees from the Halictidae family such as Agapostemon splendens, Augochlorella aurata, Augochloropsis sumptuosa, Halictus poeyi, Lasioglossum nymphalis and L. puteulanum, and leafcutting bees from the Megachilidae family such as Anthidiellum notatum rufomaculatum, A.perplexum, Coelioxys germana, Hoplitis truncata, Lithurgus gibbosus, Megachile brevis pseudobrevis, M. campanulae, M. exilis parexilis, M. georgica, M. inimica, M. mendica, M. petulans, M. policaris, M. rugifrons, M. texana and Osmia calaminthae.[9] Additionally, this species has been observed to be visited by bees from the Apidae family such as Melissodes communis and Nomada fervida, as well as leafcutting bees from the Megachilidae family such as Anthidiellum perplexum, Coelioxys sayi, Dianthidium floridiense, Megachile albitarsis, M. exilis, M. mendica and M. pruina.[10]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Controlled burning is important for management of C. ashei. It is also important to open the canopy and expose bare sand using methods such as clear cutting and root raking.[3]
Global rank: G3
Florida: S3[6]
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ [USDA Plants] Accessed December 3, 2015
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 [NatureServe]Accessed December 3, 2015
- ↑ [Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center]Accessed: December 3, 2015
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: October 2015. Collectors: John R. Bozeman, D. Burch, Buswell, L.J. Brass, Chas. C. Deam, R.K. Godfrey, O. Lakela, Sidney McDaniel, Elmer C. Prichard, D.B. Ward. States and Counties: Florida: Highlands, Marion, Polk, Volusia. Georgia: Tattnall. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 [Center for Plant Conservation] Accessed December 3, 2015
- ↑ [Georgia Wildlife] Accessed: December 3, 2015
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Carrington, M. E. (1999). "Post-fire seedling establishment in Florida sand pine scrub." Journal of Vegetation Science 10(3): 403-412.
- ↑ Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
- ↑ Discoverlife.org [1]

