Difference between revisions of "Cephalanthus occidentalis"
(→Cultivation and restoration) |
(→Conservation and Management) |
||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
==Conservation and Management== | ==Conservation and Management== | ||
| + | Herbicides can be detrimental to the species. Intense fires will decrease the response of regrowth, though the ''C.. occidentalis'' can resprout after lower intensity burns. <ref name= "USDA"> [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CEAM USDA Plant Database]</ref> | ||
==Cultivation and restoration== | ==Cultivation and restoration== | ||
Revision as of 14:14, 18 May 2018
| Cephalanthus occidentalis | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by the Atlas of Florida Plants Database | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Rubiales |
| Family: | Rubiaceae |
| Genus: | Cephalanthus |
| Species: | C. occidentalis |
| Binomial name | |
| Cephalanthus occidentalis L. | |
| |
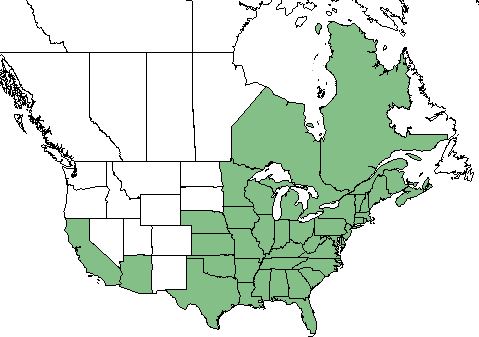
| Natural range of Cephalanthus occidentalis from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: C. pubescens
Variety: none
Description
C. occidentalis is a perennial shrub/tree of the Rubiaceae family native to North America. [1]
Distribution
The C. occidentalis is found in the eastern United States, California and Arizona, as well as eastern Canada. [1]
Ecology
Habitat
C. occidentalis habitat is primarily wetlands. It can be found on streambanks, depressional wetlands, lakes, and in other standing water. [2]
This shrub requires full sunlight for flowering and can withstand habitats of up to three feet of standing water. [1]
Use by animals
The seeds of the C. occidentalis shrub is eaten by waterfowl and wood ducks will use the structure of the shrub for nesting. Also, bees and other insects use the pollen and nectar. [1]
Conservation and Management
Herbicides can be detrimental to the species. Intense fires will decrease the response of regrowth, though the C.. occidentalis can resprout after lower intensity burns. [1]
Cultivation and restoration
C. occidentalis can be used for erosion control on shorelines. It has a strong base that can stabilize the plant and the shoreline. [1]