Difference between revisions of "Ceanothus americanus"
(→Ecology) |
(→Taxonomic Notes) |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
Synonyms: ''Ceanothus intermedius'' (Pursh) | Synonyms: ''Ceanothus intermedius'' (Pursh) | ||
| − | + | Varieties: ''Ceanothus americanus'' Linnaeus var. ''intermedius'' (Pursh) Torrey & A. Gray | |
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
Revision as of 13:36, 26 June 2018
Common Names: New Jersey Tea [1]; Red Root, Indian Tea [2]
| Ceanothus americanus | |
|---|---|
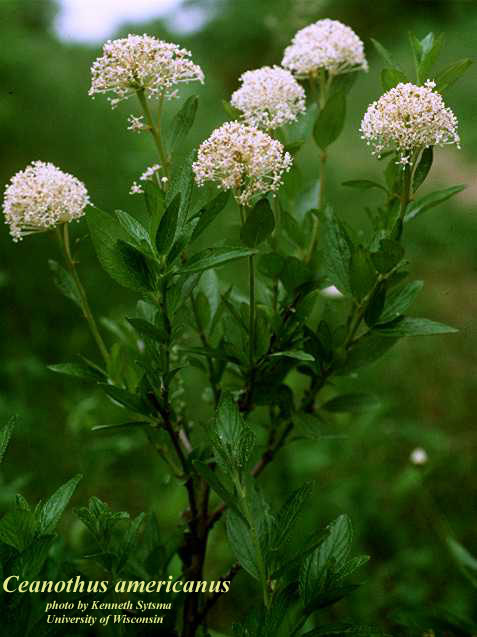

| |
| Photo by the Atlas of Florida Plants Database | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Rhamnales |
| Family: | Rhamnaceae |
| Genus: | Ceanothus |
| Species: | C. americanus |
| Binomial name | |
| Ceanothus americanus L. | |
| |
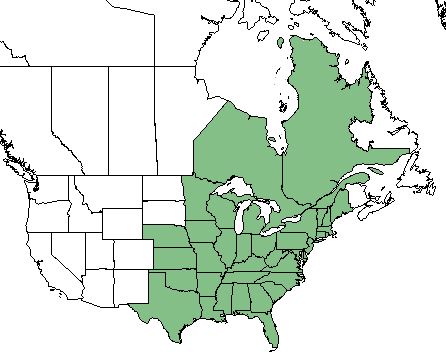
| Natural range of Ceanothus americanus from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: Ceanothus intermedius (Pursh)
Varieties: Ceanothus americanus Linnaeus var. intermedius (Pursh) Torrey & A. Gray
Description
C. americanus is a perennial shrub/subshrub of the Rhamnaceae family native to North America. [1]
Distribution
While it is more commonly found along the coastal plains of the eastern United States and Canada, C. americanus can be found inland as far west as Louisiana. [3]
Ecology
Habitat
The C. americanus is largely found in in sandy soil within woodlands and prairies. [1]
Specimens have been collected from sand in open savanna, dry sand in loam in pine-oak forests, and in open pine land. [4]
Phenology
The C. americanus commonly flowers between April and July, May being the most abundant month. [5]
Seed bank and germination
Seedling C. americanus are more likely to thrive when planted in late fall or early winter. [1]
Fire ecology
C. americanus has a high tolerance to drought and fire is a management technique for the spread of the species. [1]
Pollination
Bees may collect pollen from the plant and other insects such as butterflies and moths may just collect nectar. [1]
Use by animals
Many animals such as rabbit, elk and deer eat the grass from C. americanus while others will eat the fruit, turkey and quail for instance. [1]
Diseases and parasites
This species can acquire leaf spot and powdery mildew. [1]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 USDA Plant Database
- ↑ [Thirty-Third Annual Report of the Bureau of American Ethnology, to the secretary of the Smithsonian institution, 1911-1912]
- ↑ Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: Andre F. Clewell, Ro.K. Godfrey, R. Komarek, Loran C. Anderson, Bill Boothe, Marcia Boothe, Annie Schmidt. States and counties: Florida (Leon, Liberty, Wakulla, Washington) Georgia (Thomas, Grady)
- ↑ Pan Flora