Difference between revisions of "Campsis radicans"
(→Pollination) |
(→Pollination) |
||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
===Pollination=== | ===Pollination=== | ||
| − | Due to the plant producing large quantities of nectar and the tubular shape of the flowers, ''C. radicans'' attracts various hummingbirds, like the | + | Due to the plant producing large quantities of nectar and the tubular shape of the flowers, ''C. radicans'' attracts various hummingbirds, like the ruby-throated hummingbird, and butterflies.<ref name= "Fact sheet"/> It is also known to be pollinated by long tounged bees.<ref name= "Lady bird">[[https://www.wildflower.org/plants/search.php?search_field=&newsearch=true]] Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center. Accessed: March 29, 2019</ref> Fly species of the Syrphidae and Tachinidae (Diptera) families have been collected on the plant.<ref name= "Tooker">Tooker, J. F., et al. (2006). "Floral host plants of Syrphidae and Tachinidae (Diptera) of central Illinois." Annals of the Entomological Society of America 99(1): 96-112.</ref> |
===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
Revision as of 09:01, 29 April 2019
Common name: Trumpet Creeper [1]
| Campsis radicans | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by the Atlas of Florida Plants Database | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Scrophulariales |
| Family: | Bignoniaceae |
| Genus: | Campsis |
| Species: | C. radicans |
| Binomial name | |
| Campsis radicans L | |
| |
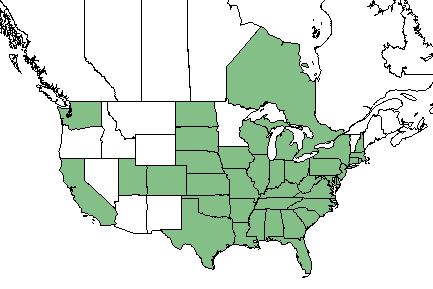
| Natural range of Campsis radicans from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: Bignonia radicans Linnaeus
Varieties: none
Description
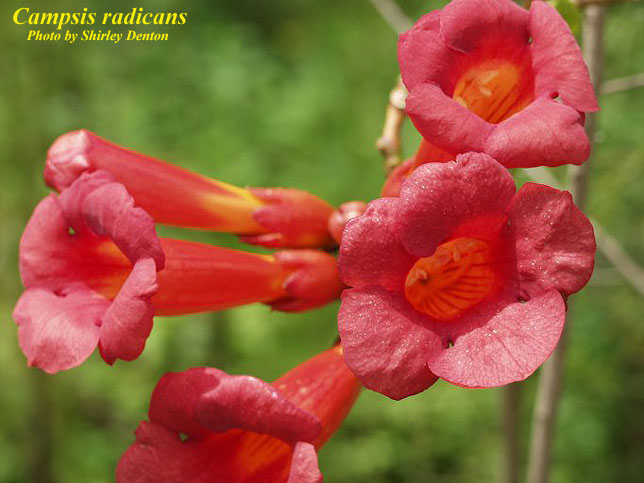
C. radicans is a perennial vine of the Bignoniaceae family native to North America and Canada. [1] It is partly evergreen or deciduous, and climbs through arial rootlets and twining stems; stems can reach lengths of up to 12 m long. Leaves oppositely arranged, somewhat shiny and dark green in color, coarsely toothed and pinnately compound, with 7-11 leaflets. Flowers red to yellow-orange, tubular shape, lengths of up to 8 cm and width 4 cm at the mouth, and arranged in sets of 4-12. Fruit a capsule, flat and tapered, with flat and winged seeds.[2] Its foliage can often be seen in canopies of 30-40 meters high, and with stems of up to 15 centimeters in diameter. C. radicans is easily recognizable by its tannish, shreddy bark. [3]
Distribution
C. radicans is found in the Ontario region of Canada, the eastern half of the United States, California, and Washington. [1]
Ecology
Habitat
C. radicans is found in bottomland forests, swamp forests, fencerows, old fields, forests, thickets, and disturbed areas. It was primarily limited to swamps and bottomlands in the pre-Columbian landscape, and has become a successful colonizer of abandoned farmland, fencerows, and thickets. [3] It has also been observed in floodplain forests and the edges of floodplain forests, loess bluffs, and river banks.[4]
Associated species: Ampelopsis arborea, Celtis laevigata, and Physalis angulata.[4]
Phenology
C. radicans has been observed flowering from April to August with peak inflorescence in May.[5]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by wind.[6][7]
Fire ecology
C. radicans is not fire resistant, but has a high fire tolerance. [1]
Pollination
Due to the plant producing large quantities of nectar and the tubular shape of the flowers, C. radicans attracts various hummingbirds, like the ruby-throated hummingbird, and butterflies.[2] It is also known to be pollinated by long tounged bees.[8] Fly species of the Syrphidae and Tachinidae (Diptera) families have been collected on the plant.[9]
Use by animals
C. radicans is an occasional food source for large mammals and terrestrial birds. [1] However, coming into contact with the leaves and flowers can result in skin redness and swelling for mammals, and is slightly toxic if ingested. The flower provides nectar for hummingbirds and butterflies, and the vines provide habitat for ants.[2] It is a larval host for the Plebeian sphinx (Paratrea plebeja).[8]
Diseases and parasites
C. radicans is a host plant for Field Dodder (Cuscuta campestris), and Cuscuta pentagona.[10]
Diseases and parasites
Diseases include leaf spots caused by various fungi, and mildew that causes white powdery growth that can be found on the leaves.[2]
Conservation and Management
C. radicans is listed as a weedy or invasive species by The University Press of Kentucky, the Cornell University Press, and the Southern Weed Science Society. [1] To combat this, the vines should be thinned throughout the growing season as well as cut back in the winter to stop aggressive spread.[2]
Cultivation and restoration
Cultivars used for ornamental purposes include 'Atropurpurea', 'Crimson trumpet', 'Flamenco', 'Flava', 'Madame Galen', 'Minor', 'Praecox', 'Speciosa', and 'Variegata'.[2]
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 USDA Plant Database https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CARA2
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Wennerberg, S. (2006). Plant Fact Sheet: Trumpet Creeper Campsis radicans. N.R.C.S. United States Department of Agriculture. Baton Rouge, LA.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: March 2019. Collectors: Jame Amoroso, Loran C. Anderson, Kurt E. Blum, Michael B. Brooks, R. Buchanan, Andre F. Clewell, R. F. Doren, Wm. H. Ellis, Robert K. Godfrey, Norlan C. Henderson, Brenda Herring, Clarke Hudson, Ed Keppner, Lisa Keppner, R. Komarek, Elmo Law, S. J. Lombardo, Karen MacClendon, Sidney McDaniel, Richard S. Mitchell, J. B. Nelson, R. A. Norris, Sara J. Noyes, Kevin Oakes, Elmer C. Prichard, A. E. Radford, Gwynn W. Ramsey, Paul L. Redfearn, Jr., R. R. Smith, Charles S. Wallis, D. B. Ward, S. S. Ward, Roomie Wilson, D. R. Windler, and Jean W. Wooten. States and Counties: Florida: Bay, Calhoun, Columbia, Dixie, Franklin, Gadsden, Gulf, Jackson, Jefferson, Leon, Liberty, Madison, Suwannee, Taylor, Volusia, Wakulla, and Washington. Georgia: Grady. Illinois: White. Kansas: Allen. Louisiana: Lafayette and Tangipahoa. Maryland: Cecil. Mississippi: Jackson and Wilkinson. Missouri: Douglas. North Carolina: Caldwell. Oklahoma: Latimer. South Carolina: Oconee. Tennessee: Rutherford. Texas: Knox and Taylor.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 16 MAY 2018
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.
- ↑ Creech, M. N., et al. (2012). "Alteration and Recovery of Slash Pile Burn Sites in the Restoration of a Fire-Maintained Ecosystem." Restoration Ecology 20(4): 505-516.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 [[1]] Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center. Accessed: March 29, 2019
- ↑ Tooker, J. F., et al. (2006). "Floral host plants of Syrphidae and Tachinidae (Diptera) of central Illinois." Annals of the Entomological Society of America 99(1): 96-112.
- ↑ Musselman, L. J. (1986). "The genus Cuscuta in Virginia." Castanea 51(3): 188-196.