Difference between revisions of "Aureolaria pedicularia"
(→Ecology) |
|||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
| − | It is a root parasite on red and black oaks. Musselman found that in all of several thousand seedlings, development was halted without attachment to a host.<ref name="Musselman et al 1969"/> | + | It is a root parasite on red and black oaks. Musselman (1969) found that in all of several thousand seedlings, development was halted without attachment to a host.<ref name="Musselman et al 1969"/> |
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
It is considered a dominant species in sand dunes.<ref name="Leicht-Young et al 2009"> Leicht-Young, S. A., N. B. Pavlovic, et al. (2009). "A comparison of seed banks across a sand dune successional gradient at Lake Michigan dunes (Indiana, USA)." Plant Ecology 202: 299-308.</ref> | It is considered a dominant species in sand dunes.<ref name="Leicht-Young et al 2009"> Leicht-Young, S. A., N. B. Pavlovic, et al. (2009). "A comparison of seed banks across a sand dune successional gradient at Lake Michigan dunes (Indiana, USA)." Plant Ecology 202: 299-308.</ref> | ||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
===Diseases and parasites=== | ===Diseases and parasites=== | ||
| + | |||
==Conservation and Management== | ==Conservation and Management== | ||
==Cultivation and restoration== | ==Cultivation and restoration== | ||
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
Revision as of 10:39, 22 September 2015
| Aureolaria pedicularia | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Scrophulariales |
| Family: | Scrophulariaceae |
| Genus: | Aureolaria |
| Species: | A. pedicularia |
| Binomial name | |
| Aureolaria pedicularia ((L.) Raf. | |
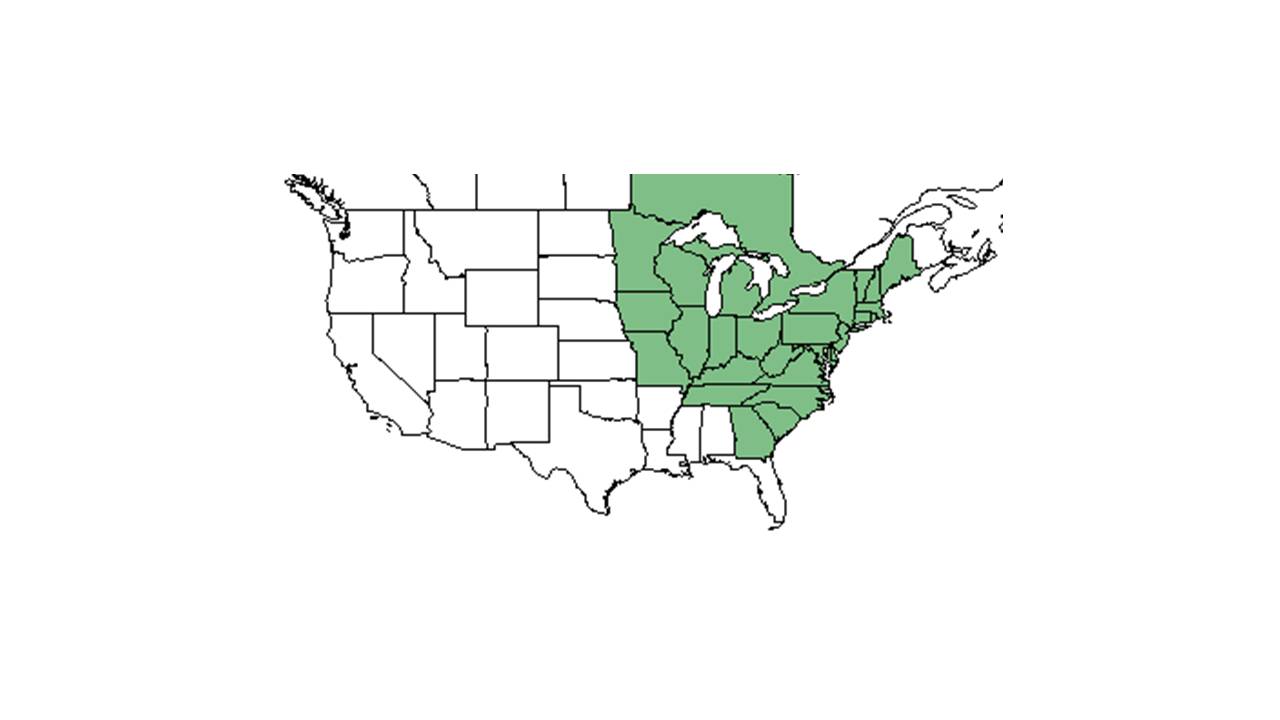
| |
| Natural range of Aureolaria pedicularia from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common Name: Fernleaf Yellow False Foxglove
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Description
Distribution
Ecology
It is a root parasite on red and black oaks. Musselman (1969) found that in all of several thousand seedlings, development was halted without attachment to a host.[1]
Habitat
It is considered a dominant species in sand dunes.[2]
Phenology
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
Germination occurs after cold treatment at 4.5 degrees Celsius for 5 months.[1]
Fire ecology
Pollination
Use by animals
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Musselman, L. J. (1969). "Observations on the life history of Aureolaria grandiflora and Aureolaria pedicularia (Scrophulariaceae)." American Midland Naturalist 82: 307-311.
- ↑ Leicht-Young, S. A., N. B. Pavlovic, et al. (2009). "A comparison of seed banks across a sand dune successional gradient at Lake Michigan dunes (Indiana, USA)." Plant Ecology 202: 299-308.