Andropogon longiberbis
| Andropogon longiberbis | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by Keith Bradley, Atlas of Florida Vascular Plants | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida – Monocotyledons |
| Order: | Poales |
| Family: | Poaceae ⁄ Gramineae |
| Genus: | Andropogon |
| Species: | A. longiberbis |
| Binomial name | |
| Andropogon longiberbis Hack. | |
| |
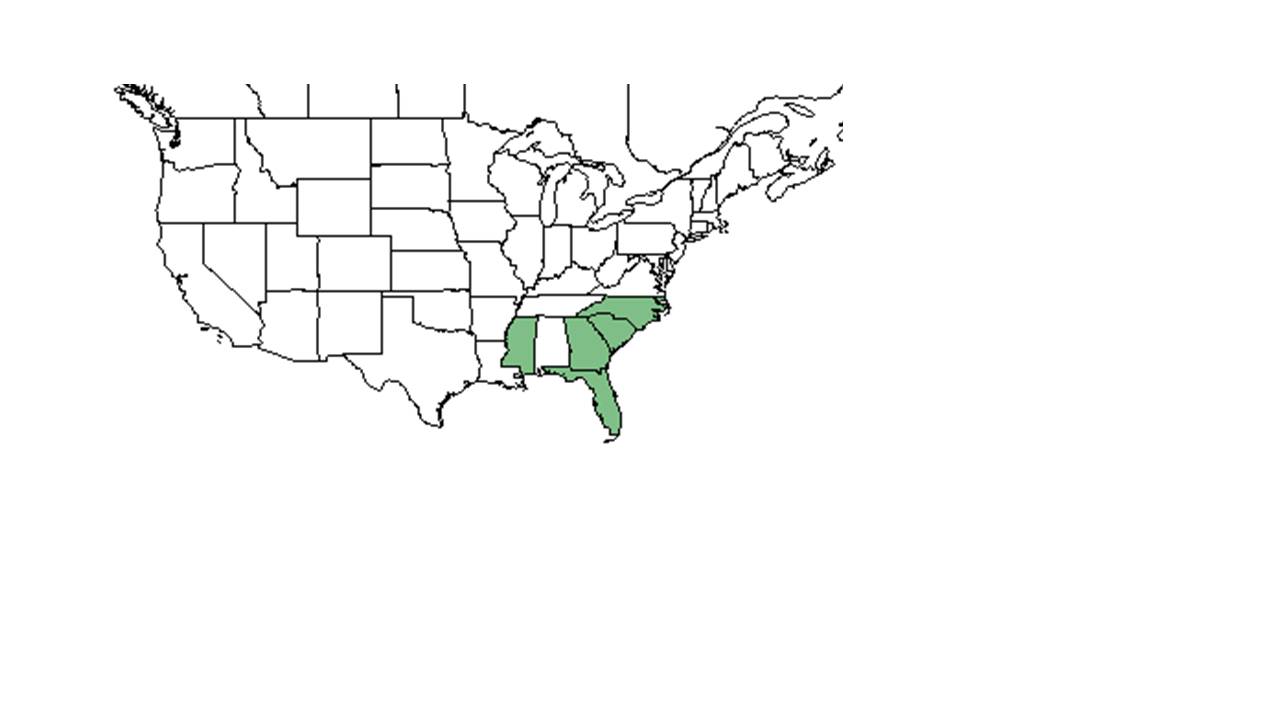
| Natural range of Andropogon longiberbis from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Longbeard bluestem
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Description
Perennials, Terrestrial, n ot aquatic, Rhizomes present, Stems nodes swollen or brittle, Stems erect or ascending, Stems geniculate, decumbent, or lax, sometimes rooting at nodes, Stems caespitose, tufted, or clustered, Stems terete, round in cross section, or polygonal, Stem internodes solid or spongy, Stems with inflorescence less than 1 m tall, Stems with inflorescence 1-2 m tall, Stems, culms, or scapes exceeding basal leaves, Leaves mostly basal, below middle of stem, Leaves mostly cauline, Leaves conspicuously 2-ranked, distichous, Leaves sheathing at base, Leaf sheath mostly open, or loose, Leaf sheath smooth, glabrous, Leaf sheath hairy, hispid or prickly, Leaf sheath and blade differentiated, Leaf blades linear, Leaf blades 2-10 mm wide, Leaf blades mostly flat, Leaf blade margins folded, involute, or conduplicate, Leaf blades more or less hairy, Ligule present, Ligule an unfringed eciliate membrane, Ligule a fringed, ciliate, or lobed membrane, Inflorescence terminal, Inflorescence solitary , with 1 spike, fascicle, glomerule, head, or cluster per stem or culm, Inflorescence a panicle with narrowly racemose or spicate branches, Inflorescence with 2-10 branches, Inflorescence branches paired or digitate at a single node, Inflorescence branches paired racemes, V-shaped, Flowers bisexual, Flowers unisexual, Spikelets pedicellate, Spikelets sessile or subsessile, Spikelets laterally compressed, Inflorescence or spikelets partially hidden in leaf sheaths, subtended by spatheole, Spikelet less than 3 mm wide, Spikelets with 2 florets, Spikelets paired at rachis nodes, Spikelets in paired units, 1 sessile, 1 pedicellate, Pedicellate spikelet rudimentary or absent, usually sterile, Spikelets bisexual, Spikelets unisexual, Inflorescence disarticulating between nodes or joints of rachis, rachis fragmenting, Spikelets disarticulating below the glumes, Spikelets falling with parts of disarticulating rachis or pedicel, Glumes present, empty bracts, Glumes 2 clearly present, Glumes equal or subequal, Glumes equal to or longer than adjacent lemma, Glumes keeled or winged, Glume surface hairy, villous or pilose, Lemmas thin, chartaceous, hyaline, cartilaginous, or membranous, Lemma 1 nerved, Lemma 3 nerved, Lemma glabrous, Lemma apex dentate, 2-fid, Lemma distinctly awned, more than 2-3 mm, Lemma with 1 awn, Lemma awn 1-2 cm long, Lemma awn 2-4 cm long or longer, Lemma awn from sinus of bifid apex, Lemma awns straight or curved to base, Lemma margins thin, lying flat, Lemma straight, Callus or base of lemma evidently hairy, Callus hairs shorter than lemma, Stamens 1, Styles 2-fid, deeply 2-branched, Stigmas 2, Fruit - caryopsis.[1]
Distribution
It is found from North Carolina south to southern and western Florida.[2] In Lake County, Florida, hybridization of A. longiberbis and A. glomeratus var. pumilus has been observed.[3]
Ecology
Habitat
Habitats of A. longiberbis include dry, well-drained, sandy soils of longleaf pine-turkey oak sandhills, limerock in pine flatwoods, dunes, wiregrass-palmetto flatwoods, sandy upland old fields, and sand pine-evergreen oak scrubs.[4][2] It grows well in areas of sunlight and semi opened areas and can be found in disturbed habitats such as sandy vacant lots, roadsides, ditches, railroad banks, pine plantations, and waste grounds.
Associated species include Pinus, Quercus, wiregrass, palmetto, turkey oak, Phoebanthus, Psoralia, Schrankia, Smilax auriculata, Helianthemum sp., Cenchrus spinifex, Panicum spp. Heterotheca subaxillaris, Monarda punctata, Quercus hemispherica, and others.[4]
Phenology
It has been seen flowering between April and October and fruiting between August to November.[4]
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ [[1]]Encyclopedia of Life. Accessed: March 29, 2016
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Weakley, Alan S. Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States: Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina Herbarium (NCU). PDF. 355.
- ↑ Campbell, C. S. (1982). "Hybridization Between Andropogon glomeratus Var. pumilus and A. longiberbis (Gramineae) in Central Florida." Brittonia 34(2): 146-150.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: W. P. Adams, L. C. Anderson, Wm. G. Atwater, R. Blaisdell, C. Campbell, A. F. Clewell, D. S. Correll, F. C. Creager, D. B. Creager, R. K. Godfrey, R. Kral, O. Lakela, W. Lindsey, R. E. Perdue Jr., C. R. Slaughter, and W. R. Stimson. States and Counties: Florida: Alachua, Brevard, Charlotte, Clay, Columbia, Dade, Duval, Franklin, Gilchrist, Hillsborough, Lafayette, Lee, Leon, Levy, Madison, Manatee, Marion, Nassau, Orange, Putnam, St. Johns, Suwannee, Taylor, and Wakulla.