Difference between revisions of "Ageratina altissima"
Ruthstetler (talk | contribs) (→References and notes) |
(→Description) |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
Synonym names: ''Eupatorium rugosum'' Houtt. | Synonym names: ''Eupatorium rugosum'' Houtt. | ||
| − | + | It flowers summer to fall (Wunderlin and Hansen 2003). It is a perennial (Hall 1993). Hall (1993) states that it is poisonous to grazing animals. | |
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
Revision as of 11:02, 9 July 2015
| Ageratina altissima | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae ⁄ Compositae |
| Genus: | Ageratina |
| Species: | A. altissima |
| Binomial name | |
| Ageratina altissima (L.) King & H. Rob. | |
| |
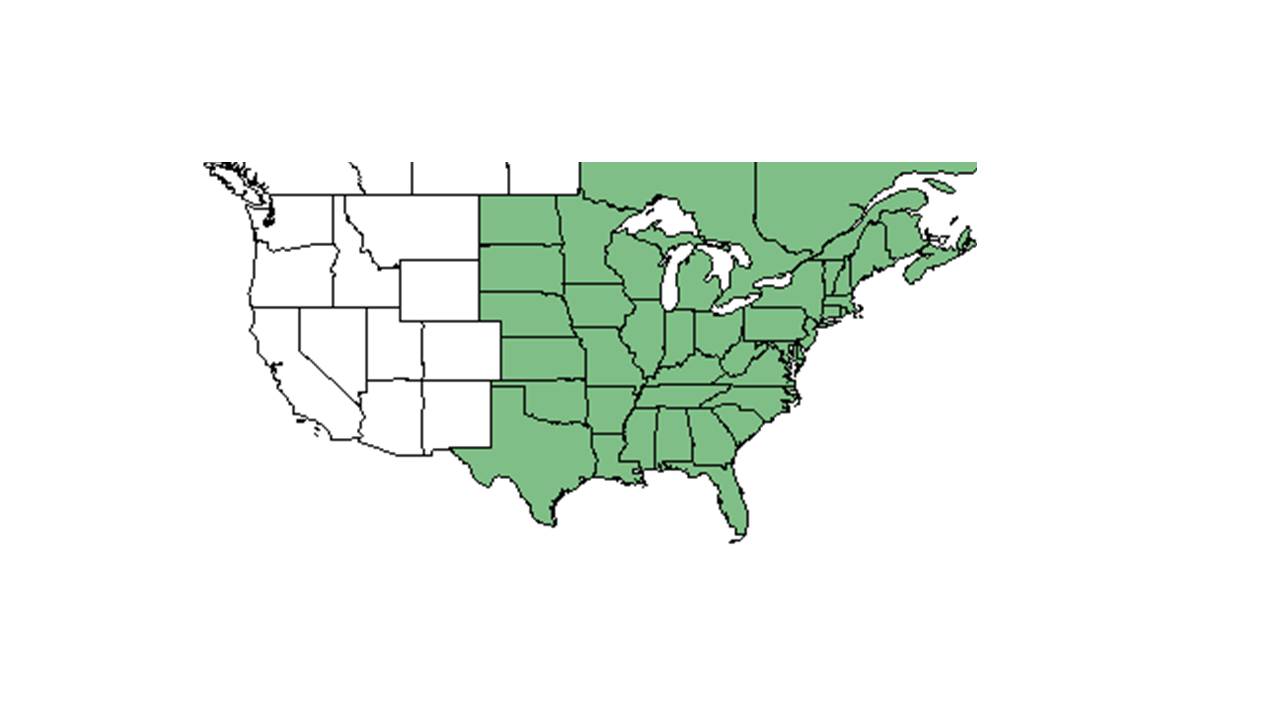
| Natural range of Ageratina altissima from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Description
Common names: Snakeroot; White Snakeroot
Synonym names: Eupatorium rugosum Houtt.
It flowers summer to fall (Wunderlin and Hansen 2003). It is a perennial (Hall 1993). Hall (1993) states that it is poisonous to grazing animals.
Distribution
Is common in north Florida. Found west to Texas and north to Canada (Hall 1993).
Ecology
Ageratina altissima competes by allelopathy. Corbett and Morrison found out that aqueous extracts from roots and especially shoots decreased the rate of germination, percentage of germination, and size of germinated Lettuce and Radish seeds in Petri dishes as well as in pots of forest soil. [1]
Habitat
Ageratina altissima grows in shady to partially shady areas (FSU Herbarium). It prefers wet or moist soils, including sandy alluvial soil, drying sandy loam, and wet loamy soil with limestone outcrops (FSU Herbarium). It is common in the eastern deciduous forest herb layer. [1] This species also occupies scrub, thicket, floodplain forest, and slope/bluff habitats (FSU Herbarium). It can also be found in disturbed areas like roadsides, old fields, clearings, and the margins of waterways.[2]
Phenology
It is a perennial, weedy herb that flowers and fruits in late summer to fall. [1] Flowering and fruiting individuals have been observed particularly in September, October, and November (FSU Herbarium).
Seed dispersal
It disseminates its mature seeds (achenes) in fall and winter. Each plant can produce thousands of seeds at a time. [3]
Seed bank and germination
Ageratina altissima usually needs light to germinate. Ageratina altissima exhibits a Type II response to stratification: Germination in the spring generally can occur at a lower temperature than germination in the fall as a result of dormancy loss in the winter. Thus, germination in the spring is more likely because of relatively higher temperatures and lower temperature requirements than in fall. [2]
Fire ecology
It is most abundant after a late-season (early October) burn. [4]
Pollination
Use by animals
It is avoided by many insects. [1]
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014.
Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Robert K. Godfrey, P. L. Redfearn, Jr., Richard S. Mitchell, Patricia Elliot, Robert L. Lazor, John B. Nelson, A. Gholson Jr., Angela M. Reid, and K. M. Robertson.
States and Counties: Florida: Leon, Jefferson, Jackson, Gadsden, Liberty, and Calhoun. South Carolina: Greenville.
Hall, David W. Illustrated Plants of Florida and the Coastal Plain: based on the collections of Leland and Lucy Baltzell. 1993. A Maupin House Book. Gainesville. 100. Print.
Wunderlin, Richard P. and Bruce F. Hansen. Guide to the Vascular Plants of Florida. Second edition. 2003. University Press of Florida: Gainesville/Tallahassee/Tampa/Boca Raton/Pensacola/Orlando/Miami/Jacksonville/Ft. Myers. 295. Print.
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Corbett, B. F. and J. A. Morrison (2012). "The allelopathic potentials of the non-native invasive plant Microstegium vimineum and the native Ageratina altissima: two dominant species of the eastern forest herb layer." Northeastern Naturalist 19: 297-312.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Walck, J. L., C. C. Baskin, et al. (1997). "Comparative achene germination requirements of the rockhouse endemic Ageratina luciae-brauniae and its widespread close relative A. altissima (Asteraceae)." American Midland Naturalist 137: 1-12.
- ↑ Lau, J. M. and D. L. Robinson (2010). "Phenotypic selection for seed dormancy in white snakeroot (Eupatorium rugosum)." Weed Biology & Management 10: 241-248.
- ↑ Pavlovic, N. B., S. A. Leicht-Young, et al. (2011). "Short-term effects of burn season on flowering phenology of savanna plants." Plant Ecology 212: 611-625.