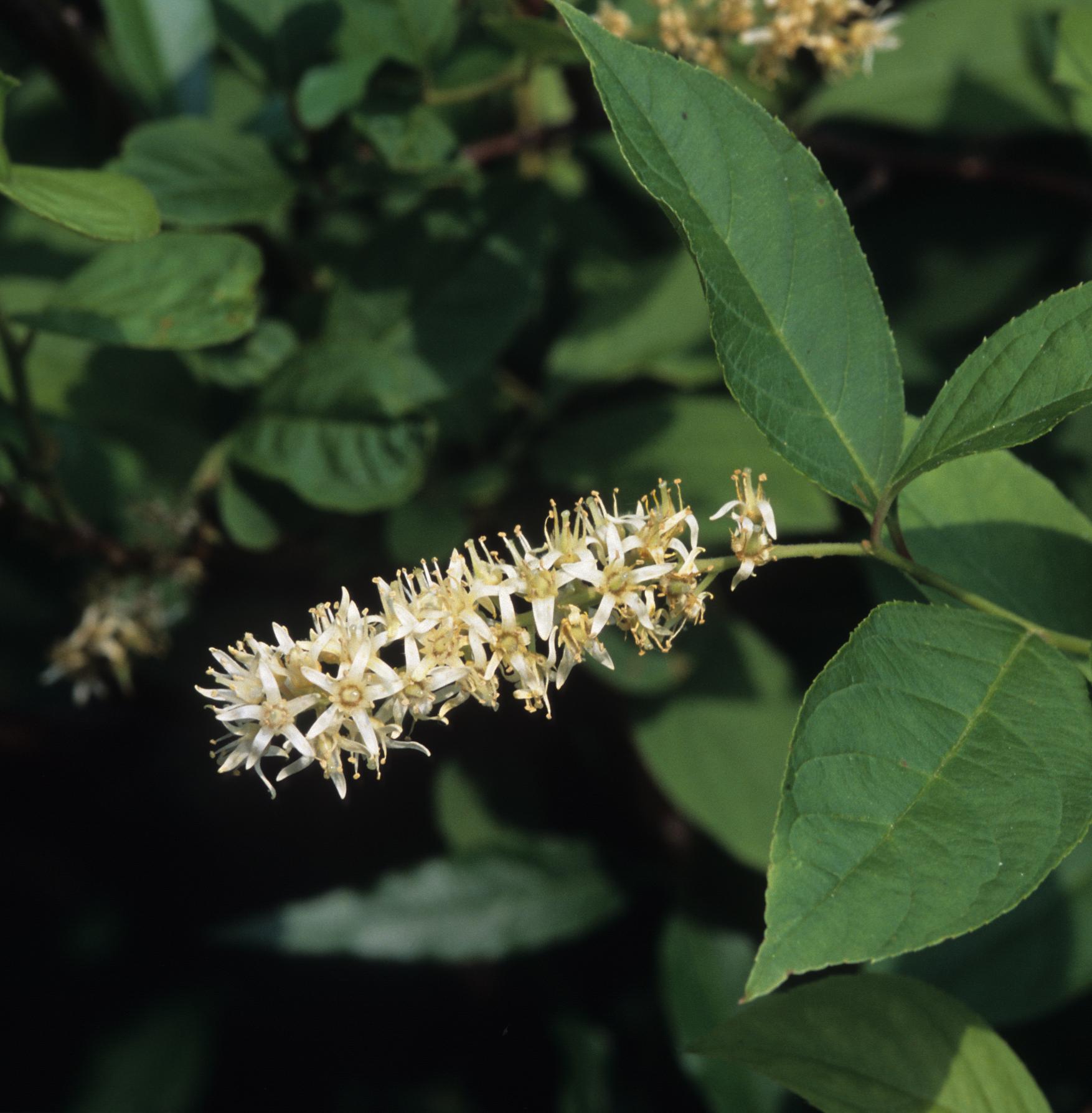
Itea virginica
| Itea virginica | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Rosales |
| Family: | Grossulariaceae |
| Genus: | Itea |
| Species: | I. virginica |
| Binomial name | |
| Itea virginica L. | |
| |
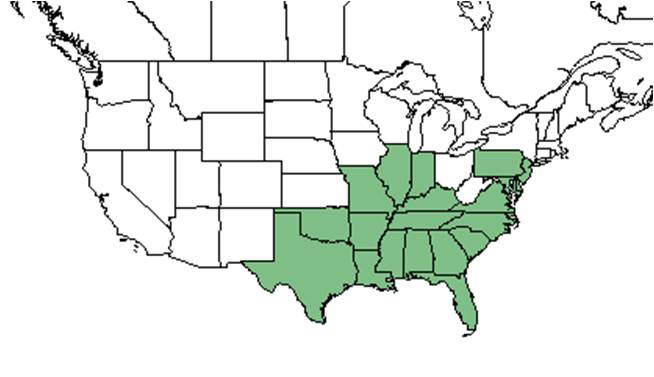
| Natural range of Itea virginica from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Virginia-willow, sweetspire, tassel-white[1]
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: none[1]
Varieties: none[1]
Description
A description of Itea virginica is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
This plant is found in southern New Jersey, south to Florida, west to Texas and Oklahoma, and north to southern Illinois and southeastern Missouri.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
I. virginica has been found in wet and shaded loamy areas, wooded floodplains, swamps, cypress gum pond banks, pine forests, and hydric hammocks.[2] It is also found in disturbed areas like along roadsides near large bogs, wastewater ponds, and recycling plants.[3][4] Associated species: Osmunda, Triadenum, Boehmeria, Magnolia virginiana, Liriodendron tulipifera, Chamaecyparis thyoides, Acer rubrum, Nyssa biflora, and Leucothoe axillaris.[2]
Phenology
I. virginica has been observed to flower from March to May and in June with peak inflorescence in April.[5]
Pollination
Itea virginica was observed at the Archbold Biological Station to host a variety of polliator species such as Apis mellifera (family Apidae), thread-waisted wasps Bicyrtes quadrifasciata (family Sphecidae), and leafcutting bees from the family Megachilidae such as Megachile parallela, and M. xylocopoides.[6] Additionally, this species was observed to host aphids such as Aphis sp. (family Aphididae), bees such as Bombus bimaculatus (family Apidae), and leafcutting bees such as Megachile xylocopoides (family Megachilidae).[7]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Weakley, A.S. 2020. Flora of the Southeastern United States. Edition of 20 October 2020. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Florida State University Herbarium Database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2021. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Kathleen Craddock Burks, Richard Carter, Robert K. Godfrey, R. Komarek,K. M. Meyer, and A. Townesmith. States and counties: Florida: Gadsden, Jefferson, Leon, Marion, and Taylor. Georgia: Thomas.
- ↑ Academy of Natural Sciences of Drexel University accessed using Southeastern Regional Network of Expertise and Collections (SERNEC) data portal. URL: http://sernecportal.org/portal/collections/index.php Last accessed: June 2021. Collectors: S.S. Van Pelt. States and Counties: New Jersey: Cape May.
- ↑ Clemson University Herbarium accessed using Southeastern Regional Network of Expertise and Collections (SERNEC) data portal. URL: http://sernecportal.org/portal/collections/index.php Last accessed: June 2021. Collectors: D.Z. Damrel and H.B. Thomas. States and Counties: South Carolina: Aiken and Anderson.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 12 DEC 2016
- ↑ Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
- ↑ Discoverlife.org [1]