Agalinis fasciculata
| Agalinis fasciculata | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo was taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Lamiales |
| Family: | Orobancheaceae |
| Genus: | Agalinis |
| Species: | A. fasciculata |
| Binomial name | |
| Agalinis fasciculata (Elliott) Raf. | |
| |
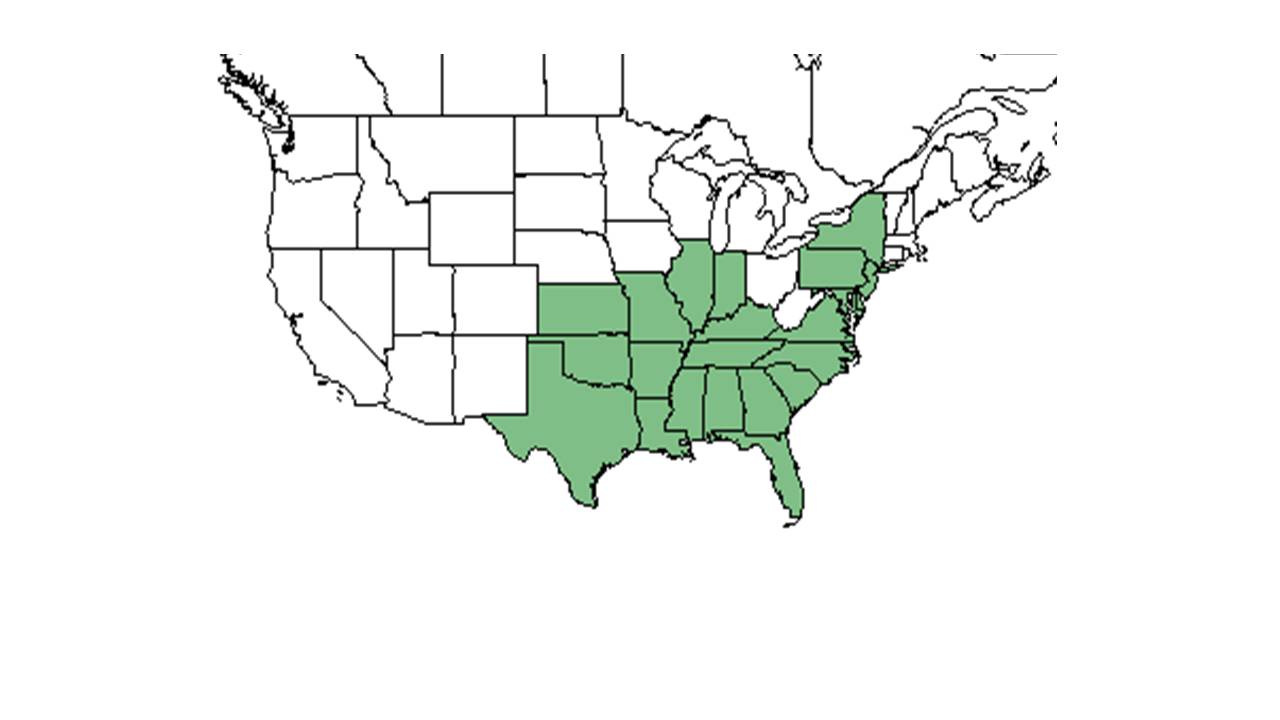
| Natural range of Agalinis fasciculata from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Beach false foxglove; Cluster-leaf gerardia
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Gerardia fasciculata Elliott; A. fasciculata (Elliott) Rafinesque; Gerardia fasciculata ssp. typica; Gerardia fasciculata ssp. peninsularis (Pennell) Pennell.[1]
Description
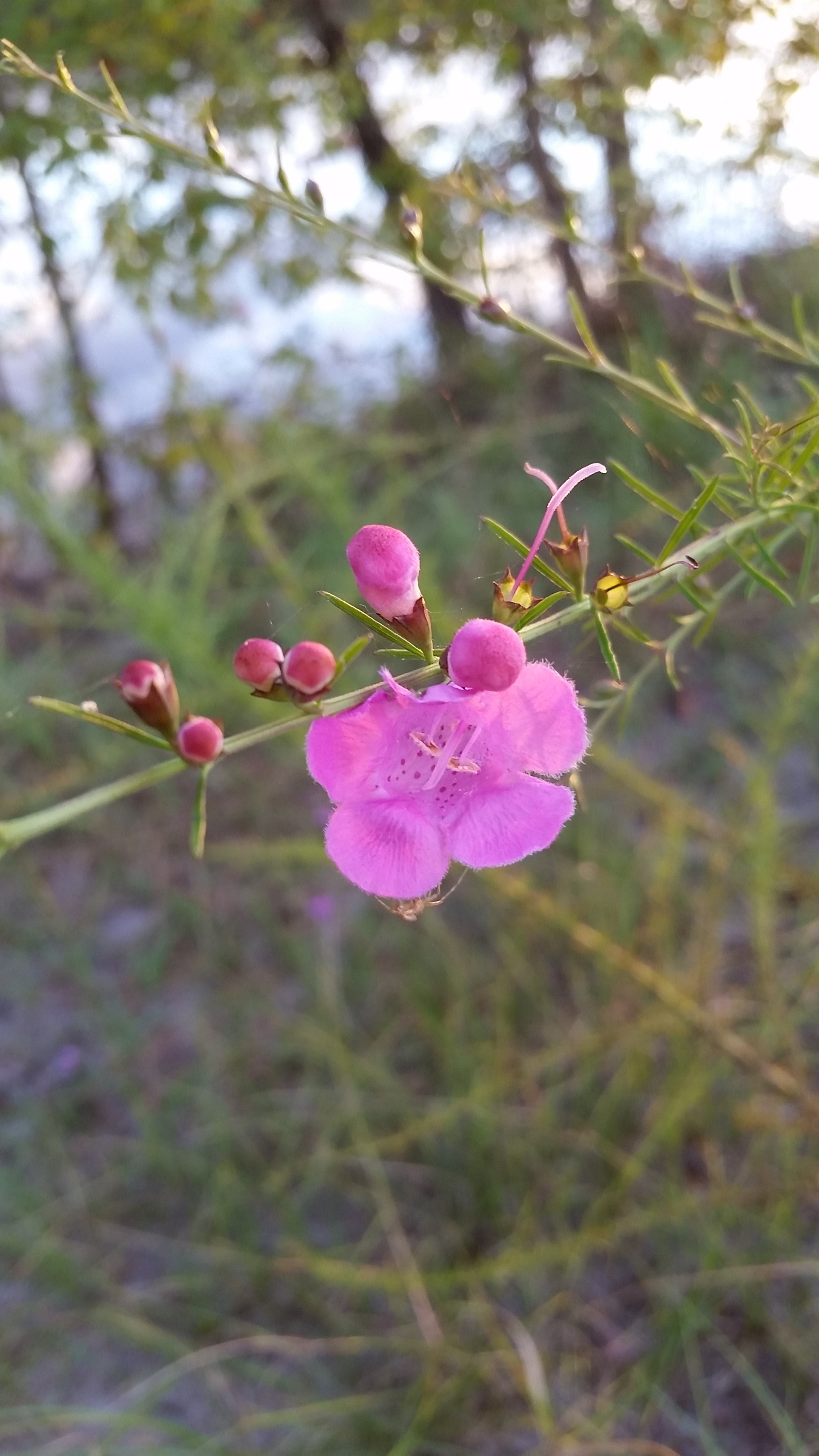
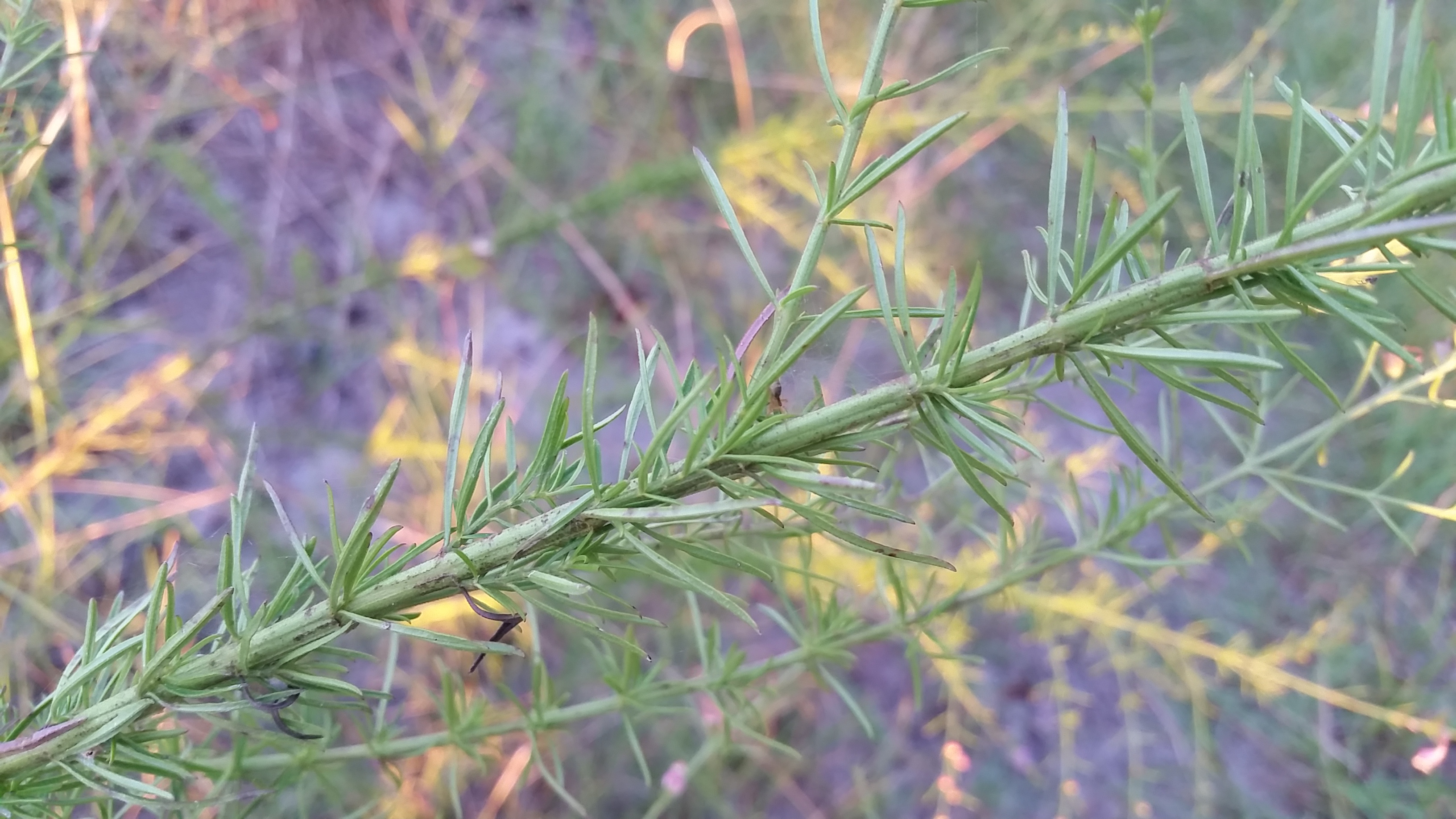
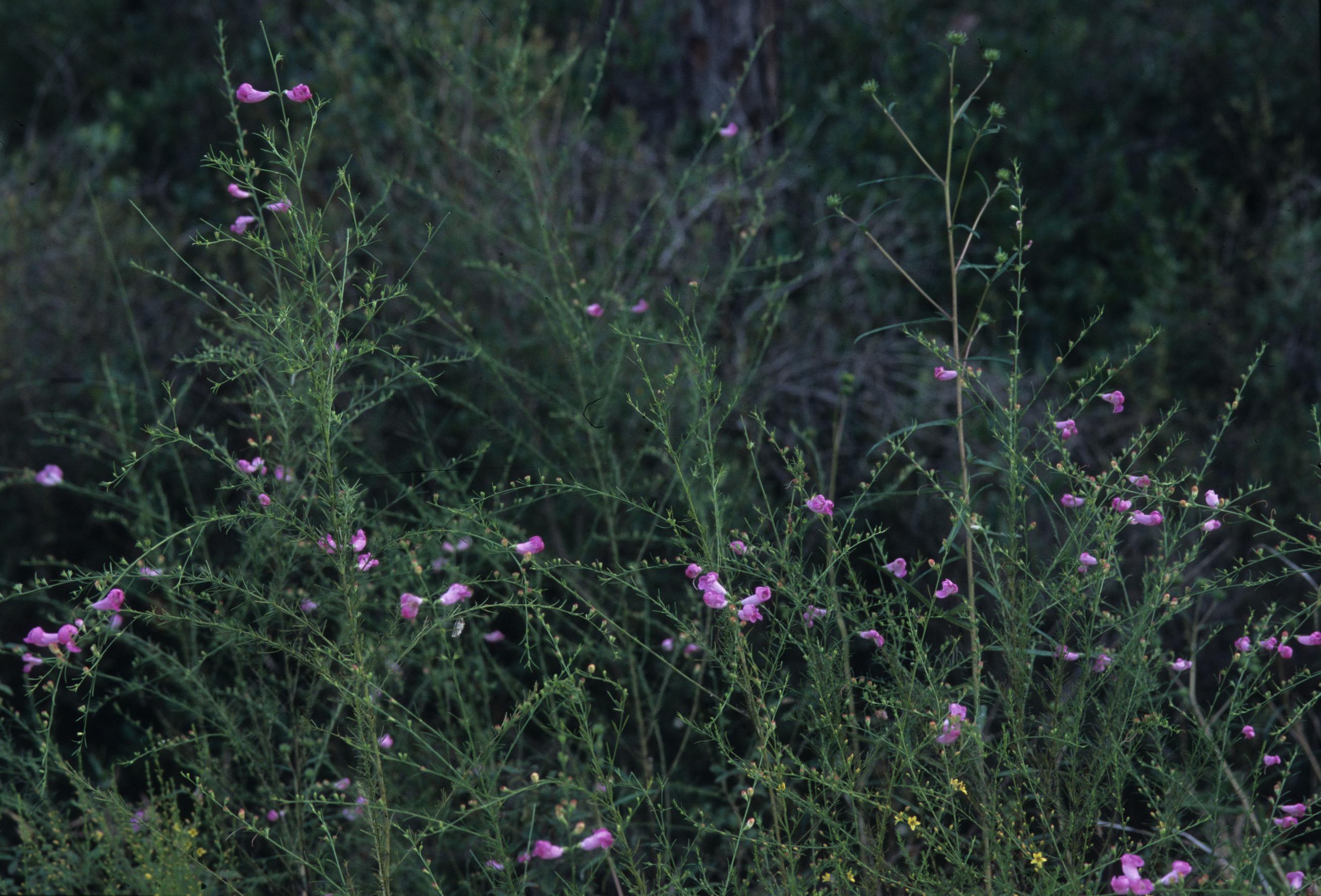
Annual. Parasitic to the roots of grasses and other herbs. Leaves are opposite, linear to filiform, and sometimes will have tufts on the shoots. Flowers are showy, in terminal racemes; the calyx is 5-parted, the lobes are shorter than the tube; the corolla is 5-parted. The flowers are rose-lavender in color and are rarely white. There are usually 2 yellow lines and numerous purple spots in the throat on the tube. The tube is broad, campanulate, and the lobes are shorter than the tube. The throat is usually lanose at the base of the 2 upper corolla lobes. There are 4 stamens, didynamous, that include filaments and anthers that are also lanose. The stigmas are elongated. The capsules are globose or subglobose, loculicidal.[2]
The stems are similar to Agalinis purpurea, but instead are scabrous to scaberulous (not puberulent). Flowers August to October.[2]
Distribution
It is common in all of Florida. Found from: west to Texas, north to North Carolina[3]
Ecology
Habitat
It can be found in frequently burned pine sandhills (Entisols), flatwoods (Spodosols), upland pine communities and shortleaf pine-oak-hickory woodlands (Ultisols), as well as calcareous glades, sandhills, coastal scrubs, margins of ponds, lakes, depressions, marshes, and wet meadows, on the borders of dunes[2][4][5] and in pine rocklands.[6] It occurs on a wide range of soil types from deep sands to loamy clay. It can occur on very disturbed soils, such as those in railroad and power line rights-of-way, clear-cut areas, disturbed roadsides, dredged up sand, and site-prepped pine forests. It appears to be somewhat salt tolerant given its proximity to salt marshes and co-existence with Spartina bakari and other brackish-salt water plants[5][4] It is considered by some sources to be an early successional species in post agricultural succession. [7] A. fasciculata is observed to do well in burned longleaf pine communities, but it experiences reduced occurrence under agricultural disturbance. Additionally, A. fasciculata shows resistance to regrowth in reestablished longleaf communities that were disturbed by agricultural practices.[8].
Associated species includes Bidens, Chrysopsis, Eupatorium, Schoenus nigricans, A. longespica, Houstonia nigricans, Rynchospora divergens, Scleria verticillata, Juniperus, Haplopappus, Rubus, Gnaphaluim, Eupatorium compositifolium, Baccharis, Andropogon, Xyris, Polygala, Solidago, Trichostema, Spartina bakeri, Myrica cerifera, Euthamia minor, Baccharis angustfolia, Hyptis, Lycopus, Drosera, and Pinus palustris.[4]
Phenology
It flowers summer to fall[9][10]; however in the southern peninsula of Florida, it can flower all year[11]. Numerous small capsules each carrying hundreds of brown honeycombed seeds mature in late autumn.[5]
Michelle Smith observed Agalinis fasciculata flowering along Piney Z Lake in Tallahassee, Florida in September 2015 & flowering at Pebble Hill Plantation in Grady County, GA in October 2015.
Agalinis fasciculata has been observed to flower in May and July to December, with peak inflorescence in September and October.[12]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by gravity.[13]
Seed bank and germination
The seeds observe physiological dormancy, are cold stratified, and germinate at 20/10 C in light.[14]
Fire ecology
A. fasciculata requires high light provided by frequently burned areas. [15]
Pollination and use by animals
Agalinis fasciculata has been observed being visited by pollinators such as Hylaeus confluens (family Colletidae), Augochlorella gratiosa (family Halictidae), and Megachile albitarsis (family Megachilidae).[16] Additionally, this species has been observed to be visited by the pollinator Perdita gerardiae (family Andrenidae).[17] Other species of Agalinis, including this one, host larvae of the common buckeye butterfly (Junonia coenia) in Florida.[18]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
A. fasciculata is listed as endangered in the state of Maryland and is listed as rare in the state of New York.[19]
Cultural use
Photo gallery
References and notes
- ↑ Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draf of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 960. Print.
- ↑ Hall, David W. Illustrated Plants of Florida and the Coastal Plain: based on the collections of Leland and Lucy Baltzell. 1993. A Maupin House Book. Gainesville. 341. Print.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: February 2019. Collectors: Frank Almeda, Loran C. Anderson, W Baker, Edwin L. Bridges, Jane Brockmann, Michael B. Brooks, L. Brouillet, J. M. Canne, Richard Carter, George R. Cooley, Richard J. Eaton, Mark A. Garland, R. K. Godfrey, J. M. Kane, Gary R. Knight, R. Komarek, R. Kral, O. Lakela, Robert L. Lazor, Sidney McDaniel, Richard S. Mitchell, Herbert Monoson, L. J. Musselman, Leon Neel, J. B. Nelson, Steve L. Orzell, James D. Ray, Jr., Paul O. Schallert, John C. Semple, and Cecil R Slaughter. States and counties: Florida: Bay, Bradford, Brevard, Calhoun, Collier, Dade, Duval, Escambia, Flagler, Franklin, Gulf, Hernando, Highlands, Hillsborough, Jackson, Lafayette, Leon, Levy, Liberty, Manatee, Monroe, Okaloosa, Putnam, Seminole, St Johns, Taylor, Wakulla, and Washington. Georgia: Grady and Thomas.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Musselman, L. J. and W. F. Mann, Jr (1979). "Agalinis fasciculata (Scrophulariaceae), a native parasitic weed on commercial tree species in the southeastern United States." American Midland Naturalist 101: 459-464.
- ↑ Observation by Jake Antonio Heaton in Everglades National Park, Homstead, FL, June 11th, 2016, posted to Florida Flora and Ecosystematics Facebook Group June 12th, 2017.
- ↑ Engle, D. M., et al. (2000). "Influence of late season fire on early successional vegetation of an Oklahoma prairie." Journal of Vegetation Science 11: 135-144.
- ↑ Brudvig, L.A. and E.I. Damchen. (2011). Land-use history, historical connectivity, and land management interact to determine longleaf pine woodland understory richness and composition. Ecography 34: 257-266.
- ↑ Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium Specimen database search.FSU's Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium
- ↑ Valdosta State University Herbarium database. Valdosta State University Herbarium
- ↑ Wunderlin, Richard P. and Bruce F. Hansen. Guide to the Vascular Plants of Florida. Second edition. 2003. University Press of Florida: Gainesville/Tallahassee/Tampa/Boca Raton/Pensacola/Orlando/Miami/Jacksonville/Ft. Myers. 546. Print.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed:12/7/16
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.
- ↑ Baskin, Jerry M.; Baskin, Carol C.. 2002. Propagation protocol for production of Container (plug) Agalinis fasciculata (Ell.) Raf. plants University of Kentucky Lexington, Kentucky. In: Native Plant Network. URL: http://NativePlantNetwork.org (accessed 2019/03/04). US Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, National Center for Reforestation, Nurseries, and Genetic Resources.
- ↑ Mehlman, D. W. (1992). "Effects of fire on plant community composition of North Florida second growth pineland." Bulletin of the Torrey Botanical Club 119(4): 376-383.
- ↑ Deyrup, M.A. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowering plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
- ↑ Discoverlife.org [1]
- ↑ Observation by Roger Hammer in Silver Springs State Park, Marion County, FL. September 2016, posted to Florida Flora and Ecosystematics Facebook Group August 4, 2017.
- ↑ USDA Plants Database URL: https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=ANGE

