Dichanthelium angustifolium
Common name: needleleaf rosette grass [1], narrow-leaved witchgrass [2]
| Dichanthelium angustifolium | |
|---|---|
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
| |
| Photo by Gary Fleming at the Digital Atlas of the Virginia Flora | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Cyperales |
| Family: | Cyperaceae |
| Genus: | Dichanthelium |
| Species: | D. angustifolium |
| Binomial name | |
| Dichanthelium angustifolium Elliot | |
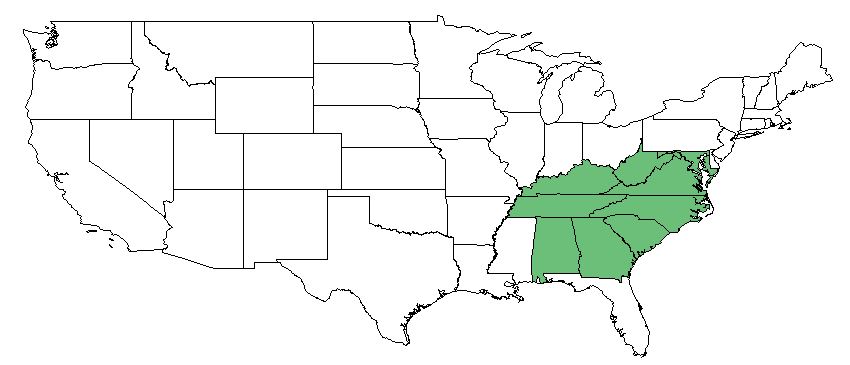
| |
| Natural range of Dichanthelium angustifolium from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
[hide]Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: Panicum angustifolium Elliott; P. aciculare Desvaux ex Poiret; D. aciculare Desvaux ex Poiret ssp. angustifolium (Elliott) Freckmann & Lelong.[3]
Varieties: none.[3]
Description
D. angustifolium is a perennial graminoid of the Poaceae family native to North America and Puerto Rico. [1] The best way to differentiate D. angustifolium from D. aciculare and D. arenicoloides in the fall is through the leaves being flat blades 2 to 4 mm wide, while the other two have involute leaf blades that are 1 to 2 mm wide. It can also be confused with D. consanguineum which has nodes that are spreading and pilose with blades 10 to 15 times as long as wide, while leaf blades of D. angustifolium are 20 or more times as long as wide in comparison.[2]
Distribution
D. angustifolium is found along the southeastern coast of the United States, from Texas to New York, as well as Puerto Rico. [1]
Ecology
Habitat
D. angustifolium is found in sandy pinelands and fields. [2] Specimens have been collected from wet pine flatwoods, open oak woodland, flatwoods with palmetto, moist soils of drainage areas, bayhead of river, old field, coastal hammock, pine savanna,sand pine scrub, wiregrass savanna, sandy margin of limesink, margin of lake, sandy fields, and slash pine flats. [4] As well, it has been recorded to be a component of the following communities in Florida: the xeric sandhills in the panhandle, the north Florida longleaf woodlands, the north Florida subxeric sandhills, the clayhill longleaf woodlands, and the panhandle silty longleaf woodlands.[5] In these sandhill habitats, D. angustifolium is only found in the upland areas and not mid-slope or in lowland areas.[6] It responds negatively to soil disturbance by agriculture in Southwest Georgia.[7] It also responds negatively to soil disturbance by roller chopping in South Florida.[8] D. angustifolium responds positively to soil disturbance by clearcutting and chopping in North Florida flatwoods forests.[9]
Dichanthelium angustifolium is frequent and abundant in the Panhandle Xeric Sandhills, North Florida Longleaf Woodlands, North Florida Subxeric Sandhills, Clayhill Longleaf Woodlands, and Panhandle Silty Longleaf Woodlands community types as described in Carr et al. (2010).[10]
Phenology
Generally, this species flowers from May until October.[2] D. angustifolium has been observed to flower in April, May, July, September, and October. [11]
Fire ecology
This witchgrass species commonly grows in communities that are fire dependent.[5] It is more frequent in the second year after fire disturbance, and grows more stalks that are seed-bearing in the second winter.[12][13] D. angustifolium is not fully fire resistant though, and has low fire tolerance. [1]
Use by animals
D. angustifolium is moderately palatable for grazing and browsing animals, but not for humans.[1] Henslow's sparrows (Ammodramus henslowii) were also observed to prefer this witchgrass for foraging, even though the species has a low energy content.[12]
Conservation and Management
D. angustifolium is listed as endangered by the New Jersey Office of Natural Lands Management Department of Environmental Protection and Energy, and by the Tennessee Natural Heritage Program Department of Environment and Conservation. [1]
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 USDA Plant Database https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=DIAC
- ↑ Jump up to: 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ Jump up to: 3.0 3.1 Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- Jump up ↑ URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: Cecil R. Slaughter, Loran C. Anderson, Ann Johnson, W.C. Brumbach, R.F> THorne, R.A. Davidson, Steve Orzell, Edwin Bridges, R.K. Godfrey, Lloyd H. Shinners, R.Kral, Tara Baridi, Rex Ellis, Sidney McDaniel, Randy Haynes, A.F. Clewell, A.E. Radford, R.B. Channel, H.R. Reed, John Thieret, H.L. Blomquist, Delzie Demaree, Richard R. Clinebell II, Richard Carter, Keith Bradley, Robert Lazor, Grady Reinert, Frank Gould, Wm. Atwater, H. Kurz, Gwynn Ramsey, R.S. Mitchell, J. Hunter, M. Knott, R. Dale Thomas, W. R. Anderson, Hurt Blum, S.W. Leonard, C.R. Bell, D. J. Banks, F. Maturo, J.B. McFarlin. States and counties: Florida (Volusia, Leon, Putnam, Wakulla, Bay, Lee, Liberty, Madison, Franklin, Escambia, washington, Calhoun, Polk, Clay, Duval, Jackson, Holmes, Gulf, Lee, Collier, Citrus, Columbia, Dixie, Dade, palm Beach, Madison, Taylor, Santa Rosa, Lafayette, Highlands) Alabama (Monroe, Monroe, Houston, Baldwin, Lee, Covington) Georgia (Mitchell, baker, Thomas, Grady, McIntosh) North Carolina (Carteret, Richmond, Brunswick, nash, Craven) Mississippi (Pearl River, Jackson, Harrison, Lauderdale) Tennessee (Lawrence) Texas (Freestone) Louisiana (Jackson, Oachita) South Carolina (Clarendon, Edgefield)
- ↑ Jump up to: 5.0 5.1 Carr, S. C., et al. (2010). "A Vegetation Classification of Fire-Dependent Pinelands of Florida." Castanea 75(2): 153-189.
- Jump up ↑ Gilliam, F. S., et al. (2006). "Natural disturbances and the physiognomy of pine savannas: A phenomenological model." Applied Vegetation Science 9: 83-96.
- Jump up ↑ Kirkman, L.K., K.L. Coffey, R.J. Mitchell, and E.B. Moser. Ground Cover Recovery Patterns and Life-History Traits: Implications for Restoration Obstacles and Opportunities in a Species-Rich Savanna. (2004). Journal of Ecology 92(3):409-421.
- Jump up ↑ Lewis, C.E. (1970). Responses to Chopping and Rock Phosphate on South Florida Ranges. Journal of Range Management 23(4):276-282.
- Jump up ↑ Moore, W.H., B.F. Swindel, and W.S. Terry. (1982). Vegetative Response to Clearcutting and Chopping in a North Florida Flatwoods Forest. Journal of Range Management 35(2):214-218.
- Jump up ↑ Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.
- Jump up ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 21 MAY 2018
- ↑ Jump up to: 12.0 12.1 DiMiceli, J. K., et al. (2007). "Seed preferences of wintering Henslow's sparrows." Condor 109: 595-604.
- Jump up ↑ Johnson, E. I. 2006. Effects of fire on habitat associations, abundance, and survival of wintering Henslow's Sparrows (Ammodramus henslowii) in southeastern Louisiana longleaf pine savannas. M.Sc. thesis, Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge, LA.