Rhexia alifanus
| Rhexia alifanus | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by John Gwaltney hosted at Southeastern Flora.com | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Myrtales |
| Family: | Melastomataceae |
| Genus: | Rhexia |
| Species: | R. alifanus |
| Binomial name | |
| Rhexia alifanus Walter | |
| |
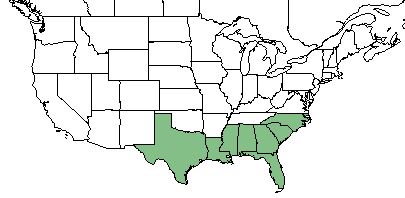
| Natural range of Rhexia alifanus from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonym: none
Variety: none
Description
R. alifanus is a perennial forb/herb of the Melastomataceae family that is native to North America. [1]
Distribution
R. alifanus is found in the southeastern United States; specifically in Florida, Georgia, South Carolina, North Carolina, Alabama, Louisiana, Mississippi, and Texas. [1]
Ecology
Habitat
R. alifanus is typically found in pine flatwoods, savannas, and pocosin borders.[2] It does not respond to soil disturbance by clearcutting and chopping in North Florida flatwoods forests.[3]
Transitions between uplands and lowlands, commonly wet praire, is another common habitat to find R. alifanus. [4]
Rhexia alifanus is frequent and abundant in the Upper Panhandle Savannas community type as described in Carr et al. (2010).[5]
Phenology
R. alifanus has been observed flowering May through July. [6]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by gravity. [7]
Pollination
Bees are pollinators for R. alifanus. [8]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 USDA Plant Database
- ↑ Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ Moore, W.H., B.F. Swindel, and W.S. Terry. (1982). Vegetative Response to Clearcutting and Chopping in a North Florida Flatwoods Forest. Journal of Range Management 35(2):214-218.
- ↑ [Crandall, R. M. and W. J. Platt (2012). "Habitat and fire heterogeneity explain the co-occurrence of congeneric resprouter and reseeder Hypericum spp. along a Florida pine savanna ecoline." Plant Ecology 213: 1643-1654.]
- ↑ Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 29 MAY 2018
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.
- ↑ [Pitts-Singer, T. L., et al. (2002). "Insect pollinators of three rare plants in a Florida longleaf pine forest." Florida Entomologist 85(2): 308-316.]