Dichanthelium chamaelonche
Common names: carpet witchgrass
| Dichanthelium chamaelonche | |
|---|---|
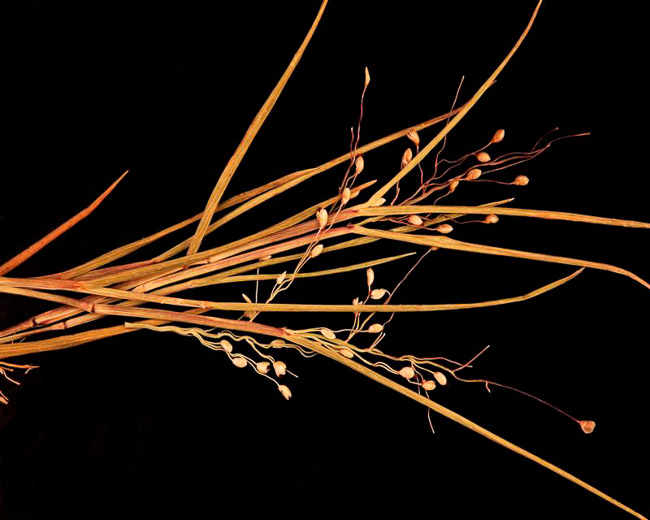

| |
| Photo by John B | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Cyperales |
| Family: | Poaceae |
| Genus: | Dichanthelium |
| Species: | D. chamaelonche |
| Binomial name | |
| Dichanthelium chamaelonche Trinius | |
| |
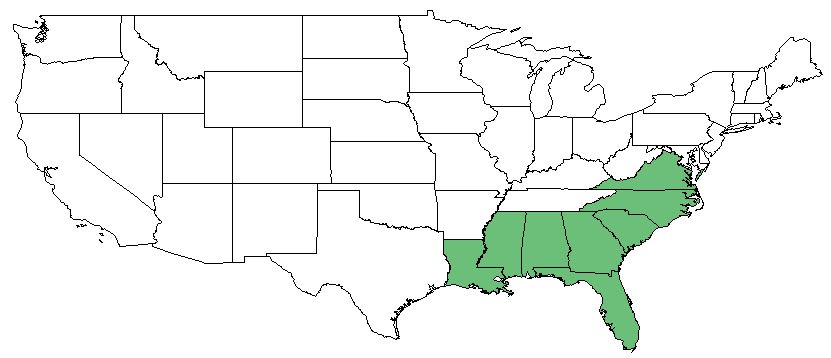
| Natural range of Dichanthelium chamaelonche from Weakley. [1] | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Subspecies: Dichanthelium chamaelonche (Trinius) Freckmann & Lelong ssp. breve (A.S. Hitchcock & Chase) Freckmann & Lelong
Synonyms: (for ssp. breve) Panicum breve A.S. Hitchcock & Chase – HC, S; D. dichotomum (Linnaeus) Gould var. breve (A.S. Hitchcock & Chase) Gould & Clark; P. chamaelonche Trinius var. breve (A.S. Hitchcock & Chase) Lelong; (for ssp. chamaelonche) Panicum chamaelonche Trinius; P. chamaelonche var. chamaelonche
Description
Internodes can be glabrous or puberulent, and nodes glabrous, pubescent, or bearded, but the glabrous spikelets 0.9-1.2 mm long are diagnostic [2].
Distribution
D. chamaelonche is found along the southeastern coast of the United States from Louisiana to Virginia. [2]
Ecology
Habitat
D. chamaelonche proliferates in moist pine savannas, flatwoods, and pineland pondshores [2]. It is commonly found in human disturbed habitats such as lawns, roadside ditches, and bulldozed flatwoods. Soil that is found in is usually sandy [3].
Associated species- very frequently found with Quercus cerris. Also with Rhynchospora chalarocephala, Ludwigia microcarpa, Serenoa repens , Deeringothamnus pulchellus, Ilex coriacea, Aristida stricta, Dichanthelium spp., Utricularia subuluata, Polygala lutea, and Calopogon barbatus [3].
Dichanthelium chamaelonche is an indicator species for the Central Florida Flatwoods/Prairies community type as described in Carr et al. (2010).[4]
Phenology
D. chamaelonche has been observed to flower from the beginning of spring through late fall [3].
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ Weakley, Alan S. 2015. Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States: Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, North Carolina. 1320 pp.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: May 2018. Collectors: R. Kral, George R. Cooley, Carroll E. Wood, Jr., Robert K. Godfrey, Loran C. Anderson, E. M. Hodgson, A. H. Curtiss, Robert L. Lazor, Jean W. Wooten, Kenneth A. Wilson, Sidney McDaniel, J. B. McFarlin, O. Lakela, H. Kurz, Richard J. Eaton, R. E. Perdue, Jr., Robert Christensen, Grady W. Reinert, and Keith A. Bradley. States and Counties: Florida: Alachua, Baker, bay, Bradford, Brevard, Clay, Dixie, Duval, Escambia, Flagler, Franklin, Gadsden, Gulf, Hamilton, Hardee, Highlands, Hillsborough, Jefferson, Lee, Leon, Levy, Manatee, Martin, Osceola, Palm Beach, Pinellas, Sarasota, St. Johns, Wakulla. South Carolina: Horry.
- ↑ Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.