Oenothera fruticosa
| Oenothera fruticosa | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by John Gwaltney at Southeastern Flora.com | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Myrtales |
| Family: | Onagraceae |
| Genus: | Oenothera |
| Species: | O. fruticosa |
| Binomial name | |
| Oenothera fruticosa L. | |
| |
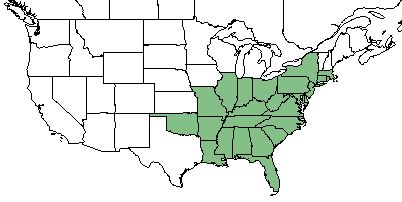
| Natural range of Oenothera fruticosa from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common Name(s): narrowleaf evening primrose,[1][2] southern sundrops, small-fruited sundrops, flatrock sundrops[3]
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Subspecies: O. fruticosa ssp. fruticosa; O. fruticosa ssp. tetragona[1]
; O. fruticosa var. linearis (Michaux) S. Watson; O. fruticosa var. humifusa Allen; Kneiffia fruticosa (Linnaeus) Raimann; Kneiffia arenicola Small; Kneiffia semiglandulosa Pennell
Varieties: O. fruticosa Linnaeus var. microcarpa Fernald; O. fruticosa Linnaeus var. subglobosa (Small) Munz; O. fruticosa Linnaeus var. unguiculata Fernald
Description
Oenothera fruticosa is a dioecious perennial forb/herb[1] that reaches 18-24 in (0.46-0.61 m) in height.[2] It can be found as a diffusely clustered system of unbranched stems containing lance shaped leaves of 2-3 in (5.1-7.6 cm) in length. During the winter months in its southern range, O. fruticosa appears as a reddish-purple basal rosette. This species requires sunlight and well-drained soils, but is also tolerant of brackish and lime soils.[2]
Distribution
O. fruticosa can be found in from Maine south to Florida and westward to Michigan, Missouri, Oklahoma, and Louisiana.[1][3] It can also be found in parts of Manitoba, Ontario, and Quebec provinces in Canada.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
This species is found in dry forests and woodlands, glades, rock outcrops, boggy depressions, granite flatrocks and domes, sandhills, and moist to wet loamy savannas.[3]
Phenology
O. fruticosa has been observed flowering from May through August,[3][4] peaking in April and May.[4] It produces four-petaled golden yellow flowers that average 2 in (5.1 cm) in diameter.[2]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by gravity. [5]
Seed bank and germination
In Illinois farmed and unfarmed baldcypress swamps, seeds of O. fruticosa averaged densities of 99 and 166 seeds m-2, respectively.[6] O. fruticosa requires at least 3 weeks of vernalization (cooling of seeds during germination) to reduce the time to flowering and produce a high percentage of flowering. Plant height would peak at 40-50 cm (15.7-19.7 in) after 9 weeks of vernalization and a 14 hour photoperiod. Increasing photoperiods from 10-16 hours also caused decreases in the time until flowering, the number of new nodes, number of flowers, and the number of lateral shoots. Temperatures from 15-30 °C (59-86 °F) were indirectly proportional to the number of flowers, flower diameter, and plant height.[7]
Pollination
It is known to attract birds, hummingbirds, and a large number of native bees.[2] Honeybees deposit, on average, 193-223 grains of pollen per visit to O. fruticosa.[8][9] Soldier beetles also pollinate O. fruticosa, leaving 114 grains of pollen per visit.[9] The number of seeds set is proportional to the number of pollen grains which asymptotes around 150 seeds set and 400 pollen grains.[8]
Use by animals
Oenothera fruticosa composes 2-5% of the diet of large mammals and 5-10% of the diet for terrestrial birds.[1]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 USDA, NRCS. (2016). The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 20 December 2017). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Plant database: ‘’Oenothera fruticosa’’. (20 December 2017).Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center. URL: https://www.wildflower.org/plants/result.php?id_plant=OEFR
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Weakley A. S.(2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 20 DEC 2017
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.
- ↑ Middleton B. A. (2003). Soil seed banks and the potential restoration of forested wetlands after farming. Journal of Applied Ecology 40:1025-1034.
- ↑ Clough E. A., Cameron A. C., Heins R. D., and Carlson W. H. (2001). Growth and development of Oenothera fruticosa is influenced by vernalization duration, photoperiod, forcing temperature, and plant growth regulators. Journal of the American Society of Horticulture Science 126(3):269-274.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Silander J. A. and Primack R. B. (1978). Pollination intensity and seed set in the evening primrose (Oenothera fruticose). The American Midland Naturalist 100(1):213-216.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Primack R. B. and Silander, Jr. J. A. (1975). Measuring the relative importance of different pollinators to plants. Nature 255(5504):143-144.