Tillandsia usneoides
| Tillandsia usneoides | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by John Gwaltney hosted at Southeastern Flora.com | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Bromeliales |
| Family: | Bromeliaceae |
| Genus: | Tillandsia |
| Species: | T. usneoides |
| Binomial name | |
| Tillandsia usneoides L. | |
| |
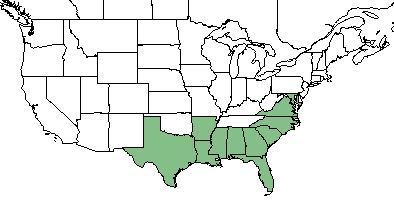
| Natural range of Tillandsia usneoides from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common Name(s): Spanish-moss[1][2]
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonym(s): Dendropogon usneoides[2]
Description
Tillandsia usneoides is an epiphyte[3] that typically is found hanging from the branches of trees.[1] It is classified as a monoecious perennial that grows as a forb/herb or vine.[2] Leaves are whitish gray in color and its flowers are white solitary inconspicuous flowers which occur at the end of short axillary branches.[3]
Distribution
This species is found along the coastal plain in eastern Texas, eastward to Florida, and northward Maryland. It also occurs in parts of Mexico, Central and South America, the West Indies.[1][2]
Ecology
Habitat
T. usneoides requires areas with high humidity and is therefore common in swamps.[1] It can also be found in dry forests, including sandhills, where frequent fog occurs.[1]
Phenology
Flowering occurs from March through June[1][4] and may also occur in the winter from September through December.[4]
Use by animals
Although not comprising a significant portion of their diet, T. usneoides is commonly found in the rumens of fallow deer throughout the year.[5] Spanish moss can also be used as a food for cattle, especially in the winter when other food may be scarce.[6] Humans also use Spanish moss for various things. When allowed to rot in water, a horse hair like black fiber remains that can be used to stuff mattresses and cushions or make ropes. During the 1800's, it was used as a stomachic, purgative, and diuretic.[6][7]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Weakley A. S.(2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 USDA, NRCS. (2016). The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 11 January 2018). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Plant database: ‘’Tillandsia usneoides’’. (11 January 2018).Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center. URL: https://www.wildflower.org/plants/result.php?id_plant=TIUS
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Nelson G. (11 January 2018) PanFlora. Retrieved from gilnelson.com/PanFlora/
- ↑ Morse BW, McElroy ML, Miller KV (2009) Seasonal diets of an introduced population of fallow deer on little St. Simons Island, Georgia. Southeastern Naturalist 8(4):571-586.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Rafinesque CS (1828) Medical Flora; or Manual of the Medical Botany of the United States of North America. Atkinson SC, Philadelphia.
- ↑ Porcher FP (1869) Resources of the Southern Fields and Forests, Medical, Economical and Agricultural. Walker, Evans and Cogswell Printers.