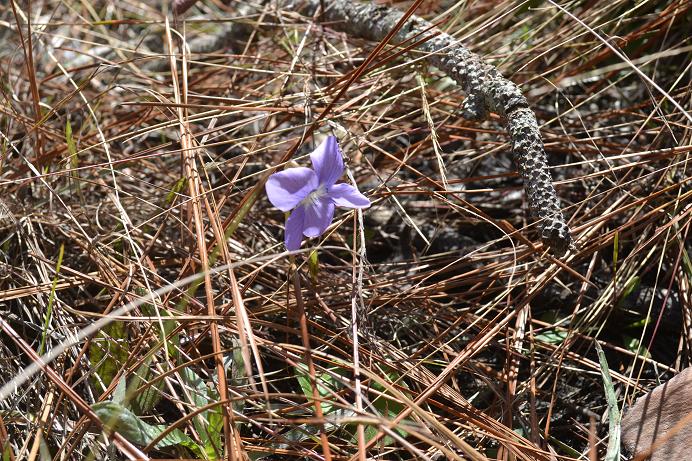
Viola palmata
| Viola palmata | |
|---|---|
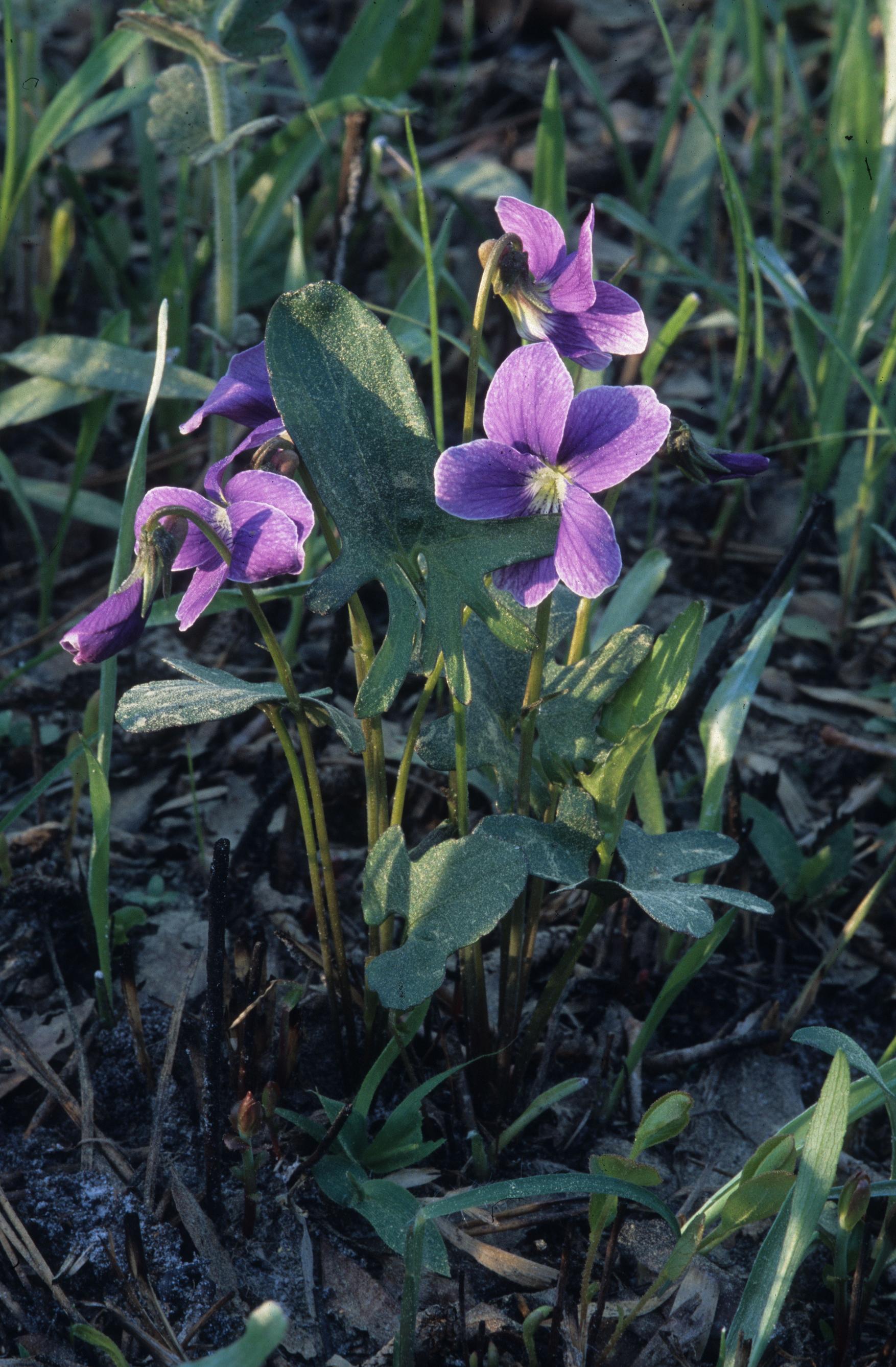

| |
| Photo was taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Violales |
| Family: | Violaceae |
| Genus: | Viola |
| Species: | V. palmata |
| Binomial name | |
| Viola palmata L. (pro sp.) | |
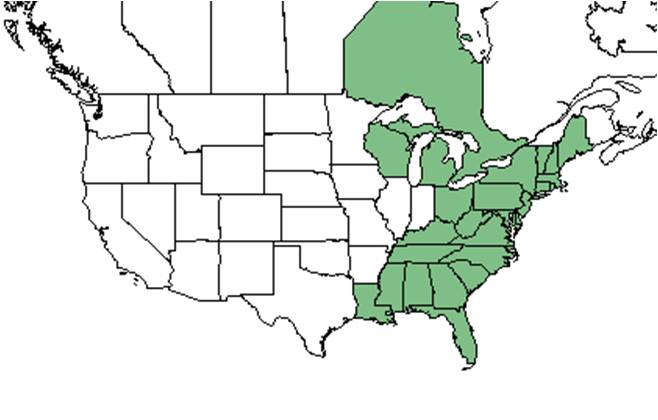
| |
| Natural range of Viola palmata from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: early blue violet
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Description
"Herbaceous, rhizomatous or stoloniferous perennials, or winter annuals. Leaves crenate or crenate-serrate, dissected, lobed or unlobed; petiolate; stipules conspicuous. Flowers zygomorphic, peduncles directly from the rhizome (acaulescent) or peduncles axillary (caulescent). Chasmogamous flowers with lateral petals often bearded, lower petal spurred; anthers usually seated in the throat, orange appendages conspicuous, lower stamens spurred; spurs fitting in to the spur of the corolla; styles usually clavate, variously shaped at the apex. Dates for Viola, except V. pedata, are for Chasmogamous flowering only, cleistogamous flowering and fruiting commence shortly after chasmogamous flowering and continues until frost. Hybrids are so numerous in this genus that space is not taken to list them." - Radford et al 1964
"Plant acaulescent; rhizomes elongate, stocky, usually more than 4 mm in diam., horizontal, often freely branched. Leaves widely ovate, 5-10 cm long, or occasionally larger, crenate, unlobed, lobed or dissected, cordate, glabrous or pubescent; petioles to 2 dm long; stipules linear to linear-lanceolate, 0.5-2 cm long, fimbriate, rarely entire. Peduncles of chasmogamous flowers nearly as long as the leaves, or slightly longer. Chasmogamous flowers 1.5-4 cm broad, not flat, petals deep reddish violet, lateral petals bearded with clavate trichomes, spurred petal usually glabrous, or occasionally with some trichomes; sepals 6-10 mm long, acute to obtuse, glabrous to ciliate or only the auricles ciliate, auricles 0.5-1 mm long; stamen appendages brilliant orange, deep in the throat of the flower; style clavate. Cleistogamous flowers on divergent peduncles 3-12 cm long or the peduncles erect and short; sepals 4-6 mm long, acute, auricles ca. 1 mm long. Capsules 6-12 mm long. Seeds brown, usually mottled, 1.5-2.3 mm long." - Radford et al 1964
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain in Florida and Georgia, V. palmata has been found in natural longleaf stands; longleaf pine-wiregrass savannas; loamy soil along mesic hardwood slopes; seepages in ravines; river banks; sandy loam under beech-magnolia forests; hardwood hammocks; oak-palmetto woods; alluvial soil of floodplain forests; between road and slash pine/wiregrass flatwoods; recently burned longleaf pine; longleaf pine-palmetto flats; loamy sand of grassy savanna; second growth loblolly pinewoods; sandy soil of turkey oak-longleaf pine flats; calcareous bluffs; upland mixed woodlands; beech-magnolia forests; and loamy humus of shallow depression of shaded limestone rock in hardwood maritime hammock (FSU Herbarium; [1]). It has been found to be extremely vulnerable to disturbance [1], however has been found growing along roadsides, sands of disturbed hillside bogs, lakesides, calcareous banks between earth road and drainage canal, ectone between oak woodland and open powerline corridor, heavily cattle grazed palmetto flatwoods, and a powerline transect through a longleaf pine-wiregrass savanna (FSU Herbarium).
Substrate types include loamy soil, loamy sand, sandy loam, peaty sand, alluvial soil, sandy-peaty soil, sandy-clayey soil, limestone and loamy humus (FSU Herbarium). Associated species include Carex crebriflora, Viola floridana, Aristida, Eleocharis, V. villosa, V. lanceolata, Chaptalia, Lycopodium, Sisyrinchium, Calopogon, and Hypericum (FSU Herbarium).
Phenology
It is a summer forb. [1] It has been recorded flowering February, March, April, December and fruiting February, March, April, August and September (FSU Herbarium).
Seed dispersal
V. palmata is dispersed myrmecochorously or explosively (Kirkman et al. 2004). According to Kay Kirkman, a plant ecologist, this species disperses by explosion mechanisms or by ants. [2]
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
It has been observed flowering February and March after a fire (FSU Herbarium).
Pollination
Use by animals
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, K. Craddock Burks, Robert K. Godfrey, S. W. Leonard, Wilson Baker, James R. Burkhalter, Robert Kral, L. B. Trott, J. P. Gillespie, D. B. Ward, J. Beckner, Patricia Elliot, Cecil R Slaughter, S. R. Harrison, C. Jackson, Nir L. Gil, Angus Gholson, Steve L. Orzell, Edwin L. Bridges, A. G. Shuey, Sidney McDaniel, S. C. Hood, Richard Carter, Mark A Garland, Richard S. Mitchell, Karen MacClendon, B. & M. Boothe, M. R. Darst, Rodie White, R. A. Norris, R. Komarek. States and Counties: Florida: Calhoun, Clay, Flagler, Franklin, Gadsden, Hamilton, Holmes, Jackson, Jefferson, Leon, Liberty, Madison, Manatee, Marion, Okaloosa, Santa Rosa, Seminole, St. Johns, Taylor, Wakulla, Washington. Georgia: Thomas. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
Kirkman, L. K., K. L. Coffey, et al. (2004). "Ground cover recovery patterns and life-history traits: implications for restoration obstacles and opportunities in a species-rich savanna." Journal of Ecology 92: 409-421.
Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 726. Print.
