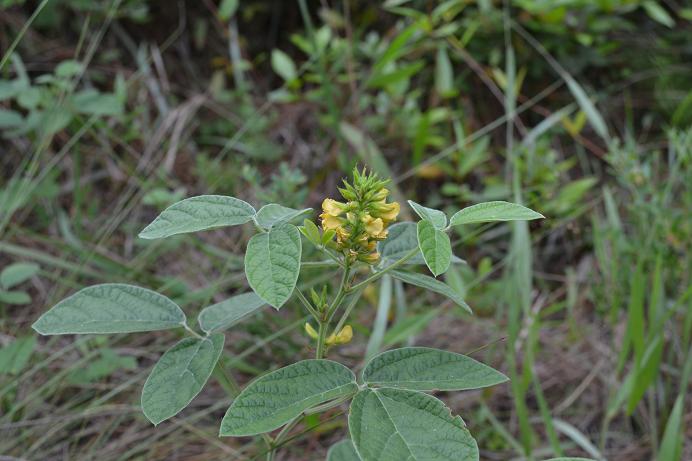
Rhynchosia tomentosa
| Rhynchosia tomentosa | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae ⁄ Leguminosae |
| Genus: | Rhynchosia |
| Species: | R. tomentosa |
| Binomial name | |
| Rhynchosia tomentosa (L.) Hook. & Arn. | |
| |
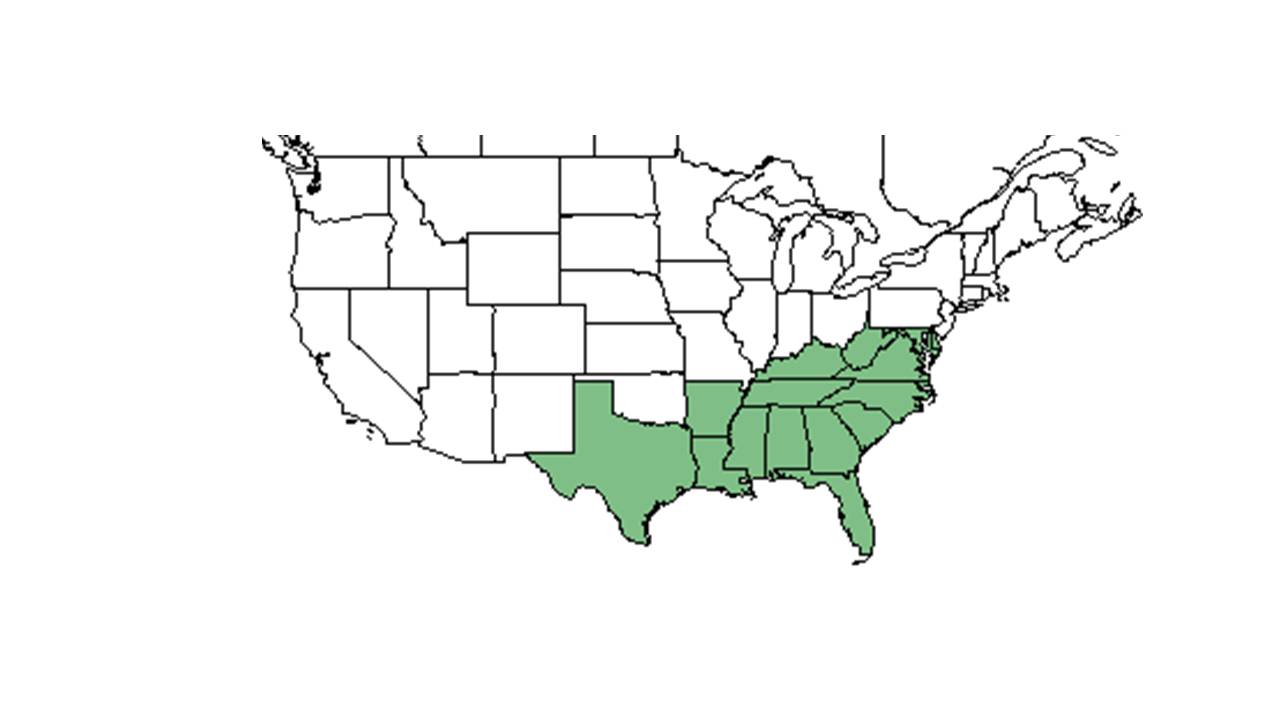
| Natural range of Rhynchosia tomentosa from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Twining snoutbean (Nelson 2005).
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Description
Is strongly paraheliotropic.[1]
Distribution
R. tomentosa was found in the study area “within the Upper Coastal Plain Ecoregion with nearly level to gently rolling topography and a maximum elevation of 240m.” (Archer et al 2007).
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plains, R. tomentosa can be found in pine-oak woodlands, old growth longleaf pine stands, frequently burned mature longleaf pine-wiregrass stands, longleaf pine sandhills, pine flatwoods, mature longleaf pine savanna, shady oak-hickory woods, hammocks, and calcareous glades (FSU Herbarium, Nelson 2005). It can also occur in recently burned scrubs of cutover pinewoods, former pine plantations, pastures, cut-over cedar glades, roadsides, near pond drains, old fields, powerline clearings, chalk prairies, and clearings of shortleaf pine stands. Associated species include Pinus palustris, Aristida stricta, Magnolia, Quercus, Rhynchosia reniformis and R. difformis (FSU Herbarium).
Soil types include sand, moist loamy soils, sandy loam, and loamy sand (FSU Herbarium).
Phenology
Flowers and fruits May through October (FSU Herbarium, Nelson 2005).
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
It was observed as an understory plant from frequently burned old-growth mountain longleaf pine stands at Fort McClellan, Alabama (Varner et al 2003).
Pollination
Use by animals
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
R. tomentosa was found to be an indicator species in areas 30-80 years after clear-cutting in a southeastern mixed pine forest (Archer et al. 2007).
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Archer, J. K., D. L. Miller, et al. 2007. Changes in understory vegetation and soil characteristics following silvicultural activities in a southeastern mixed pine forest. Journal of the Torrey Botanical Society 134: 489-504.
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, T. MacClendon, K. MacClendon, Brenda Herring, Don Herring, R. A. Norris, Rodie White, Richard R. Clinebell II, Robert Kral, Mabel Kral, Roy Komarek, John B. Nelson, A. Anrrich, Elias L Potagas, George R. Cooley, Carroll E. Wood, Jr., Robert K. Godfrey, K. Craddock Burks, Gwynn W. Ramsey, R. S. Mitchell, C. Jackson, Sidney McDaniel, G. Wilder, Roy Komarek, W. C. Coker, C. Ritchie Bell, R. L. Wilbur, James D. Ray, Jr., M. F. Buell, Jean Wooten, S. B. Jones, Carleen Jones, A. B. Seymour, H. R. Reed, A. F. Clewell, M. Morgan. States and Counties: Alabama: Baldwin, Cullman, Elmore, Jefferson, Marengo, Perry. Florida: Calhoun, Citrus, Columbia, Dixie, Gadsden, Hamilton, Jackson, Jefferson, Leon, Liberty, Nassau, Santa Rosa, Suwannee, Wakulla. Georgia: Baker, Grady, Seminole, Thomas, Turner. Mississippii: Clarke, Forrest, Jackson, Lawrence, Pearl River. North Carolina: Richmond, Robeson, Sampson, Wake, Warren. South Carolina: Darlington, Newberry. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
Varner, J. Morgan, John S. Kush, and Ralph S. Meldhal. 2003. Vegetation of Frequently Burned Old-Growth Longlef Pine (Pinus Palustris Mill.) Savannas on Choccolocco Mountain, Alabama, USA. Natural Areas Journal 23.1: 43-52.
Nelson, Gil. East Gulf Coastal Plain. a Field Guide to the Wildflowers of the East Gulf Coastal Plain, including Southwest Georgia, Northwest Florida, Southern Alabama, Southern Mississippi, and Parts of Southeastern Louisiana. Guilford, CT: Falcon, 2005. 184. Print.
