Dalea albida
| Dalea albida | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae |
| Genus: | Dalea |
| Species: | D. albida |
| Binomial name | |
| Dalea albida Torr. & A. Gray | |
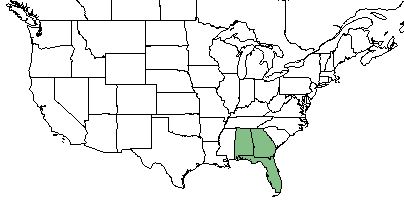
| |
| Natural range of Dalea albida from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common Name: White-tassels[1][2]
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: D. carnea var. albida (Torrey & A. Gray) Barneby; Petalostemon albidus (Torrey & A. Gray) Small.[3]
Varieties: one.[3]
Description
Dalea albida is a dioecious perennial that grows as a forb/herb or a subshrub.[2]
Distribution
This species occurs from eastern Georgia, westward to southeast Alabama, and southward to northern peninsular Florida.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
D. albida is found in pinelands.[1] It also occurs in central Florida glades where it has a 5% frequency.[4] It was found to be among the most cold-hardy legumes found in southern Georgia, where it persists through repeated frosts and was present in January and February field surveys.[5] It is found in dry-mesic to wet-mesic prairies.[4]
Phenology
In the southeastern and mid-Atlantic United States, flowering occurs from July through November.[1]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Weakley AS (2015) Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 USDA NRCS (2016) The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 02 February 2018). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Orzell SL, Bridges EL (2006) Floristic composition of the south-central Florida dry prairie landscape. Florida Ecosystem 1(3):123-133.
- ↑ Hainds, M. J. (1995). Legume population dynamics in a frequently burned longleaf pine-wiregrass ecosystem. Master of Science Thesis, Auburn University. 111 pages.