Ctenium aromaticum
Common Names: Toothache Grass; Orange Grass [1]
| Ctenium aromaticum | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by Kevin Robertson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Cyperales |
| Family: | Poaceae |
| Genus: | Ctenium |
| Species: | C. aromaticum |
| Binomial name | |
| Ctenium aromaticum Walter | |
| |
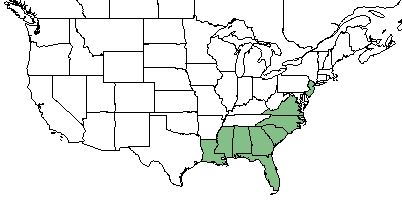
| Natural range of Ctenium aromaticum from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonym: Campulosus aromaticus (Walter) Trinius
Variety: none
Description
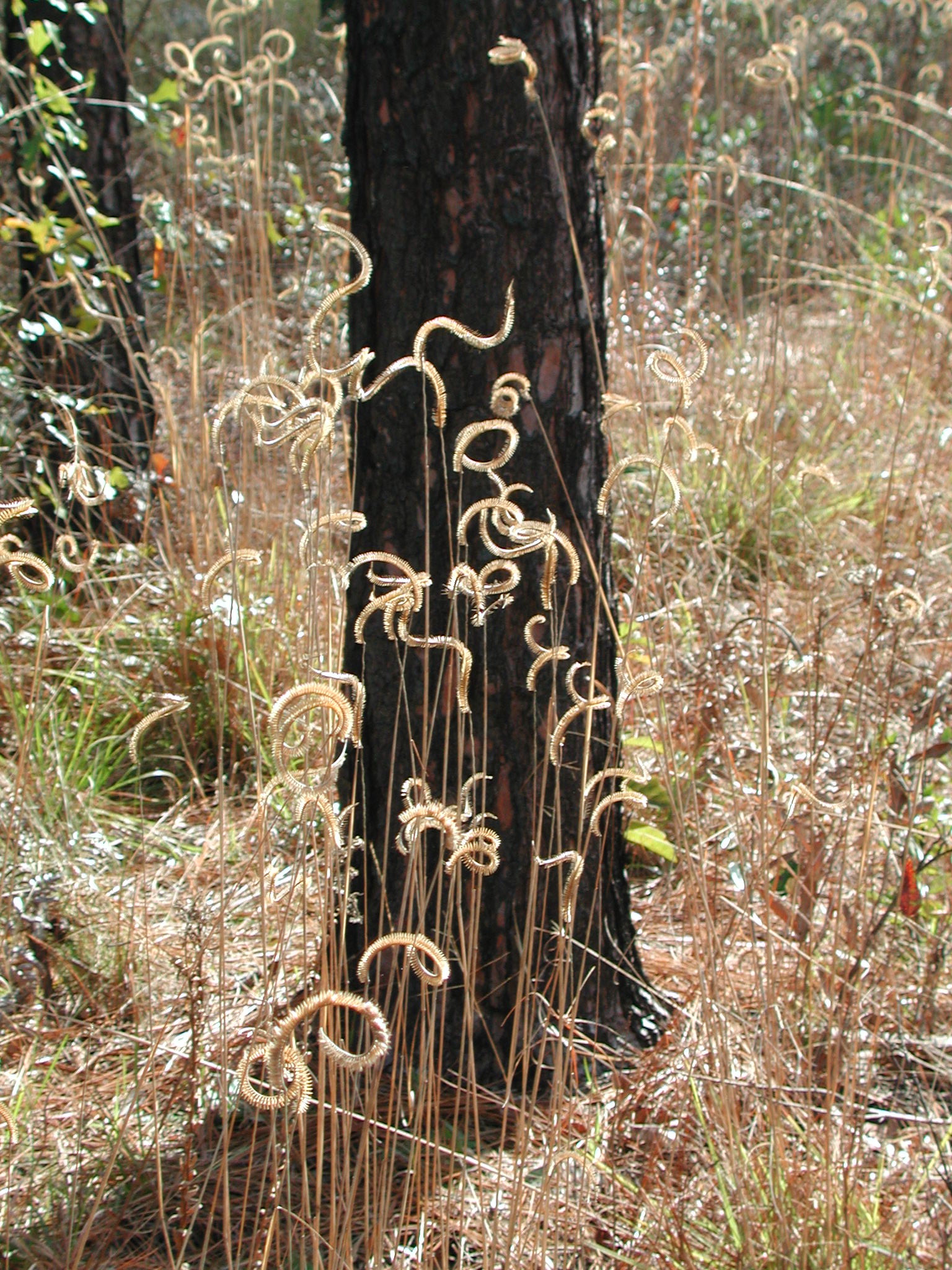
C. aromaticum is a perennial graminoid of the Poaceae family native to North America. [1] The whole plant is aromatic, which is what the specific epithet is named after. Sterile individuals can be identified by the broad and bicolored leaves that are bluish on the upper side and bright green on the under side.[2]
Distribution
C. aromaticum can be found in the southeastern part of the United States, specifically in Florida, Georgia, Alabama, Mississippi, Louisiana, South Carolina, North Carolina, and Virginia. [1] It is an endemic species of the Southeastern Coastal Plain.[2]
Ecology
Habitat
Ideal habitats for the C. aromaticum are in moist clay that may have some standing water after heavy rains. It has adapted to extremely wet conditions with acidic soils. [1] C. aromaticum is considered an indicator species in the upper Florida Panhandle wetland regions. It is also a dominant grass in lower panhandle savannas. [3] Specimens have been collected from habitats including longleaf pineland, wet loamy sands near bog, recently burned pineland, wiregrass savannas, flatwoods savannas, ponds, and prairies. [4]
Phenology
C. aromaticum flowers periodically between June and August, but can flower later in response to fires in the late summer.[2] However, it has been seen to flower earlier in the year, a few months after a prescribed burn. Edwin Bridges observed a region starting to flower in February after a prescribed fire in November in a pine savanna. .[5]
Seed bank and germination
Seed germination starts in Map and June that develop into stalks that produce plentiful seeds. [1]
Fire ecology
Seeds are produced after the region has been burned.[1]
Use by animals
This grass can be used for livestock to graze on. [1] The seeds are one of the preferred species by the Henslow's Sparrow for food in the winter. This species had long been considered an indicator species of Henslow's Sparrow habitats. [6] The entire plant if chewed by humans causes numbness to the mouth, tongue, and lips.[2]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 USDA Plant Database
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ Carr, S. C., et al. (2010). "A Vegetation Classification of Fire-Dependent Pinelands of Florida." Castanea 75(2): 153-189.
- ↑ URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Nancy E. Jordan, R.K. Godfrey, John Nelson, G. Knight, R. Wnek, John Morrill, Bruce Hansen, A. Curtiss, A. Clewell, E. Tyson, Steve L. Orzell, Edwin Bridges, Sidney McDaniel, R. Kral, O. Lakela, William Reese, Paul Redfearn, Grady W. Reinert, R.Lazor, J.B. McFarlin, P.Ferral, R. Porcher. States and counties: Florida (Wakulla, Liberty, Bay, Franklin, Nassau, Escambia, Duval, Holmes, Jefferson, Santa Rosa, Pasco, Calhoun, Leon, Osceola, Highlands, Jackson), Georgia (Thomas, Dougherty), South Carolina (Berkely)
- ↑ Observation by Edwin Bridges in Highlands County, Fl., February 12, 2016, posted to Florida Flora and Ecosystematics Facebook Group February 13, 2016.
- ↑ DiMiceli, J. K., et al. (2007). "Seed preferences of wintering Henslow's sparrows." Condor 109: 595-604.