Salix nigra
| Salix nigra | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by John Gwaltney hosted at Southeastern Flora.com | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Salicales |
| Family: | Salicaceae |
| Genus: | Salix |
| Species: | s. nigra |
| Binomial name | |
| Salix nigra Marshall | |
| |
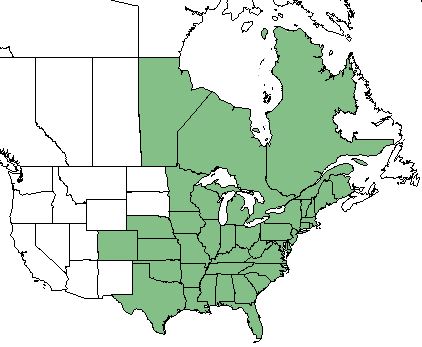
| Natural range of Salix nigra from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonym: S. marginata (Wimmers ex Andersson)
Variety: none
Description
Synonym: S. nigra is a perennial tree of the Salicaceae family that is native to North America.[1]
Distribution
S. nigra is found throughout the eastern United States and Canada, as far west as Texas, Colorado, and Manitoba. [1]
Ecology
Habitat
Moist environments such as stream banks, lakes, swamps, or pasture sloughs are ideal for S. nigra.[1]
Phenology
February to April is common flowering season in the southern range of the species with April producing the most recorded flowers, and May to June is more common in the northern region.[1] [2]
Seed dispersal
Seeds are commonly dispersed by wind and water. [1]
Fire ecology
Fires are not common to the native habitats of S nigra and can be devastating when they occur, killing the entire population in some cases, especially young seedlings.[1]
Use by animals
Bees utilize the plant for its nectar and pollen. Domestic animals or livestock will use it for grazing. Elk and beavers will use it for browse in the summer. Beavers, hares, and rabbits will eat the shoots. The willow is also a host for butterflies. [1]
Diseases and parasites
Many insects are pests for the S. nigra; including forest tent caterpillar, gypsy moth, cotton wood leaf beetle, and willow beetle which can inhibit growth. Others such as stem borers will attack the base of the plant, killing it, or twig borers which will cause branch deformities. [1]
Diseases are brought to the species due to the pest insects that are common to the S. nigra. Diseases include willow blight that cause leaves and stems to die due to the fungus. Phytophthora cactorum is a canker that can cause lesions of the stalks. Cytospora chrysosperma can also cause cankers. [1]
Conservation and Management
Salix nigra can be used as a soil binder when it grows along the banks of streams which helps soil from being washed away and prevent erosion. [1]