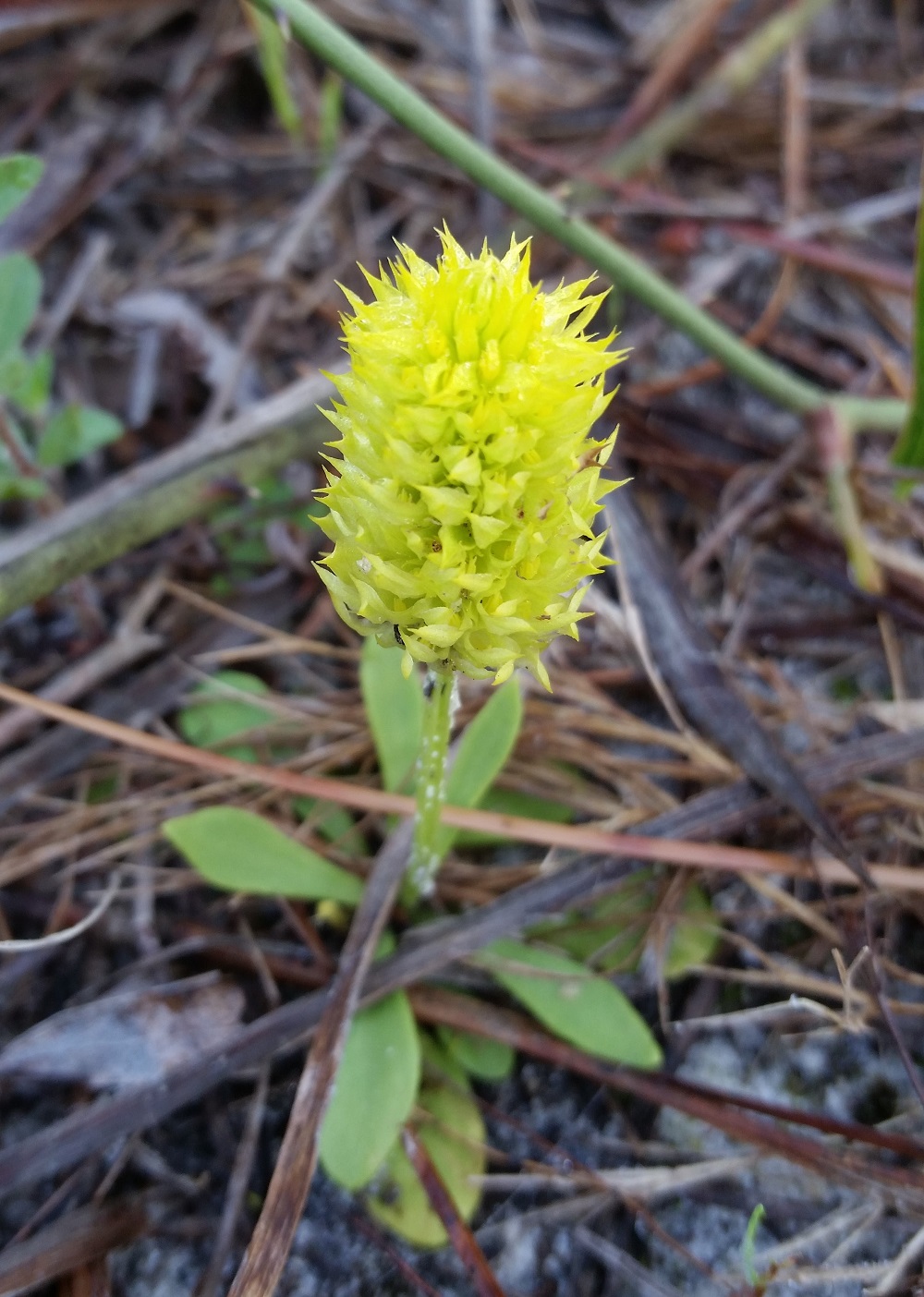
Polygala nana
| Polygala nana | |
|---|---|
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
| |
| Photo taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Polygalales |
| Family: | Polygalaceae |
| Genus: | Polygala |
| Species: | P. nana |
| Binomial name | |
| Polygala nana (Michx.) DC. | |
| |
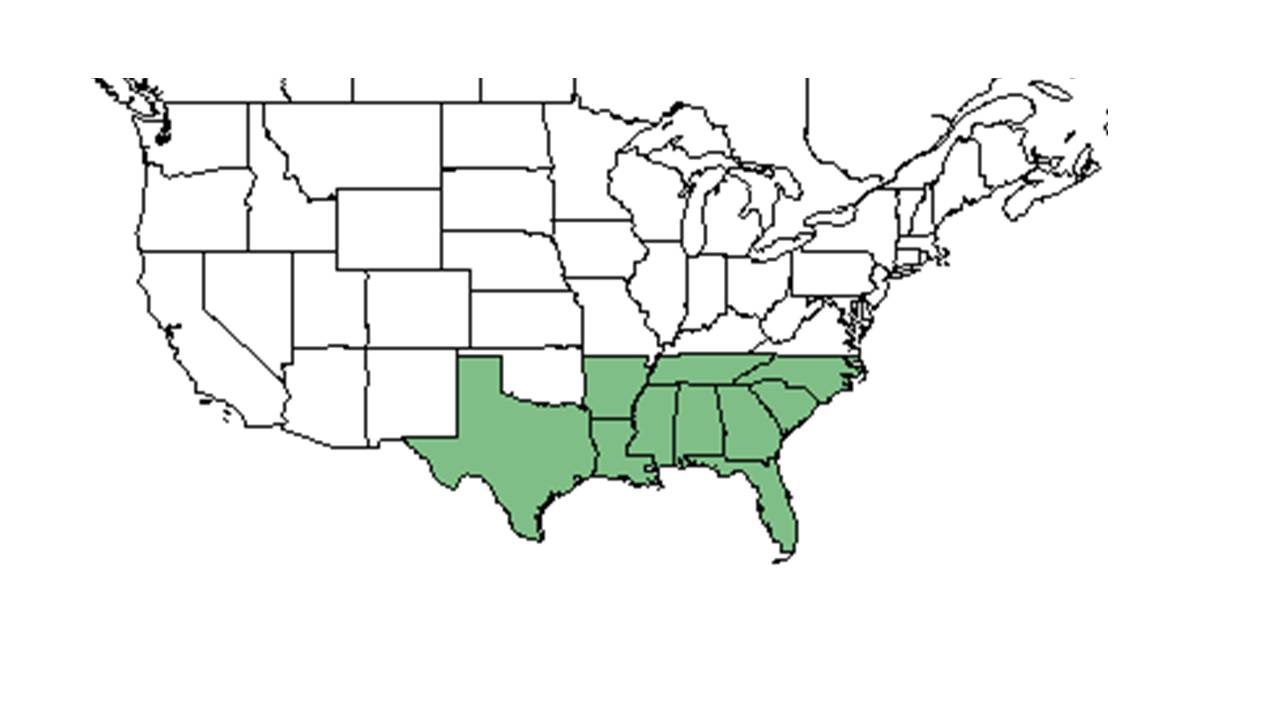
| Natural range of Polygala nana from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: candyroot
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Pilostaxis nana (Michaux) Rafinesque; Pylostachya nana (Michaux) Rafinesque
Description
"Herbs, whorled or alternate rarely opposite, entire leaves. Flowers lavender, pink, white or yellow, in racemes or spikes, terminating the branches or in terminal corymbs. Flowers perfect, zygomorphic, with 3 small sepals, frequently one of these slightly larger than the others, and 2 larger petaloid sepals (wigs). The 3 petals are united into a tube, 3-lobed at apex, the 2 lateral lobes usually the longer, the center lobe usually lacerate, often thicker in texture; stamens 6-8, united to the corolla tube in 2 rows. Capsule 2 –locular, with one seed in each locule. Seeds dark brown or black, ellipsoid or ovoid, rarely globose, 0.5-3 mm long, usually densely pubescent. The genus has been divided into several genera none of which have distinct characteristics. Orange flowers turn pale yellow on drying, yellow ones bluish green; the pink or lavender ones remain the same color or fade slightly." [1]
"Similar to P. lutea. 3-15 cm tall, with leaves mostly confined to a basal rosette; stem leaves few. Flowers lemon yellow. Wings 7-8 mm long, long acuminate." [1]
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
This species has been found in open, well-drained wiregrass-pine flatwoods and interdune swales growing on both dry and moist sands. [2] Observed species in sandhill longleaf pine habitat that has 1 to 3 year fire return intervals. Also seen near a cypress pond, about 1 to 2 feet from water’s edge of Pebble Hill Plantation C plots. (Michelle M. Smith – early summer 2014 and 2015).P. nana has also been found growing along the sides of highways and in the wetlands of clear cut areas. [2] Associated species include Pinus palustris and Aristida stricta. [2]
Phenology
Flowers in April. [2]
Seed dispersal
According to Kay Kirkman, a plant ecologist, this species disperses by explosion mechanisms or by ants. [3]
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 660. Print.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: : Loran C. Anderson, Leon Neel, R. A. Norris, Robert K. Godfrey, Walter Kittredge, R. Komarek, Lisa Keppner. States and Counties: Florida: Franklin, Gadsden, Leon, Wakulla, Washington. Georgia: Grady, Thomas. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ Kay Kirkman, unpublished data, 2015.
