Richardia scabra
| Richardia scabra | |
|---|---|
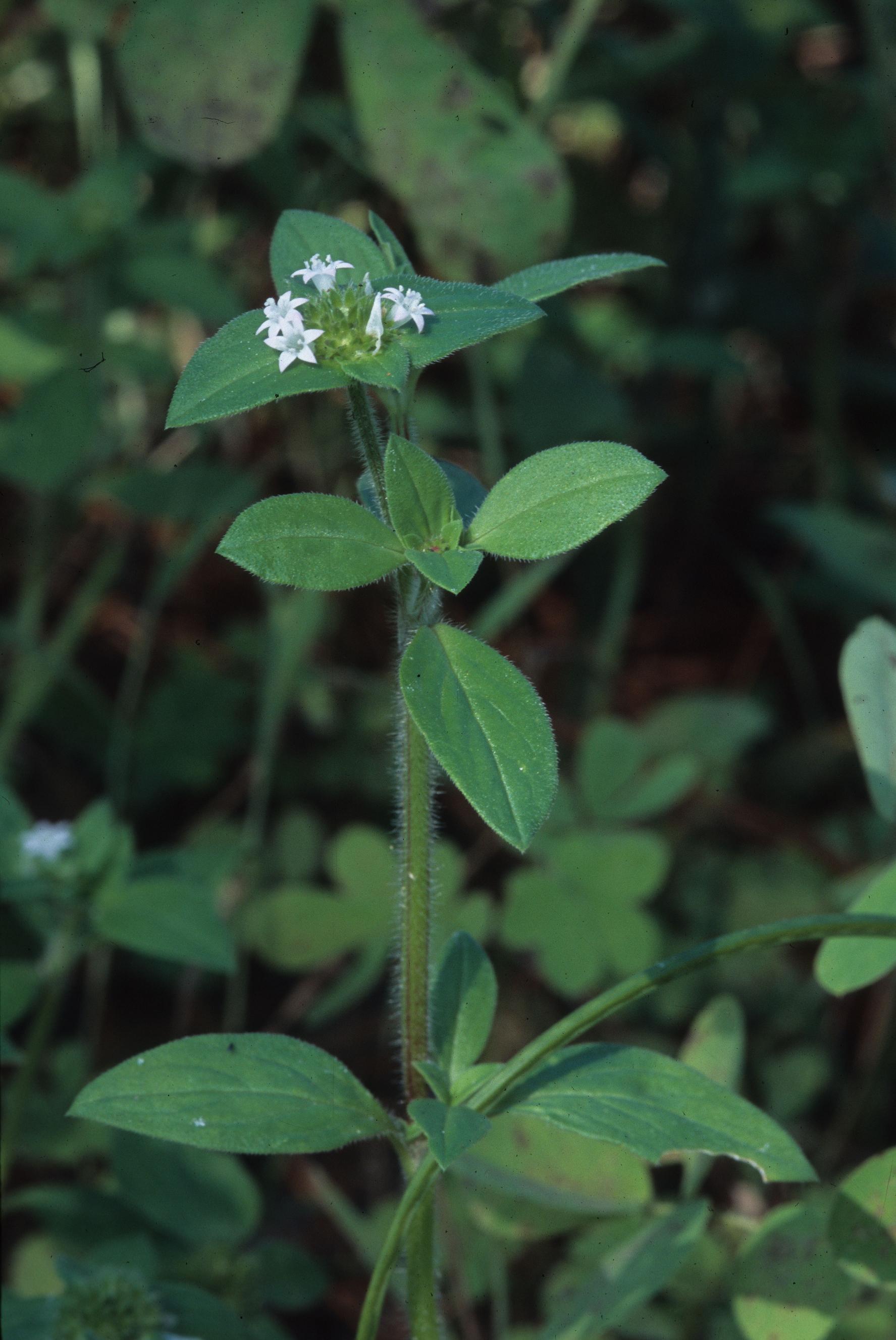

| |
| Photo was taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Rubiales |
| Family: | Rubiaceae |
| Genus: | Richardia |
| Species: | R. scabra |
| Binomial name | |
| Richardia scabra L. | |
| |
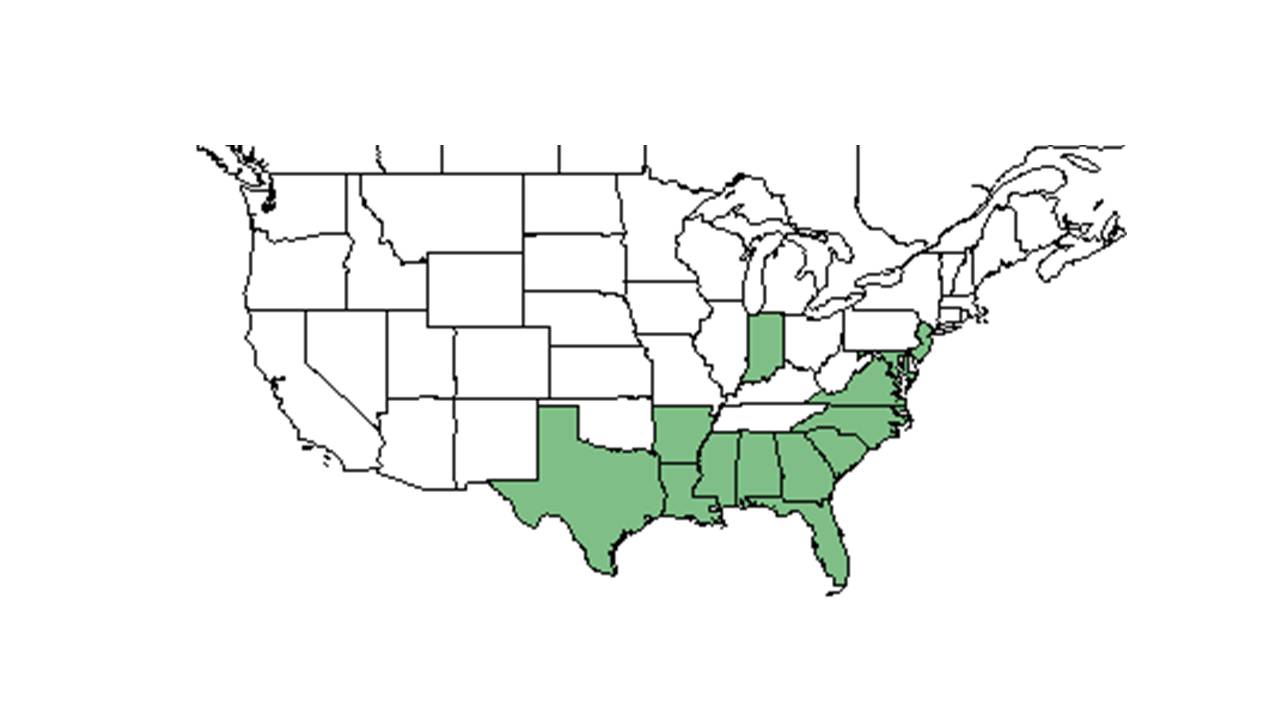
| Natural range of Richardia scabra from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Rough Mexican flower[1], Rough Mexican clover
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: none
Varieties: none
Description
"Diffuse, decumbent, pubescent to pilose annuals or perennials, the stem 1-7 dm long or tall. Leaves opposite, connected by fimbriate stipules, lanceolate to elliptic or weakly oblanceolate, 2.5-7 cm long including the often indehiscent petioles, 1-2 cm wide. Inflorescences terminal, glomerate, involucrate, the bracts ovate or widely ovate-lanceolate, often dimorphic; corolla white, funnelform, lobes shorter than tube, anthers inserted at the rim of the tube. Fruit leathery, 3-4 mm long, separating into 4 in dehiscent carpels."[2]
"Annual. Corolla 5-6 mm long, lobes less than 1/3 the length of the tube. Fruit tuberculate."[2]
Distribution
It is observed in South Carolina Coastal Plain.[3]
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain region, R. scabra can be found in woodlands and upland pine communities.[4] It can also be found in vacant lots, roadsides, abandoned fields, and powerline corridors.[4][1] It grows in fine sandy loams, that are poorly drained with slow permeability.[3] R. scabra does not respond to soil disturbance by clearcutting and chopping in North Florida flatwoods forests.[5]
Phenology
R. scabra has been observed flowering in March, May, and from June through December.[1][6]
Pollination
Richardia scabra has been observed at the Archbold Biological Station to host members of the Apidae family such as Apis mellifera and Bombus pennsylvanicus, as well as members of the Halictidae family such as Agapostemon splendens, Augochloropsis sumptuosa, and Lasioglossum lepidii, members of the Megachilidae family such as Anthidiellum notatum rufomaculatum, and Megachile mendica, members of the Sphecidae family such as Ammophila pictipennis, Cerceris tolteca, Prionyx thomae, Stictia carolina, and Tachytes pepticus, and members of the Vespidae family such as Leptochilus republicanus, and Parancistrocerus salcularis rufulus.[7] Deyrup observed Agapostemon splendens, Augochloropsis sumptuosa, Anthidiellum maculatum rufimaculatum, Megachile mendica, M. texana, Apis mellifera, and Bombus pennsylvanicus, on R. scabra.[8] Additionally, R. scabra has been observed to host species such as Florilegus condignus (family Apidae) and Aphis sp. (family Aphididae).[9] R. scabra was heavily fed on by Gopher tortoises in agricultural areas of southwestern Georgia.[10]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Nelson, Gil. Atlantic Coastal Plain Wildflowers: A Field Guide to the Wildflowers of the Coastal Regions of Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia, and Northeastern Florida. Guilford, CT: FalconGuide, 2006. 159. Print.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 981. Print.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Lewis, C. E. and T. J. Harshbarger. 1976. Shrub and herbaceous vegetation after 20 years of prescribed burning in the South Carolina coastal plain. Journal of Range Management 29:13-18.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: : R. Komarek, Robert K. Godfrey, Andre F. Clewell, R. A. Norris, Loran C. Anderson, Edwin L. Tyson, D. E. Breedlove, Peter H. Raven, K E Blum, J. Dwyer, H. Loftin, Edwin L. Tyson, C. Kupfer, H. Smith, G. Martinez Calderon. States and Counties: Florida: Leon, Lafayette, Liberty. Georgia: Baker, Thomas. Country: Panama, Mexico. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ Moore, W.H., B.F. Swindel, and W.S. Terry. (1982). Vegetative Response to Clearcutting and Chopping in a North Florida Flatwoods Forest. Journal of Range Management 35(2):214-218.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 13 DEC 2016
- ↑ Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
- ↑ Deyrup, Mark, Jayanthi Edirisinghe, and Beth Norden. 2002. The Diversity and Floral Hosts of Bees at the Archbold Biological Station, Florida (Hymenoptera: Apoidea). Insect Mundi 16.1-3: 87-120.
- ↑ Discoverlife.org [1]
- ↑ Garner, J. A. and J. L. Landers. 1981. Foods and habitat of the gopher tortoise in southwestern Georgia. Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the Southeastern Association of Fish and Wildlife Agencies 35:120-134.