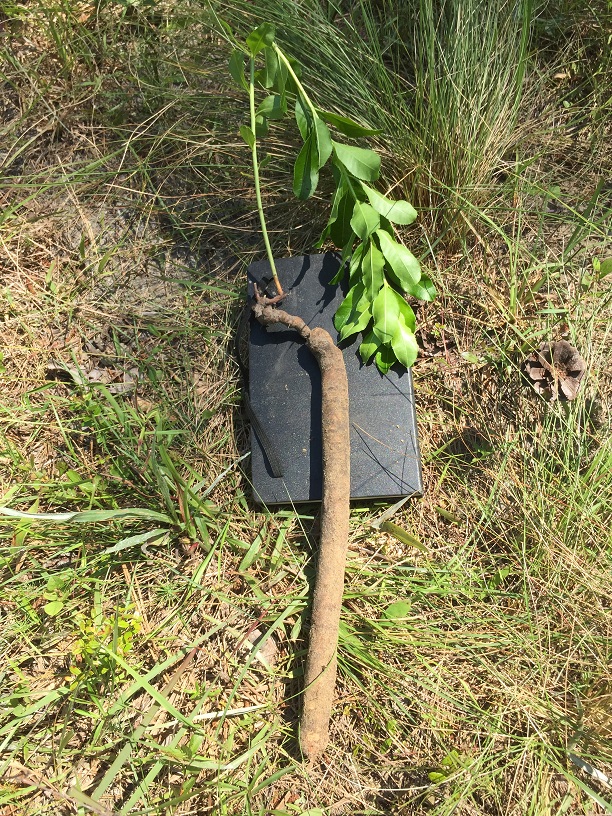
Stillingia sylvatica
| Stillingia sylvatica | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo taken by Michelle M. Smith | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Euphorbiales |
| Family: | Euphorbiaceae |
| Genus: | Stillingia |
| Species: | S. sylvatica |
| Binomial name | |
| Stillingia sylvatica L. | |
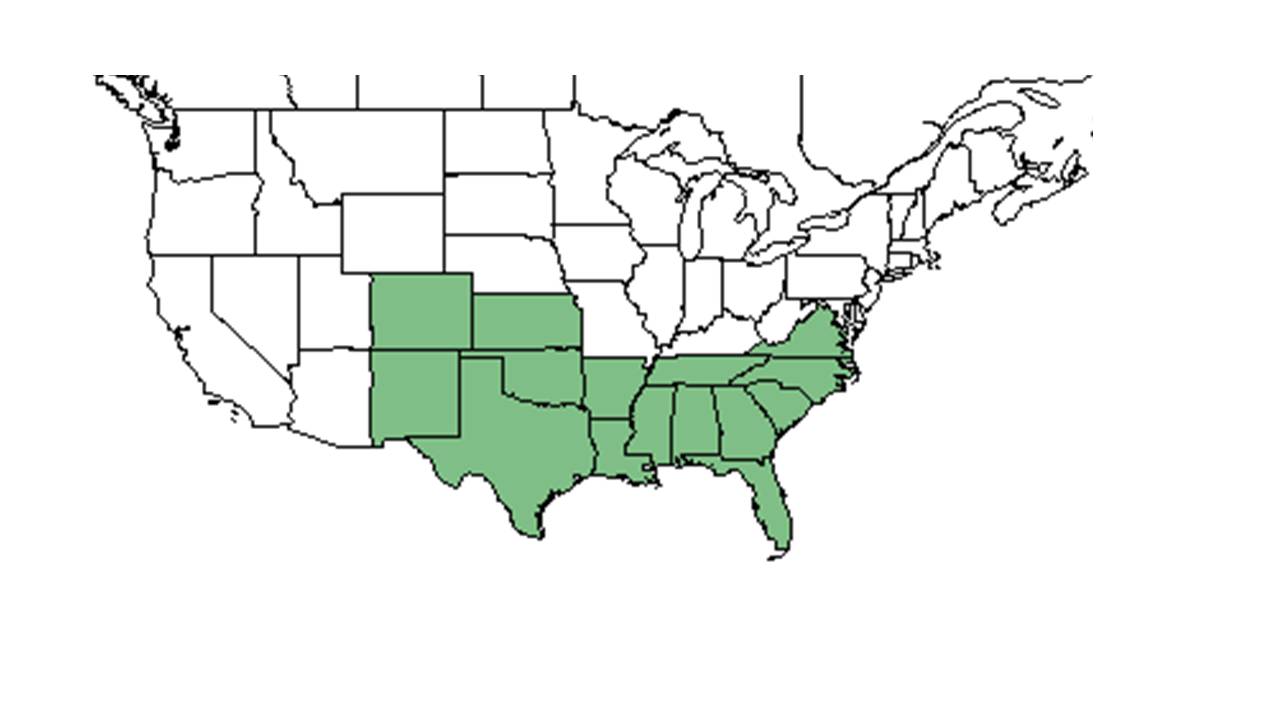
| |
| Natural range of Stillingia sylvatica from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Queen's-delight
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Stillingia sylvatica var. sylvatica; S. sylvatica ssp. sylvatica; S. spathulata (Müller of Aargau) Small
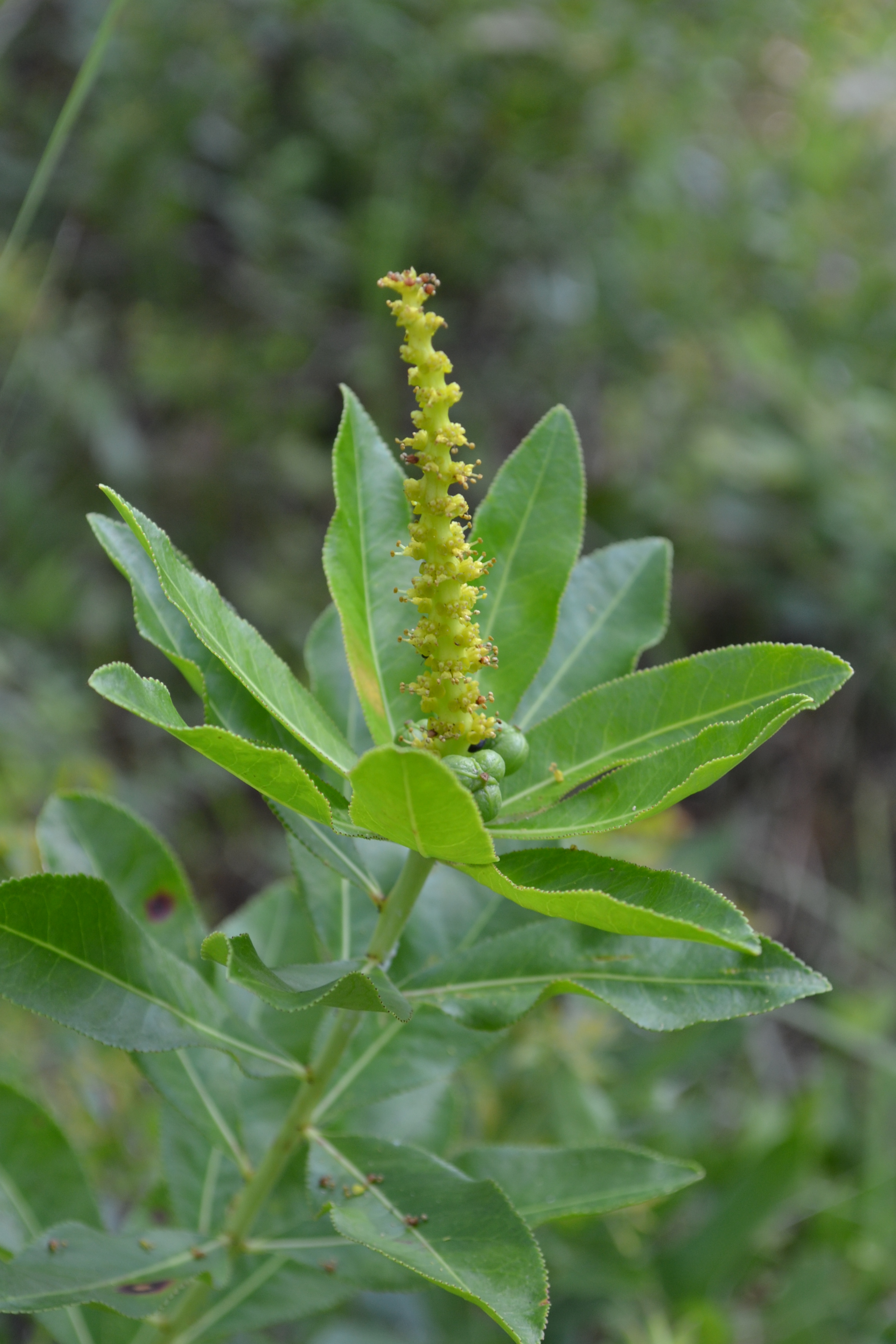
Description
"Glabrous, monoecious, perennial herbs or shrubs with alternate leaves. Leaves finely crenate, the teeth with pointed, callous spicules, sessile or short-petiolate. Spike terminal, rachis with numerous large glands, the lower portion pistillate flowered, the upper staminate. Calyx 2-3 parted, yellow; petals none; stamens 2; stigmas 3, red. Capsules as long as broad, leaving a 3-lobed disc upon falling from plant. Seeds grayish white, ovoid; caruncle small." [1]
"Herbaceous perennial, to 8 dm tall, with few to numerous stems arising from a crown; stems branching only immediately below an inflorescence with 2-4 branches. These usually terminated in an inflorescence. Leaves elliptic, 3.5-9 cm long, 1-4.5 cm wide; petioles 0-4 mm long, base glandular-stipulate. Spike 5-12 cm long. Capsules 8-10 mm long. Seeds nearly smooth, 5-6 mm long." [1]
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain in Florida and Georgia, S. sylvatica can be found in sandhills (FSU Herbarium), [2] pine flatwoods, open pine-oak woodlands, recently burned pine-oak scrubs, longleaf pine-wiregrass stands, longleaf pine-turkey oak-wiregrass, and annually burned pinelands (FSU Herbarium). Substrate types include loamy sand, sand (FSU Herbarium), and siliceous, hypothermic Ultic haplaquod of the Pomona series. [3] S. sylvatica does not respond to soil disturbance by clearcutting and chopping in North Florida flatwoods forests.[4]
Associated species include Stillingia aquatica, Phlox floridana, Asimina longifolia var. spathulata, Lactuca graminifolia, Pterocaulon undulatum, Asclepias humistrata and Quercus hemisphaerica (FSU Herbarium).
Stillingia sylvatica is frequent and abundant in the Peninsula Xeric Sandhills community type as described in Carr et al. (2010).[5]
Phenology
S. sylvatica has been observed flowering April through August with peak inflorescence in April and May (FSU Herbarium).[6]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by ants and/or explosive dehiscence. [7] It is dispersed explosively (up to 3 meters); seeds are forcefully expelled after the fruit matures and dries. It can also be dispersed by ants. [2]
Fire ecology
It seems to respond positively to burning. In an experiment by Greenberg (2003), and he noted that the percent cover of S. sylvatica was highest 16 months after a May burn. [8]
Use by animals
The seeds of S. sylvatica contain elaiosomes and have been found in middens of Florida harvester ants, Pogonomyrmex badius. [2]
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 667. Print.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Stamp, N. E. and J. R. Lucas. 1990. Spatial patterns and dispersal distances of explosively dispersing plants in Florida sandhill vegetation. Journal of Ecology 78:589-600.
- ↑ Moore, W. H., B. F. Swindel and W. S. Terry. 1982. Vegetative response to prescribed fire in a north Florida flatwoods forest. Journal of Range Management 35:386-389.
- ↑ Moore, W.H., B.F. Swindel, and W.S. Terry. (1982). Vegetative Response to Clearcutting and Chopping in a North Florida Flatwoods Forest. Journal of Range Management 35(2):214-218.
- ↑ Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 14 DEC 2016
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.
- ↑ Greenberg, C. H. 2003. Vegetation recovery and stand structure following a prescribed stand-replacement burn in sand pine scrub. Natural Areas Journal 23:141-151.
