Coleataenia rigidula
Common Names: Redtop Panic Grass; Dense Panic Grass
| Coleataenia rigidula | |
|---|---|
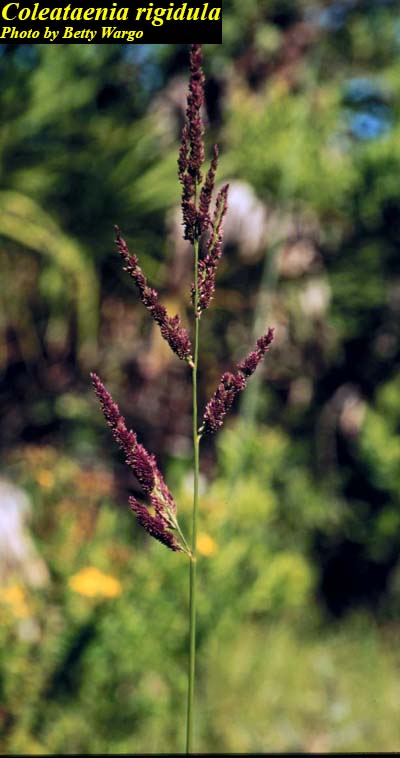

| |
| Photo by the Atlas of Florida Plants Database | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Cyperales |
| Family: | Poaceae |
| Genus: | Coleataenia |
| Species: | C. rigidula |
| Binomial name | |
| Coleataenia rigidula (Bosc ex Nees) | |
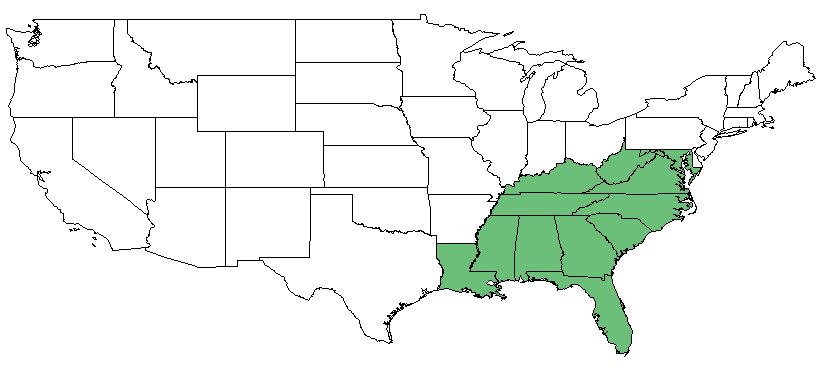
| |
| Natural range of Coleataenia rigidula from Weakley [1] | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: Coleataenia longifolia (Torrey) Soreng ssp. rigidula (Bosc ex Nees) Soreng; Sorengia longifolia (Torrey) Zuloaga & Morrone ssp. rigidula (Bosc ex Nees) Zuloaga & Morrone; Panicum agrostoides Sprengel var. condensum (Nash) Fernald; Panicum rigidulum Bosc ex Nees; P. rigidulum Bosc ex Nees ssp. rigidulum; P. agrostoides Sprengel; P. condensum Nash; P. rigidulum Bosc ex Nees var. rigidulum; Panicum rigidulum Bosc ex Nees var. condensum (Nash) Mohlenbrock; P. agrostoides Sprengel var. agrostoides; P. agrostoides var. ramosius (C. Mohr) Fernald
Varieties: none
Subspecies: C. rigidula (Bosc ex Nees) LeBlond ssp. condensa (Nash) LeBlond; C. rigidula (Bosc ex Nees) LeBlond ssp. rigidula
Description
C. rigidula is a perennial gaminoid of the Poaceae family that is native to North America. [2] C. rigidula ssp. condensa is easily identified by its compact inflorescence and tall stature. This subspecies can also resemble C. anceps ssp rhizomata, and can be differentiated by having sheaths that are glabrous to appressed pubescent distally.[1]
Distribution
C. rigidula can be found across the eastern side of North America and along the western coast of the United States and Canada. [2] C. rigidula ssp. condensa can be found in the Coastal Plain from southeast Massachusetts south to Florida and west to southeast Texas as well as disjunct in the West Indies, while C. rigidula ssp. rigidula can be found across the rest of its native range.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
Common areas C. rigidula can be found include marshes, meadows, peaty or wet sandy soils in low woods, shores of streams and ponds, swamps, ditches, and it can often be quite weedy.[1] Ideal habitat for C. rigidula is in moist regions, for instance, wooded floodplains, marshes, moist loamy sand at edge of woods, moist depressions, lower tidal hammock, swamp forests, pine flatwoods, edge of rivers, bottomland of wooded areas, and shores of lakes. [3]
Associated species: Taxodium distichum, Sabal palmetto, Pinus taeda, Osmunda cinnamomea, Berchemia sp., Polygonum sp., Fraxinus sp., Acer sp., Amelopsis sp., Hydrocotyle sp. [3] FINISH THIS
Phenology
This species has been observed to flower in December.[4]
Conservation and Management
It is listed as a species of special concern by the Rhode Island Department of Environmental Management.[2]
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 USDA Plant Database
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Cecil R. Slaughter, M.Darst, H. Light, L. Peed, D.L. Martin, S. T. Cooper, J.B. McFarlin, R. Kral, F.C. Craighead, R.K. Godfrey, Richard Houk, John Palis, Sandy Thompson, J.P. Gillespie, Sydney Thompson, Culver Gidden, R.J. Eaton, Olga Lakela, A.F.Clewell, Robt. Blaisdell, Gary R. Knight, Keith Bradley. States and counties: Florida (Franklin, Oscelola, Wakulla, Levy, Madison, Marion, Hardee, Brevard, Dade, Charlotte, Pinellas, Dixie, Putnam, Santa Rosa, Liberty, Gadsden, Leon, Jefferson, Suwannee, Washington, Hamilton, Calhoun, Nassau, Collier, Gulf, Taylor) South Carolina (Laurens)
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 8 APR 2019