Monarda punctata
| Monarda punctata | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by John B | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Lamiales |
| Family: | Lamiaceae |
| Genus: | Monarda |
| Species: | M. punctata |
| Binomial name | |
| Monarda punctata L. | |
| |
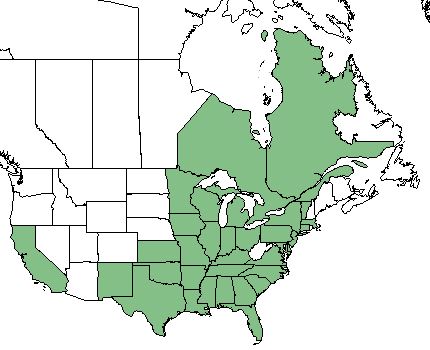
| Natural range of Monarda punctata from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common Names: Arkansas horse mint; eastern horse-mint; hairy-stem horse mint;[1] spotted beebalm[2]
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Varieties: M. punctata var. arkansana; M. punctata var. punctata; M. punctata var. villicaulis[1][2] M. punctata var. correllii; M. punctata var. coryi; M. punctata var. intermedia; M. punctata var. lasiodonta; M. punctata var. occidentalis[2]
Description
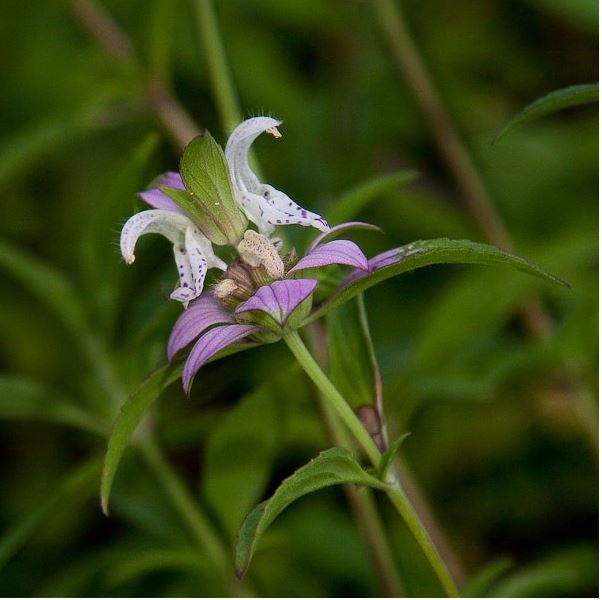
Monarda punctata is a dioecious species, classified as an annual, biennial, and perennial. It grows as a forb/herb or subshrub.[2] It is an aromatic species that reaches heights of 1-3 ft (0.30-0.91 m). Inflorescence are tubular and yellowish/purple spotted, occurring in whorls that form a dense elongated spike at the end of the stem or leaf axil. It also has bracts that can be purple, pink, white, or yellow.[3]
Distribution
This species is found from New Mexico and Kansas, eastward to Florida, northward to Vermont and Massachusetts, and inland to Iowa and Minnesota. Exceptions to this are Delaware and West Virginia, where no mounted specimens have been reported to the USDA. It also occurs in the Canadian provinces of Ontario and Quebec and has a disjunct population in California.[2]
Ecology
Habitat
M. punctata occurs in dryish forests over mafic rock, maritime forests, dunes, roadsides, rocky or sandy woodlands, and disturbed areas.[1]
Phenology
In the southeastern and mid-Atlantic United States, flowering occurs from July through October.[1] On the Florida panhandle, flowering occurs in September and October.[4]
Pollination
This species is insect pollinated and is of special value to native bees, bumble bees, honey bees, butterflies (including the endangered Karner blue butterfly, Lycaeides melissa samuelis[5]), and predatory and parasitoid insects that prey upon other insects.[3] When blooming in Wisconsin, pollinator visits occurred up to 1.1 visits min-1.[6]
Use by animals
M. punctata composes 5-10% of the diets of large mammals.[7] It is also found in about 25% of the crops of mourning doves (Zenaida macroura)[8] and 28% of the crops of scaled quail (Callipepla squamata)[9] in southeastern New Mexico.
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Weakley AS (2015) Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 USDA NRCS (2016) The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 29 January 2018). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Plant database: Monarda punctata. (29 January 2018) Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center. URL: https://www.wildflower.org/plants/result.php?id_plant=MOPU
- ↑ Nelson G (29 January 2018) PanFlora. Retrieved from gilnelson.com/PanFlora/
- ↑ Grundel R, Pavlovic NB (2000) Nectar plant selection by the Karner blue butterfly (Lycaeides melissa samuelis) at the Indiana Dunes national Lakeshore. The American Midland Naturalist 144(1):1-10.
- ↑ Rafferty NE, Ives AR (2011) Effects of experimental shifts in flowering phenology on plant-pollinator interactions. Ecology Letters 14:69-74.
- ↑ Miller JH, Miller KV (1999) Forest plants of the southeast and their wildlife uses. Southern Weed Science Society.
- ↑ Best TL, Smartt RA (1986) Feeding ecology of mourning doves (Zenaida macroura) in southeastern New Mexico. The Southwestern Naturalist 31(1):33-38.
- ↑ Best TL, Smartt RA (1985) Foods of scaled quail (Callipepla squamata) in southeastern New Mexico. Texas Journal of Science 37(2&3):155-162.