Vernonia angustifolia
| Vernonia angustifolia | |
|---|---|
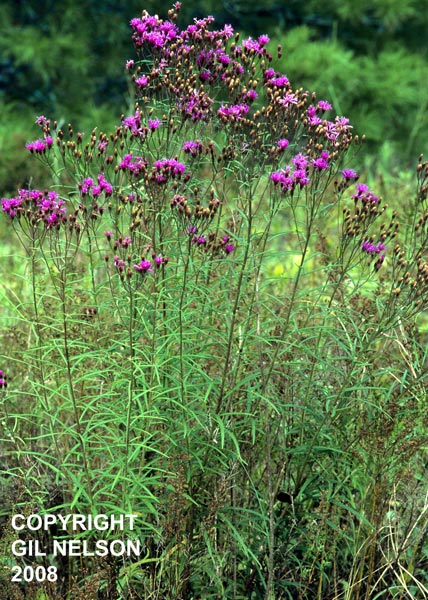

| |
| Photo taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae ⁄ Compositae |
| Genus: | Vernonia |
| Species: | V. angustifolia |
| Binomial name | |
| Vernonia angustifolia Michx. | |
| |
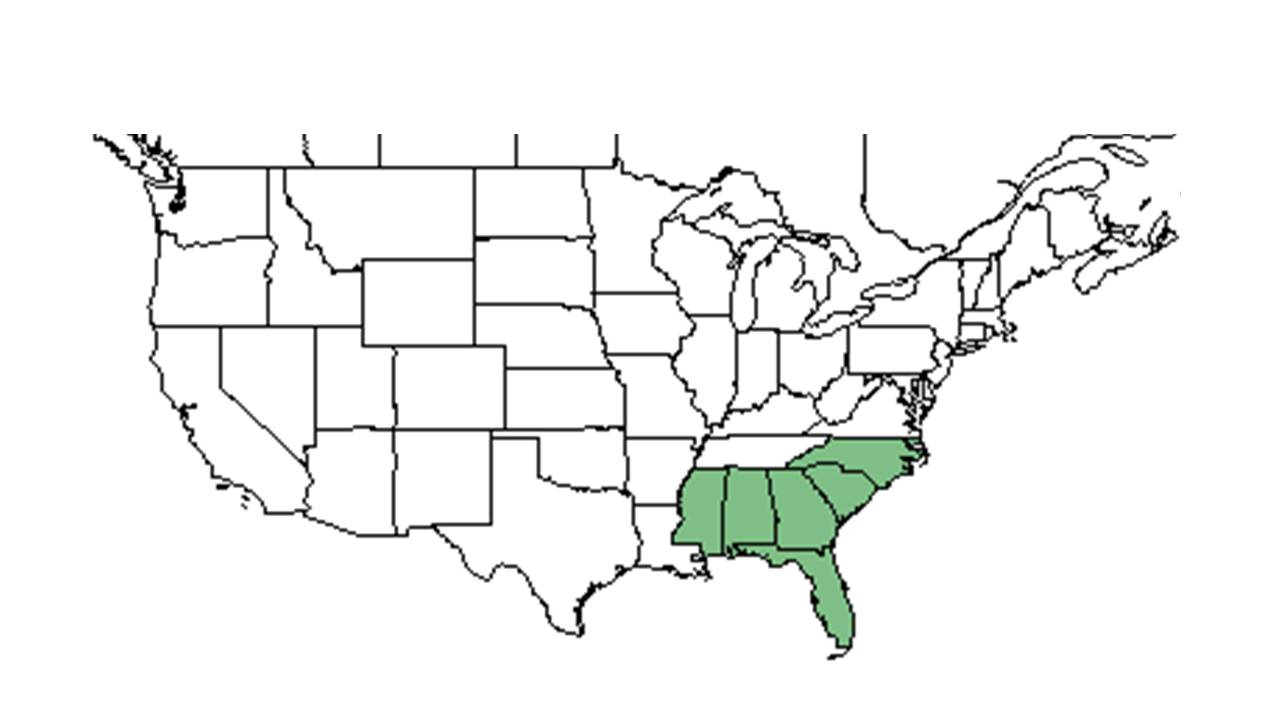
| Natural range of Vernonia angustifolia from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: tall ironweed
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Description
A description of Vernonia angustifolia is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain region, V. angustifolia can be found in sand pine scrubs, longleaf pine-wiregrass flatwoods, edges of meadows, pine-turkey oak flats, longleaf pine savannas, mixed woodlands adjacent to floodplains, annually burned pinelands, longleaf pine-sedge-andropogon savannas, slash pine-wiregrass flats, oak scrubs, second growth hardwoods, cabbage palm hammocks, annually burned upland pines (Birkhead et al. 2005; FSU Herbarium) and sandhill communities (Heuberger et al. 2003). It can also be found along roadsides, powerline cooridors, bulldozed pine-oak scrubs, and clobbered slash pine forests. Soil types include sandy loam, loose sand, loamy sands, sandy peat (FSU Herbarium), and Utisols (Coffey and Kirkman 2006).
Associated species include Aristida berichiana, Serenoa repens, Ilex glabra, Liatris, Andropogon, Panicum, and Leptoloma cognatum (FSU Herbarium).
Phenology
It is a fall forb (Kirkman et al 2004). Showy-flowered sandhill species (Heuberger et al 2003).
Seed dispersal
It is dispersed by wind (Kirkman et al 2004).
Seed bank and germination
Less than 1% of V. angustifolia seeds remained viable after two years of burial by Coffey and Kirkman (2006). Thus, V. angustifolia doesn't have a short-term persistent soil seed bank and has little seed dormancy.
Fire ecology
It can live in areas frequently burned (Coffey and Kirkman 2006).
Pollination
Use by animals
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Birkhead, R. D., C. Guyer, et al. (2005). "Patterns of folivory and seed ingestion by gopher tortoises (Gopherus polyphemus) in a southeastern pine savanna." American Midland Naturalist 154: 143-151.
Brewer, J. S. and S. P. Cralle (2003). "Phosphorus addition reduces invasion of a longleaf pine savanna (southeastern USA) by a non-indigenous grass (Imperata cylindrica)." Plant Ecology 167: 237-245.
Coffey, K. L. and L. K. Kirkman (2006). "Seed germination strategies of species with restoration potential in a fire-maintained pine savanna." Natural Areas Journal 26: 289-299.
Heuberger, K. A. and F. E. Putz (2003). "Fire in the suburbs: ecological impacts of prescribed fire in small remnants of longleaf pine (Pinus palustris) sandhill." Restoration Ecology 11: 72-81.
Kirkman, L. K., K. L. Coffey, et al. (2004). "Ground cover recovery patterns and life-history traits: implications for restoration obstacles and opportunities in a species-rich savanna." Journal of Ecology 92: 409-421.