Dichanthelium dichotomum
| Dichanthelium dichotomum | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida – Monocotyledons |
| Order: | Cyperales |
| Family: | Poaceae ⁄ Gramineae |
| Genus: | Dichanthelium |
| Species: | D. dichotomum |
| Binomial name | |
| Dichanthelium dichotomum (L.) Gould | |
| |
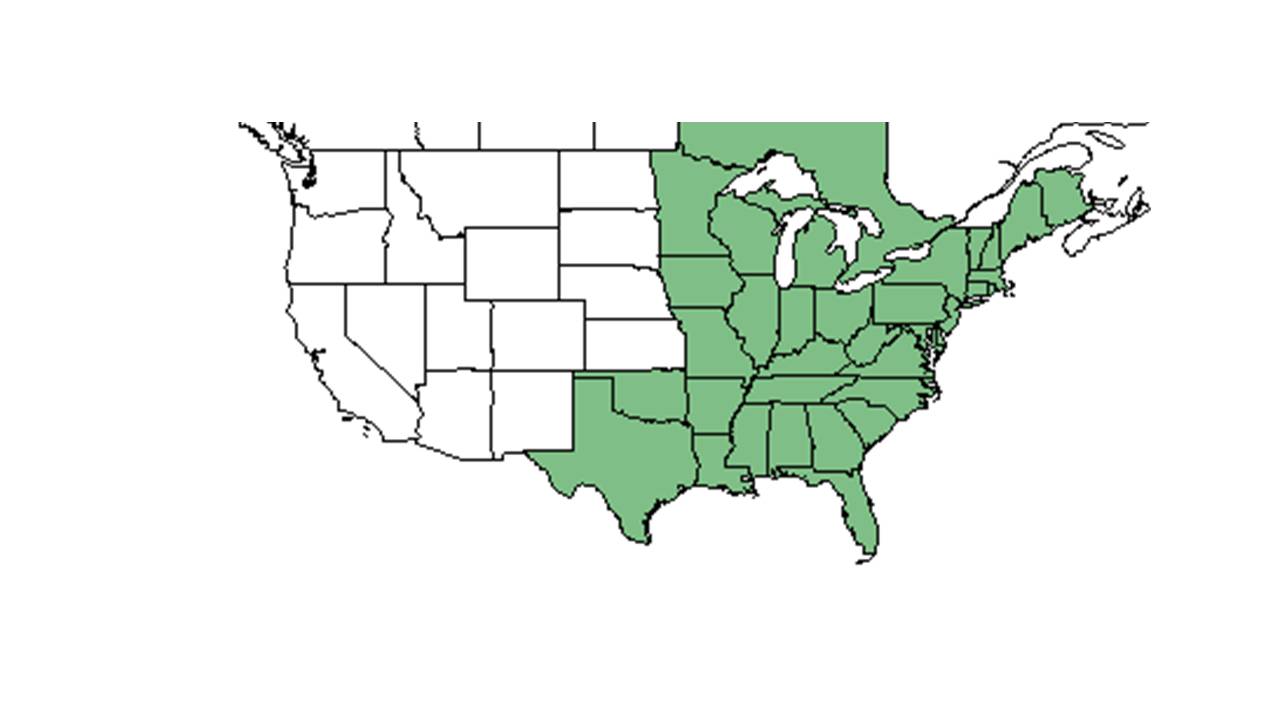
| Natural range of Dichanthelium dichotomum from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Description
Common Name: cypress panicgrass
Synonym Name: Panicum dichotomum L.
Dichanthelium dichotomum is a perennial graminoid. It tends to grow cespitose and despitose, in sprawling, loosely tangled mats (FSU Herbarium). It is a single-stemmed grass (FSU Herbarium).
Distribution
Ecology
D. dichotomum was among the species that responded positively to reduction of woody vegetation using triclopyr herbicide[1].
Habitat
It can live in wet areas[2]. Dichanthelium dichotomum var. dichotomum can be found in disturbed sites[3].Dichanthelium dichotomum var. ensifolium can live in wet pine savannas[2]. It can also be found in longleaf pine communities[4], loblolly pine communities[1], and flatwoods communities [5].
Phenology
Seed dispersal
Dichanthelium dichotomum was common in the seed bank of a Florida flatwoods community[5] Dichanthelium dichotomum var. nitidum was found in the seed bank of both disturbed and undisturbed sites[3]
Seed bank and germination
From observing the results of Taft's prescribed burns, fire seems to be required for germination[6].
Fire ecology
It is fire-tolerant[2] Following an early, moderate-intensity dormant-season burn (November) in a dry sandstone barrens, D. dichotomum increased rapidly, probably as a result of the widespread stimulation of the seed bank. It was still observed on site six years after the burn[6].
Pollination
Use by animals
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014.
Collectors: Sidney McDaniel, Loran C. Anderson, Travis MacClendon, Karen MacClendon, John B. Nelson, Frank W. Gould, R. K. Godfrey, Bayard Long, W. T. Batson Jr., Robert F. Thorne, Robert Kral, Delzie Demaree, H. A. Wahl, Duane Isely, S. L. Welsh, Dwight Isely, D. Windler, W. Gill, Harry E. Ahles, J. A. Duke, Brenda Herring, Walter Judd, Steve L. Orzell, E. L. Bridges, D. Kennemore, William P. Adams, R. A. Davidson, H. Kurz, Cecil R. Slaughter, Marc Minno, Bian Tan, R. J. Eaton, George R. Cooley, O. Lakela, Ann F. Johnson, Wilson Baker, R. A. Norris, K. Craddock Burks, C. J. Hansen, C. M. Morton, A. E. Radford, H. L. Blomquist, S. F. Blake, H. R. Reed, H. K. Svenson, F. H. Sargent, Randy Haynes, Annie Schmidt, G. R. Knight, and W. W. Ashe.
States and Counties: Arkansas: Cleburne. Alabama: Chilton, Lee, and Mobile. Florida: Alachua, Baker, Brevard, Calhoun, Clay, Collier, Columbia, Flagler, Franklin, Gadsden, Holmes, Jackson, Jefferson, Lee, Leon, Levy, Liberty, Martin, Monroe, Nassau, Okaloosa, Osceola, Putnam, Taylor, Volusia, and Wakulla. Georgia: Baker, Chatnam, Clinch, DeKalb, Echols, Grady, McIntosh, and Thomas. Louisiana: Ouchita. Maryland: Baltimore, and Prince Georges. Mississippi: Pearl River, Stone, and Webster. New Jersey: Atlantic and Cape May. North Carolina: Avery, Beaufort, Carteret, Clay, Granville, Onslow, Pender, and Wake. Pennsylvania: Lycoming and Monroe. South Carolina: Edgefield, Jasper, Lee, and Richland. Tennessee: Blount, Maury, and Putnam. Texas: Van Zandt. Virginia: Giles, Patrick, Roanoke, and Smyth.
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Miller, J. H., R. S. Boyd, et al. (1999). "Floristic diversity, stand structure, and composition 11 years after herbicide site preparation." Canadian Journal of Forest Research 29: 1073-1083.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Brewer, J. S., D. J. Baker, et al. (2011). "Carnivory in plants as a beneficial trait in wetlands." Aquatic Botany 94: 62-70.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Cohen, S., R. Braham, et al. (2004). "Seed bank viability in disturbed longleaf pine sites." Restoration Ecology 12: 503-515.
- ↑ Glitzenstein, J. S., D. R. Streng, et al. (2003). "Fire frequency effects on longleaf pine (Pinus palustris, P.Miller) vegetation in South Carolina and northeast Florida, USA." Natural Areas Journal 23: 22-37 Cohen, S., R. Braham, et al. (2004). "Seed bank viability in disturbed longleaf pine sites." Restoration Ecology 12: 503-515.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Kalmbacher, R., N. Cellinese, et al. (2005). "Seeds obtained by vacuuming the soil surface after fire compared with soil seedbank in a flatwoods plant community." Native Plants Journal 6: 233-241.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Taft, J. B. (2003). "Fire effects on community structure, composition, and diversity in a dry sandstone barrens." Journal of the Torrey Botanical Society 130: 170-192.