Difference between revisions of "Juncus marginatus"
(→Ecology) |
HaleighJoM (talk | contribs) (→Ecology) |
||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
<!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
<!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | <!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| − | <!--===Pollination and | + | <!--===Pollination===--> |
| − | <!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | + | <!--===Herbivory and toxicology===--> |
| + | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | ||
==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== | ||
Latest revision as of 17:11, 14 July 2022
Common names: grassleaf rush; grass-leaved rush; marginal rush[1]
| Juncus marginatus | |
|---|---|

| |
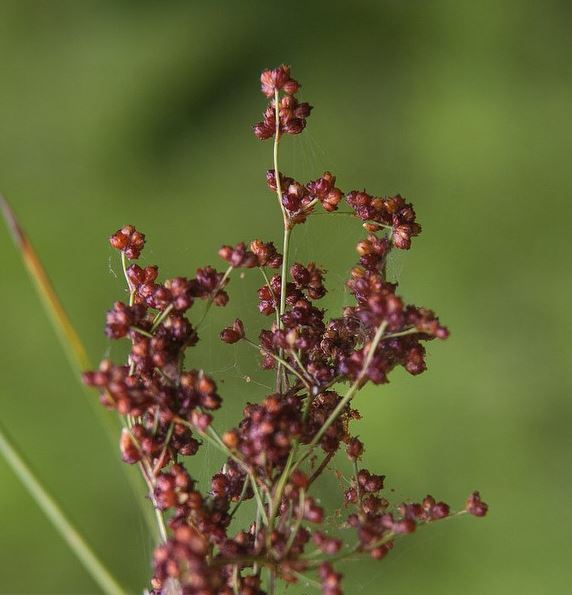
| Photo by John B | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Juncales |
| Family: | Juncaceae |
| Genus: | Juncus |
| Species: | J. marginatus |
| Binomial name | |
| Juncus marginatuss Rostk. | |
| |
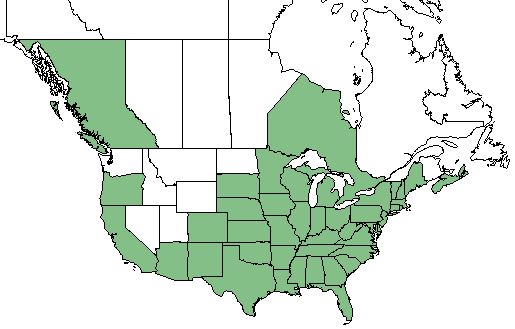
| Natural range of Juncus marginatus from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: J. setosus (Coville) Small.[1]
Varieties: none.[1]
Description
J. marginatus is a perennial graminoid in the Juncaceae family. It is native to North America [2]. This species is very similar to the many other species of rush "stems clump-forming, somewhat flattened, to 4 ft. tall; leaf blades flat, to 1/4 in. wide, pointed tips; inflorescences at stem tip, from very compact to much-branched and open, having several-200 clusters of flowers and fruits; flowers dark brown, stiff; seed capsules to 1/8 in. long, elliptic with rounded 3-lobed tops, reddish-brown, shiny; seeds irregular, amber" [3].
Distribution
This range of this species extends north to Novia Scotia, Ontario, Michigan, and Nebraska, south to peninsular Florida, and west to Texas. There are also disjunct populations in California and South America.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
This species lives in "wet meadows, bogs, generally throughout in wet, sandy or peaty soil" [4]. Specimens have been collected from open pine-oak forests, moist loamy sands, pondshores, cypress gum ponds, cleared pine flatwood savannas, planted slash pine flatwoods, streambanks, and basin swamps. [5]
Phenology
J. marginatus flowers June through September [4].
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ USDA Plants Database URL: https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=JUMA4
- ↑ UF IFAS Plant Directory URL: https://plants.ifas.ufl.edu/plant-directory/juncus-marginatus/
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, R.K. Godfrey, R.A. Norris, R.F. Doren, R. Komarek, Chris Buddenhagen, Austin Mast, Herbert Monoson, P.L. Redfearn, R. Kral, R. Kral, Jean Wooten, Richard Carter, Sharon Carter, M. Darst, A. Stiles. States and counties: Florida (Gadsden, Liberty, Wakulla, Hamilton, Leon, Franklin, Jackson, Holmes, Gulf, Charlotte, Washington, Okaloosa) Georgia (Brantley, Grady, Clinch, Atkinson)