Difference between revisions of "Symphyotrichum concolor"
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | In the Coastal Plain region, ''S. concolor'' can be found at the edges of limestone glades, longleaf pine-wiregrass flatwoods, pine-oak-hickory woods, scrub oak sand ridges, edges of brackish marshes, annually burned pinelands, former longleaf pine savannas, longleaf pine-scrub oaks, sandhills, and along roadways.<ref name=fsu> Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Wilson Baker, Ann F. Johnson, R. A. Norris, Andre F. Clewell, Robert K. Godfrey, R. Komarek. States and Counties: Florida: Bay, Calhoun, Jackson, Jefferson, Liberty, Wakulla, Walton, Washington. Georgia: Thomas. South Carolina: Lee. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.</ref> It is restricted to native groundcover and can be found in upland pines of South Georgia.<ref name=ost> Ostertag, T.E., and K.M. Robertson. 2007. A comparison of native versus old-field vegetation in upland pinelands managed with frequent fire, South Georgia, USA. Pages 109–120 in R.E. Masters and K.E.M. Galley (eds.). Proceedings of the 23rd Tall Timbers Fire Ecology Conference: Fire in Grassland and Shrubland Ecosystems.</ref> | + | In the Coastal Plain region, ''S. concolor'' can be found at the edges of limestone glades, longleaf pine-wiregrass flatwoods, pine-oak-hickory woods, scrub oak sand ridges, edges of brackish marshes, annually burned pinelands, former longleaf pine savannas, longleaf pine-scrub oaks, sandhills, and along roadways.<ref name=fsu> Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Wilson Baker, Ann F. Johnson, R. A. Norris, Andre F. Clewell, Robert K. Godfrey, R. Komarek. States and Counties: Florida: Bay, Calhoun, Jackson, Jefferson, Liberty, Wakulla, Walton, Washington. Georgia: Thomas. South Carolina: Lee. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.</ref> It is restricted to native groundcover and can be found in upland pines of South Georgia.<ref name=ost> Ostertag, T.E., and K.M. Robertson. 2007. A comparison of native versus old-field vegetation in upland pinelands managed with frequent fire, South Georgia, USA. Pages 109–120 in R.E. Masters and K.E.M. Galley (eds.). Proceedings of the 23rd Tall Timbers Fire Ecology Conference: Fire in Grassland and Shrubland Ecosystems.</ref> ''Symphyotrichum concolor'' is frequent and abundant in the North Florida Subxeric Sandhills and Clayhill Longleaf Woodlands community types as described in Carr et al. (2010).<ref>Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.</ref> A study exploring longleaf pine patch dynamics found ''S. concolor'' to be most strongly represented within longleaf pine gaps and under patches of longleaf that are up to 50 years of age.<ref>Mugnani et al. (2019). “Longleaf Pine Patch Dynamics Influence Ground-Layer Vegetation in Old-Growth Pine Savanna”.</ref> |
''S. concolor'' became absent or reduced its occurrence in response to agriculture in South Carolina longleaf woodlands<ref name=brudvig>Brudvig, L. A. and E. I. Damschen 2011. Land-use history, historical connectivity, and savannas land management interact to determine longleaf pine woodland understory richness and composition. Ecography 34: 257-266.</ref> and southwest Georgia savannas and pinelands.<ref name=ost/><ref name=kirkman>Kirkman, L.K., K.L. Coffey, R.J. Mitchell, and E.B. Moser. Ground Cover Recovery Patterns and Life-History Traits: Implications for Restoration Obstacles and Opportunities in a Species-Rich Savanna. (2004). Journal of Ecology 92(3):409-421.</ref> This species became absent in response to military training in west Georgia pinelands.<ref name=dale>Dale, V.H., S.C. Beyeler, and B. Jackson. (2002). Understory vegetation indicators of anthropogenic disturbance in longleaf pine forests at Fort Benning, Georgia, USA. Ecological Indicators 1(3):155-170.</ref> | ''S. concolor'' became absent or reduced its occurrence in response to agriculture in South Carolina longleaf woodlands<ref name=brudvig>Brudvig, L. A. and E. I. Damschen 2011. Land-use history, historical connectivity, and savannas land management interact to determine longleaf pine woodland understory richness and composition. Ecography 34: 257-266.</ref> and southwest Georgia savannas and pinelands.<ref name=ost/><ref name=kirkman>Kirkman, L.K., K.L. Coffey, R.J. Mitchell, and E.B. Moser. Ground Cover Recovery Patterns and Life-History Traits: Implications for Restoration Obstacles and Opportunities in a Species-Rich Savanna. (2004). Journal of Ecology 92(3):409-421.</ref> This species became absent in response to military training in west Georgia pinelands.<ref name=dale>Dale, V.H., S.C. Beyeler, and B. Jackson. (2002). Understory vegetation indicators of anthropogenic disturbance in longleaf pine forests at Fort Benning, Georgia, USA. Ecological Indicators 1(3):155-170.</ref> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Associated species include ''Schoenus nigricans, Muhlenbergia capillaris, Quercus laevis, Q. incana, Q. minima, Q. margaretta, Aristida stricta, Polygonella gracilis, Smilax auriculata, Licania michauxii, Eupatorium compositifolium, Pinus taeda, Aster adnatus, Ilex vomitoria, Pteridium aquilinum, Polygonella gracilis, Solidago puberula, Liatris gracilis, Chrysopsis lanuginosa, Vaccinium darrow, Warea sessilifolia, Pityopsis graminifolia var. tenuifolia, Liatris chapmanii, Aster linarrifolius, Andropogon, Schizachyrium, Serenoa repens, Smilax auriculata, Solidago odora, Helianthus radula, Tridens ambiguous, Ilex opaca, Baptisia lanceolata, Lespedeza hirta, Petalostemum carolinianum, Agaritina aromatica, Pityopsis aspera var. adenolepsi'', and ''Vaccinium lanuginosa''.<ref name=fsu/> | Associated species include ''Schoenus nigricans, Muhlenbergia capillaris, Quercus laevis, Q. incana, Q. minima, Q. margaretta, Aristida stricta, Polygonella gracilis, Smilax auriculata, Licania michauxii, Eupatorium compositifolium, Pinus taeda, Aster adnatus, Ilex vomitoria, Pteridium aquilinum, Polygonella gracilis, Solidago puberula, Liatris gracilis, Chrysopsis lanuginosa, Vaccinium darrow, Warea sessilifolia, Pityopsis graminifolia var. tenuifolia, Liatris chapmanii, Aster linarrifolius, Andropogon, Schizachyrium, Serenoa repens, Smilax auriculata, Solidago odora, Helianthus radula, Tridens ambiguous, Ilex opaca, Baptisia lanceolata, Lespedeza hirta, Petalostemum carolinianum, Agaritina aromatica, Pityopsis aspera var. adenolepsi'', and ''Vaccinium lanuginosa''.<ref name=fsu/> | ||
Revision as of 19:13, 16 August 2021
| Symphyotrichum concolor | |
|---|---|
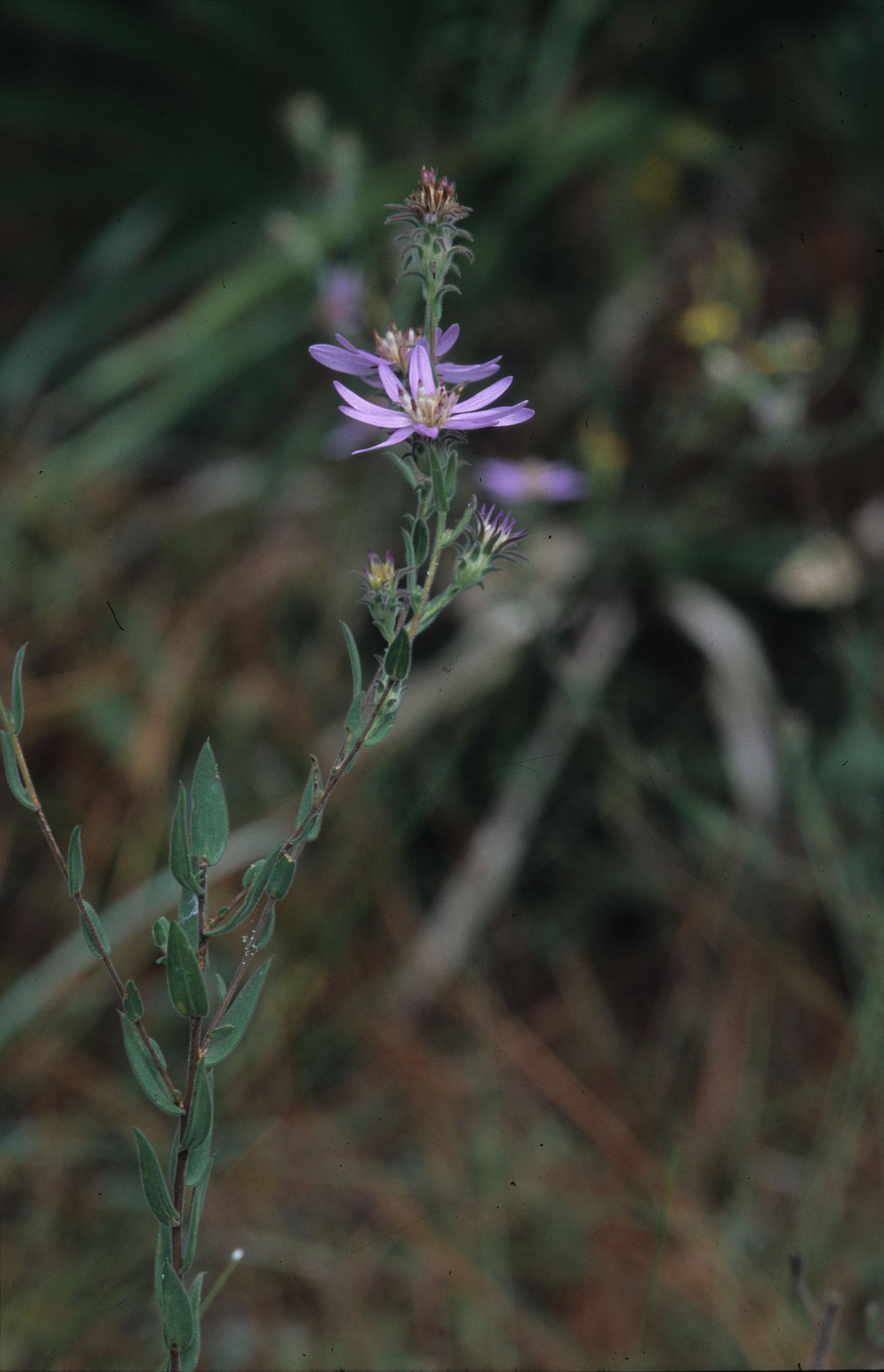

| |
| Photo taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteracae/Compositae |
| Genus: | Symphyotrichum |
| Species: | S. concolor |
| Binomial name | |
| Symphyotrichum concolor (L.) G.L. Nesom | |
| |
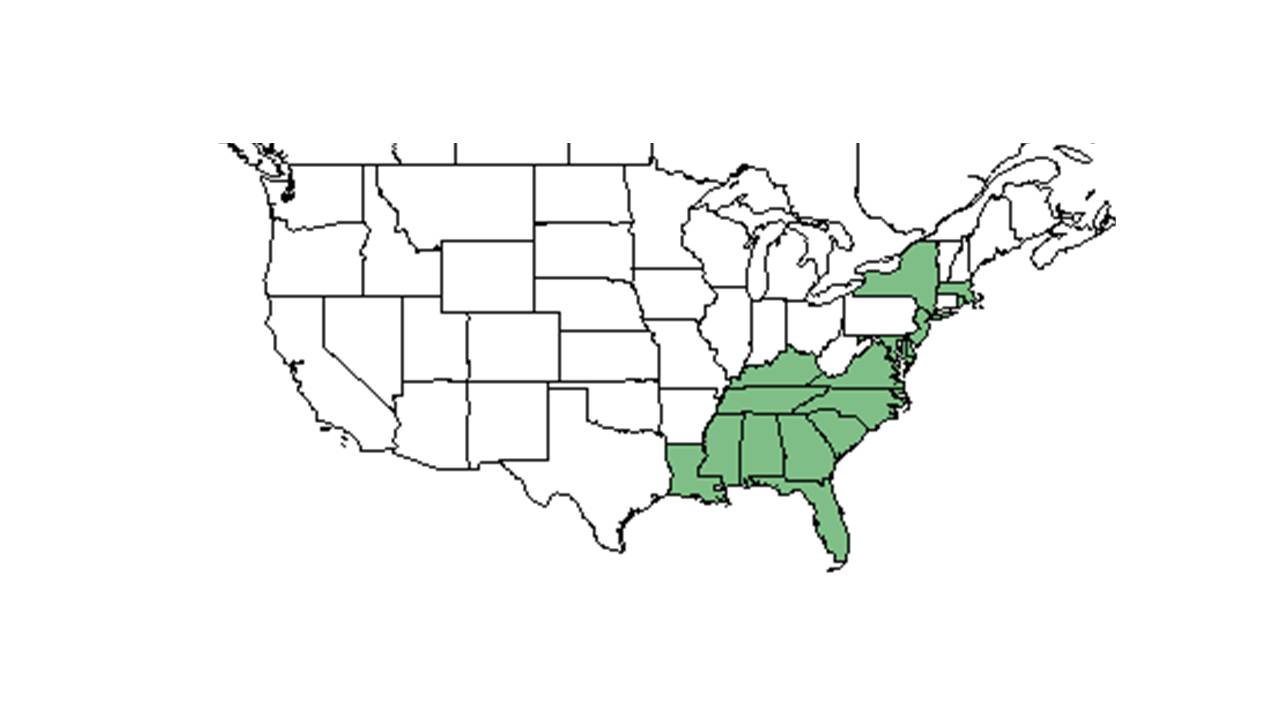
| Natural range of Symphyotrichum concolor from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Eastern silver aster, Eastern silvery aster
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Aster concolor Linnaeus; Virgulus concolor (Linnaeus) Reveal & Keener.[1]
Description
A description of Symphyotrichum concolor is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain region, S. concolor can be found at the edges of limestone glades, longleaf pine-wiregrass flatwoods, pine-oak-hickory woods, scrub oak sand ridges, edges of brackish marshes, annually burned pinelands, former longleaf pine savannas, longleaf pine-scrub oaks, sandhills, and along roadways.[2] It is restricted to native groundcover and can be found in upland pines of South Georgia.[3] Symphyotrichum concolor is frequent and abundant in the North Florida Subxeric Sandhills and Clayhill Longleaf Woodlands community types as described in Carr et al. (2010).[4] A study exploring longleaf pine patch dynamics found S. concolor to be most strongly represented within longleaf pine gaps and under patches of longleaf that are up to 50 years of age.[5]
S. concolor became absent or reduced its occurrence in response to agriculture in South Carolina longleaf woodlands[6] and southwest Georgia savannas and pinelands.[3][7] This species became absent in response to military training in west Georgia pinelands.[8]
Associated species include Schoenus nigricans, Muhlenbergia capillaris, Quercus laevis, Q. incana, Q. minima, Q. margaretta, Aristida stricta, Polygonella gracilis, Smilax auriculata, Licania michauxii, Eupatorium compositifolium, Pinus taeda, Aster adnatus, Ilex vomitoria, Pteridium aquilinum, Polygonella gracilis, Solidago puberula, Liatris gracilis, Chrysopsis lanuginosa, Vaccinium darrow, Warea sessilifolia, Pityopsis graminifolia var. tenuifolia, Liatris chapmanii, Aster linarrifolius, Andropogon, Schizachyrium, Serenoa repens, Smilax auriculata, Solidago odora, Helianthus radula, Tridens ambiguous, Ilex opaca, Baptisia lanceolata, Lespedeza hirta, Petalostemum carolinianum, Agaritina aromatica, Pityopsis aspera var. adenolepsi, and Vaccinium lanuginosa.[2]
Phenology
S. concolor has been observed to flower in January, February, May, October, and November and fruit in October and November.[2][9] Michelle Smith observed this species flowering in April at Quailridge Plantation, in Georgia.
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by wind.[10]
Fire ecology
Populations of Symphyotrichum concolor have been known to persist through repeated annual burns.[11][12]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Symphyotrichum concolor should avoid soil disturbance by agriculture and military training to conserve its presence in pine communities.[3][6][7][8]
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draf of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Wilson Baker, Ann F. Johnson, R. A. Norris, Andre F. Clewell, Robert K. Godfrey, R. Komarek. States and Counties: Florida: Bay, Calhoun, Jackson, Jefferson, Liberty, Wakulla, Walton, Washington. Georgia: Thomas. South Carolina: Lee. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Ostertag, T.E., and K.M. Robertson. 2007. A comparison of native versus old-field vegetation in upland pinelands managed with frequent fire, South Georgia, USA. Pages 109–120 in R.E. Masters and K.E.M. Galley (eds.). Proceedings of the 23rd Tall Timbers Fire Ecology Conference: Fire in Grassland and Shrubland Ecosystems.
- ↑ Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.
- ↑ Mugnani et al. (2019). “Longleaf Pine Patch Dynamics Influence Ground-Layer Vegetation in Old-Growth Pine Savanna”.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Brudvig, L. A. and E. I. Damschen 2011. Land-use history, historical connectivity, and savannas land management interact to determine longleaf pine woodland understory richness and composition. Ecography 34: 257-266.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Kirkman, L.K., K.L. Coffey, R.J. Mitchell, and E.B. Moser. Ground Cover Recovery Patterns and Life-History Traits: Implications for Restoration Obstacles and Opportunities in a Species-Rich Savanna. (2004). Journal of Ecology 92(3):409-421.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Dale, V.H., S.C. Beyeler, and B. Jackson. (2002). Understory vegetation indicators of anthropogenic disturbance in longleaf pine forests at Fort Benning, Georgia, USA. Ecological Indicators 1(3):155-170.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 14 DEC 2016
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.
- ↑ Robertson, K.M. Unpublished data collected from Pebble Hill Fire Plots, Pebble Hill Plantation, Thomasville, Georgia.
- ↑ Platt, W.J., R. Carter, G. Nelson, W. Baker, S. Hermann, J. Kane, L. Anderson, M. Smith, K. Robertson. 2021. Unpublished species list of Wade Tract old-growth longleaf pine savanna, Thomasville, Georgia.