Difference between revisions of "Silphium asteriscus"
(→Ecology) |
|||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | In the Coastal Plain in Florida and Georgia, ''S. asteriscus'' can be found in red oak/mockernut woods, sandy hillslopes, mixed hardwoods, upland pine forests, longleaf pine forests, annually burned pinelands, deciduous woods, upland oak-pine woodlands, pine flatwoods, calcareous outcrops, and longleaf pine-deciduous live oak flats.<ref name="FSU Herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Andre F. Clewell, Steve L. Orzell, Robert K. Godfrey, R. A. Norris, R. Komarek, Loran C. Anderson, Wilbur H Duncan, George R. Cooley, Richard J. Eaton, James D. Ray, Jr., R L Lazor, Gary R. Knight, C. Jackson, K. Craddock Burks, Richard S. Mitchell, A. H. Curtiss, R. Kral, Paul L. Redfearn, Jr. States and Counties: Florida: Bay, Dixie, Franklin, Gadsden, Jackson, Jefferson, Leon, Liberty, Levy, Okaloosa, Taylor, Wakulla. Georgia: Brooks, Grady, Hall, Thomas. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.</ref> In disturbed habitats it can be found in cutover upland longleaf pine savannas, along highways, along roads, and sandy fallow fields. Soil types include loamy sand, sandy loam and clay.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> It has been observed to grow with ''Polymnia.''<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> Associated species include shortleaf pine, post oak, red oak, mockernut hickory, longleaf pine, live oak, loblolly pine, and a ''Polymnia'' species.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> | + | In the Coastal Plain in Florida and Georgia, ''S. asteriscus'' can be found in red oak/mockernut woods, sandy hillslopes, mixed hardwoods, upland pine forests, longleaf pine forests, annually burned pinelands, deciduous woods, upland oak-pine woodlands, pine flatwoods, calcareous outcrops, and longleaf pine-deciduous live oak flats.<ref name="FSU Herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Andre F. Clewell, Steve L. Orzell, Robert K. Godfrey, R. A. Norris, R. Komarek, Loran C. Anderson, Wilbur H Duncan, George R. Cooley, Richard J. Eaton, James D. Ray, Jr., R L Lazor, Gary R. Knight, C. Jackson, K. Craddock Burks, Richard S. Mitchell, A. H. Curtiss, R. Kral, Paul L. Redfearn, Jr. States and Counties: Florida: Bay, Dixie, Franklin, Gadsden, Jackson, Jefferson, Leon, Liberty, Levy, Okaloosa, Taylor, Wakulla. Georgia: Brooks, Grady, Hall, Thomas. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.</ref> In disturbed habitats it can be found in cutover upland longleaf pine savannas, along highways, along roads, and sandy fallow fields. Soil types include loamy sand, sandy loam and clay.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> It has been observed to grow with ''Polymnia.''<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> |
| + | |||
| + | Associated species include shortleaf pine, post oak, red oak, mockernut hickory, longleaf pine, live oak, loblolly pine, and a ''Polymnia'' species.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> | ||
Outside of the Coastal Plain, it can be found in the Cross Timbers in wooded-open ecotones of oaks, ashes, elms, and hickories<ref name="Gee 1994">Gee, K. L. (1994). White-tailed deer : their foods and management in the cross timbers. Ardmore, OK, Samuel Roberts Noble Foundation.</ref> and the Midland Plateau Central Highlands where the surface soil texture is sandy clay loam and clay subsoil.<ref name="Miller, Boyd, Edwards 1999">Miller, J. H., R. S. Boyd, et al. (1999). "Floristic diversity, stand structure, and composition 11 years after herbicide site preparation." Canadian Journal of Forest Research 29: 1073-1083.</ref> | Outside of the Coastal Plain, it can be found in the Cross Timbers in wooded-open ecotones of oaks, ashes, elms, and hickories<ref name="Gee 1994">Gee, K. L. (1994). White-tailed deer : their foods and management in the cross timbers. Ardmore, OK, Samuel Roberts Noble Foundation.</ref> and the Midland Plateau Central Highlands where the surface soil texture is sandy clay loam and clay subsoil.<ref name="Miller, Boyd, Edwards 1999">Miller, J. H., R. S. Boyd, et al. (1999). "Floristic diversity, stand structure, and composition 11 years after herbicide site preparation." Canadian Journal of Forest Research 29: 1073-1083.</ref> | ||
Revision as of 19:23, 21 June 2021
| Silphium asteriscus | |
|---|---|
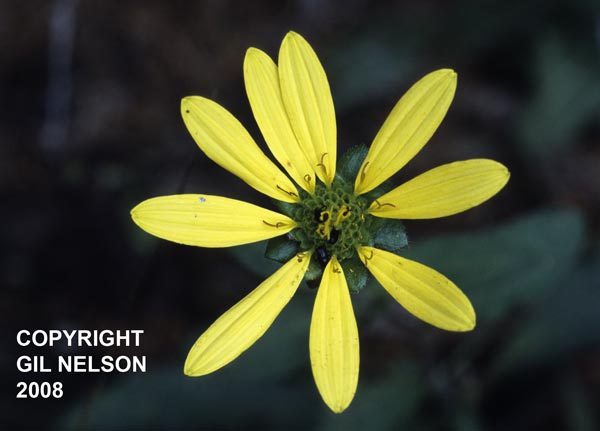

| |
| Photo taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae ⁄ Compositae |
| Genus: | Silphium |
| Species: | S. asteriscus |
| Binomial name | |
| Silphium asteriscus L. | |
| |
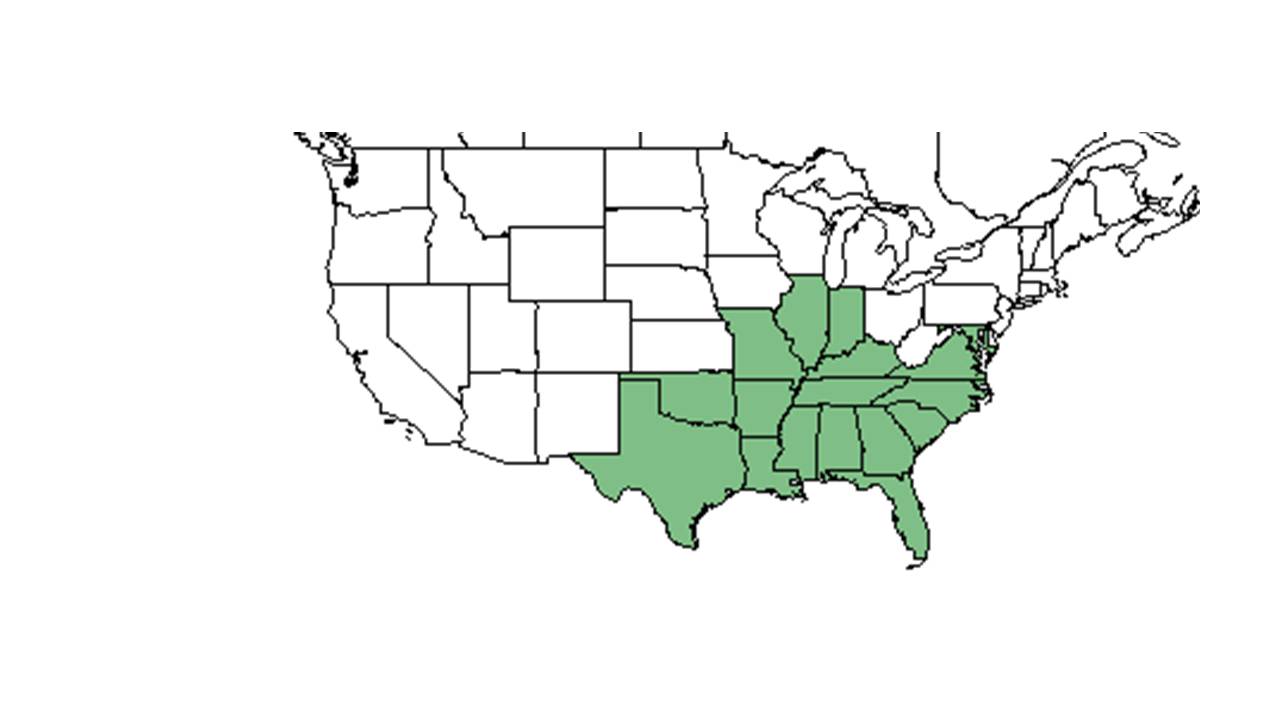
| Natural range of Silphium asteriscus from USDA NRCS NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Starry rosinweed
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: S. scaberrimum Elliott; S. gatesii C. Mohr
Variety: Silphium asteriscus Linnaeus var. dentatum (Elliott) Chapman; Silphium asteriscu Linnaeus var. latifolium (A. Gray) J.A. Clevinger; Silphium asteriscus Linnaeus var. simpsonii (Greene) J.A. Clevinger; Silphium asteriscus Linnaeus var. trifoliatum (Linnaeus) J.A. Clevinger; Silphium asteriscus Linnaeus var. asteriscus; S. dentatum var. gatesii (Mohr) H.E. Ahles; S. asteriscus var. scabrum Nuttall
Description
A description of Silphium asteriscus is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain in Florida and Georgia, S. asteriscus can be found in red oak/mockernut woods, sandy hillslopes, mixed hardwoods, upland pine forests, longleaf pine forests, annually burned pinelands, deciduous woods, upland oak-pine woodlands, pine flatwoods, calcareous outcrops, and longleaf pine-deciduous live oak flats.[1] In disturbed habitats it can be found in cutover upland longleaf pine savannas, along highways, along roads, and sandy fallow fields. Soil types include loamy sand, sandy loam and clay.[1] It has been observed to grow with Polymnia.[1]
Associated species include shortleaf pine, post oak, red oak, mockernut hickory, longleaf pine, live oak, loblolly pine, and a Polymnia species.[1]
Outside of the Coastal Plain, it can be found in the Cross Timbers in wooded-open ecotones of oaks, ashes, elms, and hickories[2] and the Midland Plateau Central Highlands where the surface soil texture is sandy clay loam and clay subsoil.[3]
Phenology
S. asteriscus is a perennial species; stems have prickly hairs and can grow up to five feet high. The lower leaves are alternate and the upper are opposite and sessil. The flowers are yellow and have nine florets in the ray.[4] Kevin Robertson has observed this species flower within three months of burning. KMR It has been observed flowering in February, and from May to September.[5]
Fire ecology
It resprouts and flowers within two months of burning in the spring (Robertson observation).
Pollination and use by animals
In the Cross Timbers ecosystem of Texas, it has been found in white-tailed deer diets.[2]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Andre F. Clewell, Steve L. Orzell, Robert K. Godfrey, R. A. Norris, R. Komarek, Loran C. Anderson, Wilbur H Duncan, George R. Cooley, Richard J. Eaton, James D. Ray, Jr., R L Lazor, Gary R. Knight, C. Jackson, K. Craddock Burks, Richard S. Mitchell, A. H. Curtiss, R. Kral, Paul L. Redfearn, Jr. States and Counties: Florida: Bay, Dixie, Franklin, Gadsden, Jackson, Jefferson, Leon, Liberty, Levy, Okaloosa, Taylor, Wakulla. Georgia: Brooks, Grady, Hall, Thomas. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Gee, K. L. (1994). White-tailed deer : their foods and management in the cross timbers. Ardmore, OK, Samuel Roberts Noble Foundation.
- ↑ Miller, J. H., R. S. Boyd, et al. (1999). "Floristic diversity, stand structure, and composition 11 years after herbicide site preparation." Canadian Journal of Forest Research 29: 1073-1083.
- ↑ Strong, A. B. (1848). The American flora, or history of plants and wildflowers: containing a systematic and general decription, natural history, chemical and medical properties of over six thousand plants, accompanied with a circumstantial detail of the medicinal effects, and of the diseases in which they have been most successfully employed. New York City, NY, Green & Spencer.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 13 DEC 2016