Difference between revisions of "Ampelopsis arborea"
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
In the Coastal Plain in Florida, ''A. arborea'' can be found in river floodplains, wax myrtle thickets, hedgerows, coastal scrub savannas, and calcareous banks of drainage ditches.<ref name="FSU">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: October 2015. Collectors: R.K. Godfrey, R.F. Doren, R. Komarek, Loran Anderson. States and Counties: Florida: Gadsden, Leon, Wakulla, Franklin. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.</ref> Associated species include ''Vitis rotundifolia, Juniperus virginiana, Ilex vomitoria, Ilex cassine, Bumelia lanuginosa'', and wax myrtle.<ref name=FSU></ref> | In the Coastal Plain in Florida, ''A. arborea'' can be found in river floodplains, wax myrtle thickets, hedgerows, coastal scrub savannas, and calcareous banks of drainage ditches.<ref name="FSU">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: October 2015. Collectors: R.K. Godfrey, R.F. Doren, R. Komarek, Loran Anderson. States and Counties: Florida: Gadsden, Leon, Wakulla, Franklin. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.</ref> Associated species include ''Vitis rotundifolia, Juniperus virginiana, Ilex vomitoria, Ilex cassine, Bumelia lanuginosa'', and wax myrtle.<ref name=FSU></ref> | ||
| − | ''A. arborea'' has shown regrowth in reestablished South Carolina longleaf pine savannah communities that were agriculturally disturbed | + | ''A. arborea'' has shown regrowth in reestablished South Carolina longleaf pine savannah communities that were agriculturally disturbed, making it an indicator species for post-agricultural woodlands.<ref>Brudvig, L.A., E Grman, C.W. Habeck, and J.A. Ledvina. (2013). Strong legacy of agricultural land use on soils and understory plant communities in longleaf pine woodlands. Forest Ecology and Management 310: 944-955.</ref> |
===Phenology===<!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology===<!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
Revision as of 13:08, 21 June 2021
| Ampelopsis arborea | |
|---|---|

| |
| John R. Gwaltney, Southeastern Flora.com | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Tracheophyta - Vascular plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Vitales |
| Family: | Vitaceae |
| Genus: | Ampelopsis |
| Species: | A. arborea |
| Binomial name | |
| Ampelopsis arborea (L.) Koehne | |
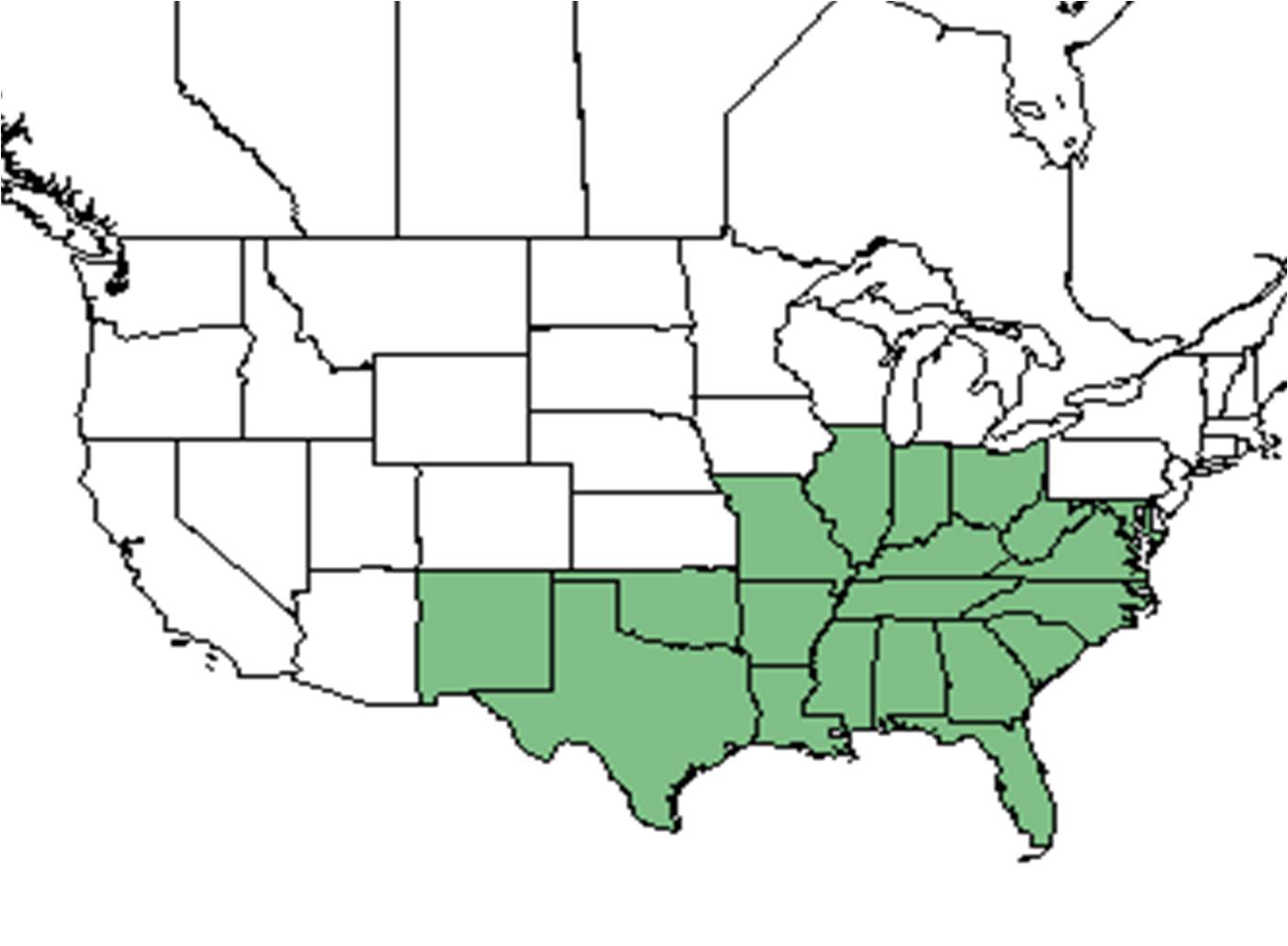
| |
| Natural range of Ampelopsis arborea from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Peppervine
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonym: Ampelopsis arborea (Linnaeus) Koehne
Description
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain in Florida, A. arborea can be found in river floodplains, wax myrtle thickets, hedgerows, coastal scrub savannas, and calcareous banks of drainage ditches.[1] Associated species include Vitis rotundifolia, Juniperus virginiana, Ilex vomitoria, Ilex cassine, Bumelia lanuginosa, and wax myrtle.[1] A. arborea has shown regrowth in reestablished South Carolina longleaf pine savannah communities that were agriculturally disturbed, making it an indicator species for post-agricultural woodlands.[2]
Phenology
Ampelopsis arborea has been observed to flower between June and July.[3]
Pollination and use by animals
Many insects from the order Hymenoptera were observed visiting flowers of Ampelopsis arborea at the Archbold Biological Station. These insects include members of the Leucospididae family Leucospis robertsoni, and L.slossonae, as well as Sericopompilus apicalis (family Pompilidae), and members of the Sphecidae family Cerceris flavofasciata floridensis, Isodontia auripes, I.exornata, Larra bicolor, Pseudoplisus smithii floridanus, Sphex ichneumoneus, and Tanyoprymnus moneduloides.[4] Additionally, Ampelopsis arborea has been observed to host members of the family Lygaeidae Lygaeus kalmii and Oncopeltus fasciatus.[5]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: October 2015. Collectors: R.K. Godfrey, R.F. Doren, R. Komarek, Loran Anderson. States and Counties: Florida: Gadsden, Leon, Wakulla, Franklin. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ Brudvig, L.A., E Grman, C.W. Habeck, and J.A. Ledvina. (2013). Strong legacy of agricultural land use on soils and understory plant communities in longleaf pine woodlands. Forest Ecology and Management 310: 944-955.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 7 DEC 2016
- ↑ Deyrup, M.A. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
- ↑ Discoverlife.org [1]