Difference between revisions of "Stylisma villosa"
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
<!--===Use by animals===--> <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | <!--===Use by animals===--> <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
<!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | ||
| − | ==Conservation and | + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== |
| − | == | + | |
| + | ==Cultural use== | ||
| + | |||
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
<gallery widths=180px> | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
Revision as of 12:42, 9 June 2021
| Stylisma villosa | |
|---|---|

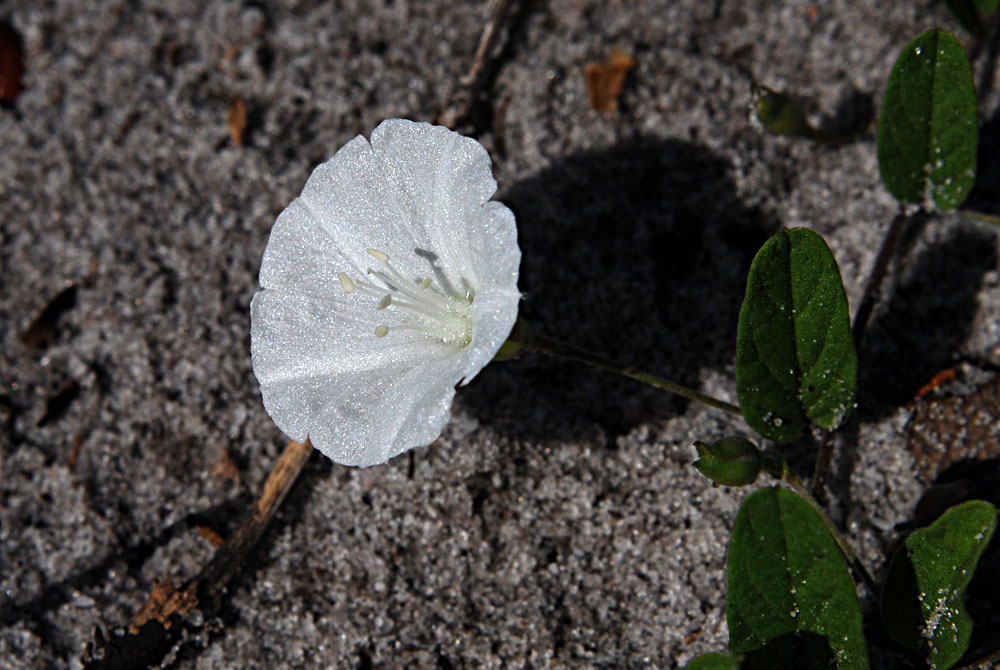
| |
| Photo by Wayne Matchett, SpaceCoastWildflowers.com | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Solanales |
| Family: | Convolvulaceae |
| Genus: | Stylisma |
| Species: | S. villosa |
| Binomial name | |
| Stylisma villosa (Nash) House | |
| |
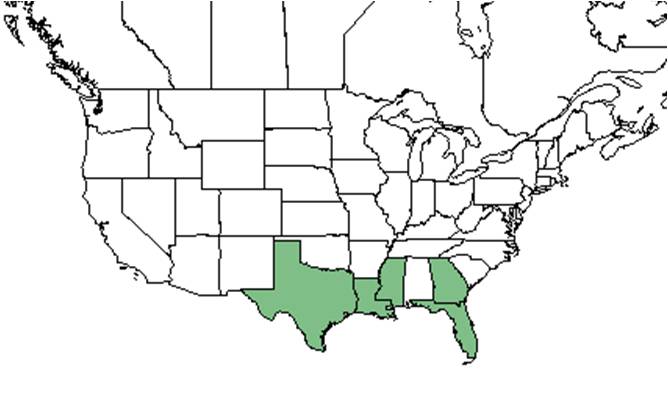
| Natural range of Stylisma villosa from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Hairy dawnflower
Contents
[hide]Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Bonamia villosa (Nash) K.A. Wilson; Breweria villosa Nash.[1]
Description
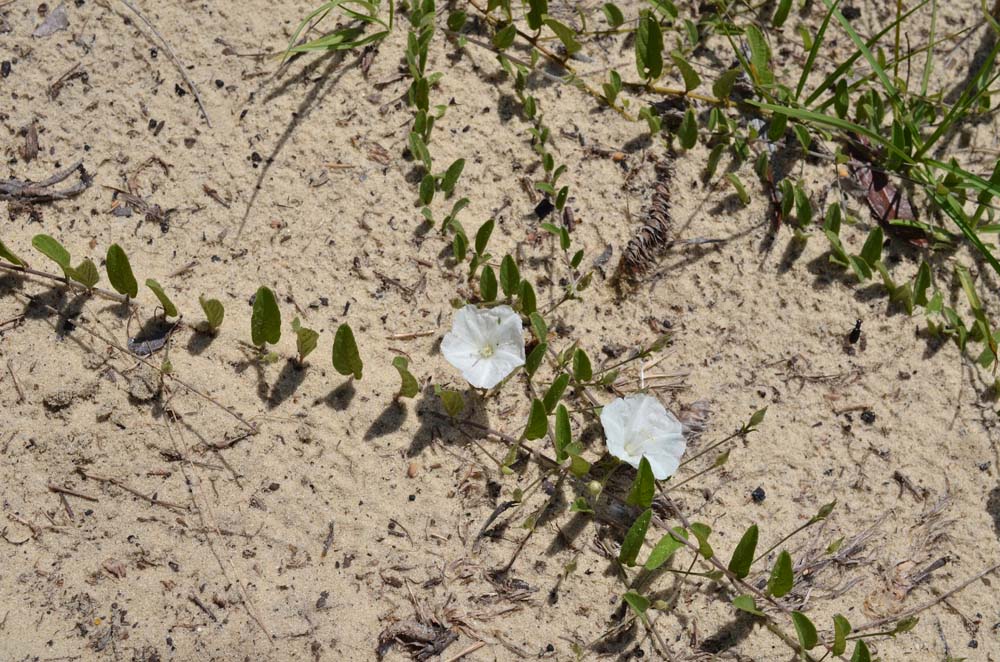
S. villosa is a perennial vine that has wiry, twining, thick, pubescent stems. The leaves are alternate, elliptical/oval, densely covered with white hairs and are held upright at a right angle to the ground, which reduces water loss from transpiration during the heat of the day. Inflorescence are solitary or in cymes of 3-7 flowers.[2][3] Flowers have white corollas and are about two centimeters broad.[4] This species is commonly mistaken for S. aquatica when not flowering.[3]
Distribution
Found in Florida, Georgia, Mississippi, Louisiana, and Texas. Listed as vulnerable in Texas.[5]
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain in Florida, S. villosa habitats include longleaf pine/scrub oak sand ridges, moist lake shores, and sandy longleaf pine-scrub hickory-oak woods. It can be found in disturbed scrubs, hammocks and along canals through a burned wetland slash pine savanna. Associated species include Quercus laevis, Q. incana, Q. virginiana, Q. myrtifolia, Q. chapmanii, Serenoa repens, and Ceanothus.[4]
Phenology
Flowers May through June and fruits June through November.[4]
Fire ecology
It has been observed growing in burned wetland slash pine savannas.[4]
Pollination
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of Stylisma villosa at Archbold Biological Station:[6]
Megachilidae: Dianthidium floridiense
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
Flowers of Stylisma villosa Photo by Wayne Matchett, SpaceCoastWildflowers.com
References and notes
- Jump up ↑ Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draf of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- Jump up ↑ [[1]]Native Florida Wildflowers. Accessed: March 16, 2016.
- ↑ Jump up to: 3.0 3.1 Hoffman, S.J.. Taxonomic and phylogenetic evaluation of Stylisma (Convolvulaceae). Thesis: University of North Carolina Wilmington
- ↑ Jump up to: 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: November 2015. Collectors: Edwin L. Bridges, Robert K. Godfrey, Robert Kral, O. Lakela, Sidney McDaniel, J.B. McFarlin, Steve L. Orzell, Allen G. Shuey. States and Counties: Florida: DeSoto, Highlands, Martin, Palm Beach, Orange, Polk. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- Jump up ↑ [[2]]NatureServe. Accessed: March 16, 2016
- Jump up ↑ Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
