Difference between revisions of "Phyllanthus tenellus"
Emmazeitler (talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
<!--===Use by animals===--> <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | <!--===Use by animals===--> <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
<!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | ||
| − | ==Conservation and | + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== |
| − | == | + | |
| + | ==Cultural use== | ||
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
<gallery widths=180px> | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
Revision as of 18:12, 8 June 2021
| Phyllanthus tenellus | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by Keith Bradley, Atlas of Florida Vascular Plants | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Euphorbiales |
| Family: | Euphorbiaceae |
| Genus: | Phyllanthus |
| Species: | P. tenellus |
| Binomial name | |
| Phyllanthus tenellus Roxb. | |
| |
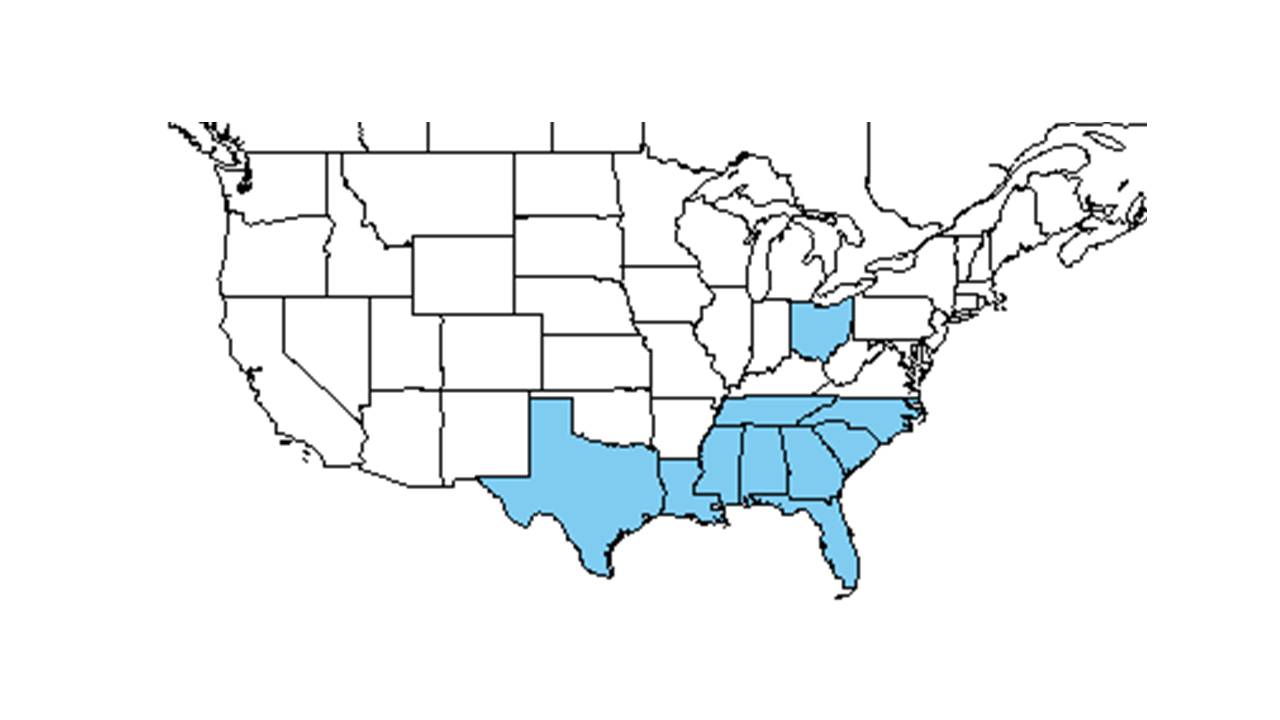
| Natural range of Phyllanthus tenellus from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Mascarene Island leaf-flower[1]
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: P. amarus.[1]
Varieties: none.[1]
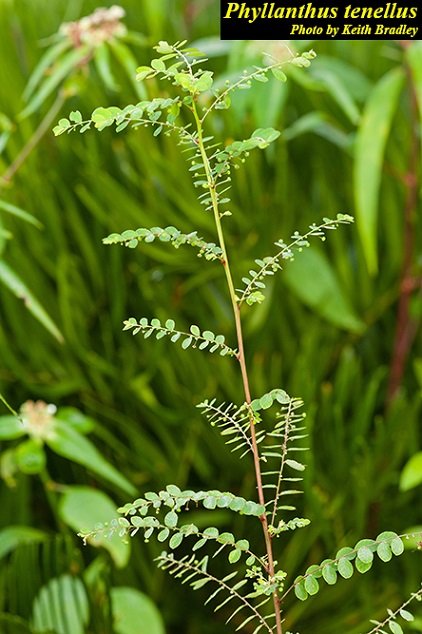
Description
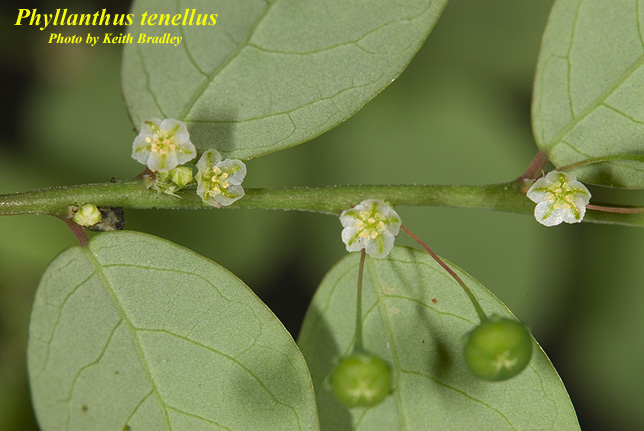
This plant has a “phyllanthoid” arrangement of branches, leaves, and flowers. It has 5 stamens, free filaments, fruiting pedicels, that are 3-7 mm long. The seeds are densely papillose.[1]
Distribution
P. tenellus is a native of the Mascarene Islands and began spreading throughout the U.S. in the mid-20th century. It extends from Florida to southern Georgia, South Carolina, North Carolina, and Tennessee.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
It can be found growing along buildings, under trees in dry loamy sand of cultivated fields, and in moist loam in cultivated flower gardens and lawns.[2]
Phenology
It has been observed flowering in January.[3]
Seed bank and germination
Seed density observed to be highest three years post-fire.[4]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
Phyllanthus tenellus flowers Photo by Keith Bradley, Atlas of Florida Vascular Plants
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Robert K. Godfrey, R. L. Wilbur, E. L. Dunn, H. A. Hespenheide, D. R. Wiseman, Loran C. Anderson, T. MacClendon, K. MacClendon, Geo. Wilder. States and Counties: Florida: Calhoun, Jefferson, Leon. Dominica. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 12 DEC 2016
- ↑ Navarra, J. J., N. Kohfeldt, et al. (2011). "Seed bank changes with time since fire in Florida rosemary scrub." Fire Ecology 7(2).
